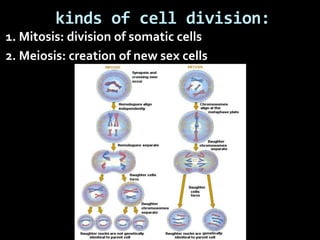
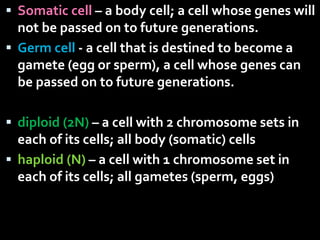
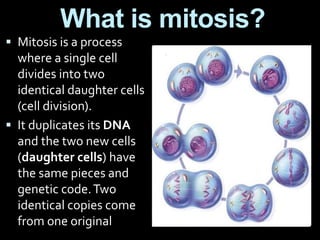
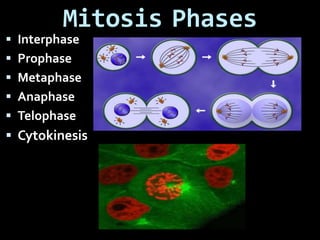
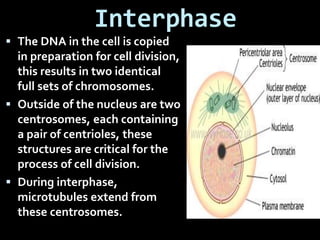
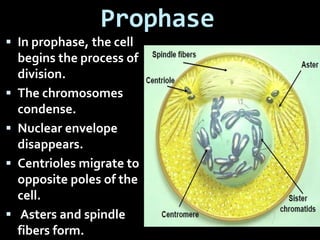
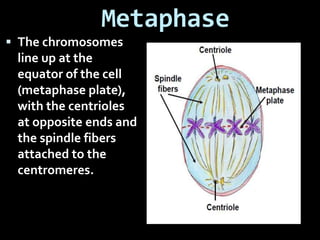
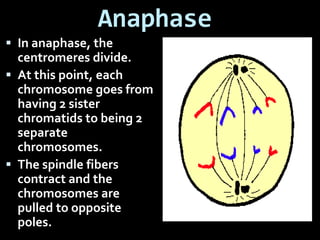
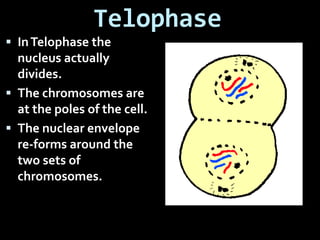
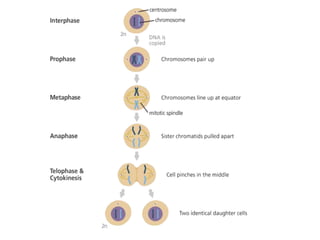
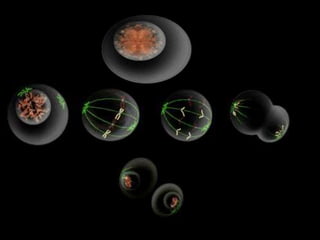
This document summarizes the two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is the process where a somatic cell duplicates its DNA and divides into two identical daughter cells. The key phases of mitosis are interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis. Meiosis involves the creation of sex cells and results in four haploid cells from one original cell.