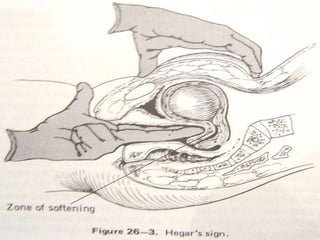
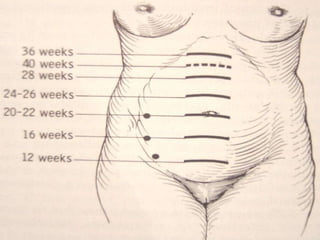
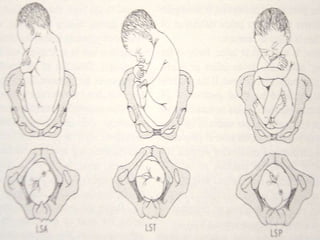
This document discusses the diagnosis of early and mid-late pregnancy. It outlines several subjective and objective signs that can indicate pregnancy, including amenorrhea, morning sickness, breast changes, fetal movement, and fetal heart tones detectable by ultrasound. Laboratory tests that can confirm pregnancy include urine and blood tests to detect human chorionic gonadotropin and ultrasound to visualize the gestational sac, embryo, or fetus. In mid-late pregnancy, quickening may be felt at 18 weeks, the uterus enlarges and rises out of the pelvis, and fetal presentation, position, and growth can be evaluated by ultrasound.