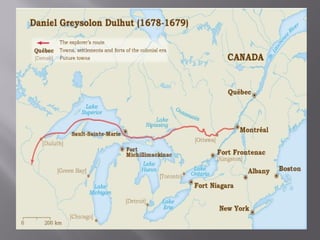
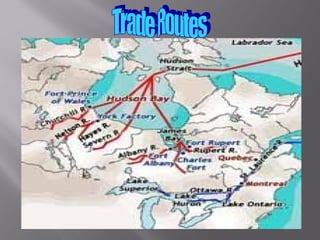
French cartographer Nicolas Sanson prints the first map showing all five Great Lakes in the 1600s, though Minnesota is not yet included. French explorers Radisson and Groseilliers reach Lake Superior's south shore by canoe in the 1650s and meet Dakota Indians. Fur traders interacted with Dakota and Ojibwe Indians in Minnesota for hundreds of years, trading European goods for beaver and other furs.