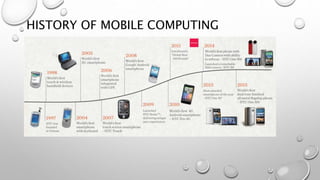
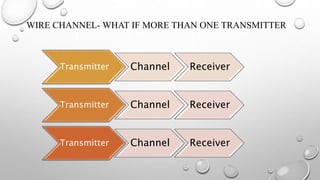
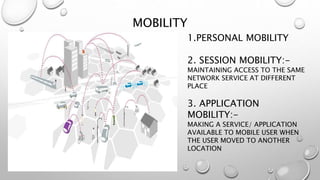
The document discusses the history and applications of mobile computing. Mobile computing allows transmission of data, voice, and video through wireless devices without a fixed connection. It has a variety of uses including transmitting news, traffic information, and vehicle maintenance data. Challenges include maintaining signal strength over wireless channels and achieving high data transfer rates. Advantages are portability and cloud computing access from any location, while disadvantages include connectivity quality and security concerns. Mobile computing continues to evolve with new devices and applications.