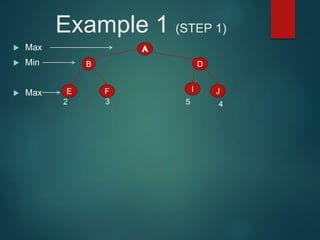
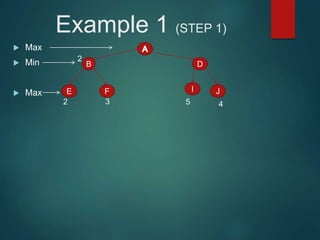
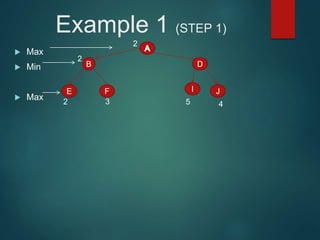
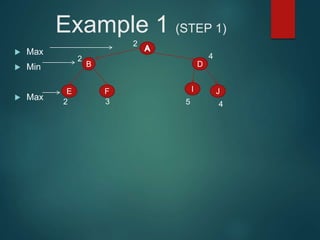
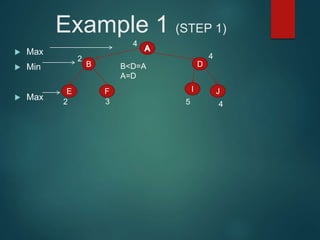
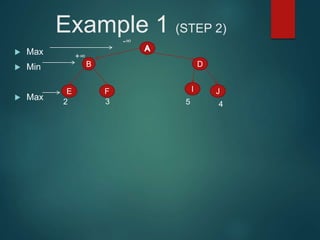
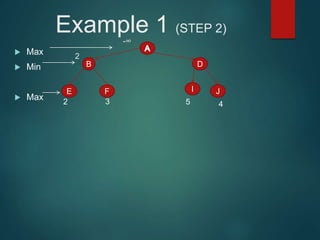
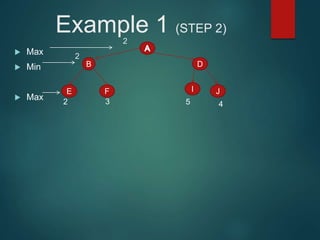
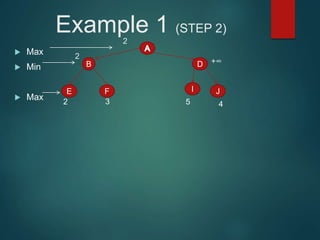
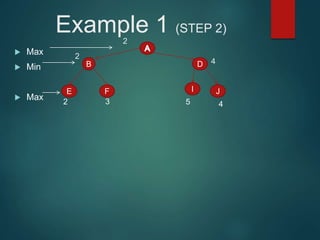
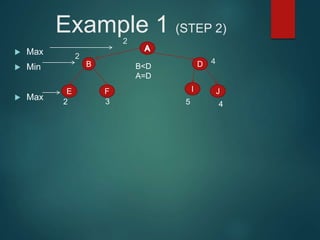
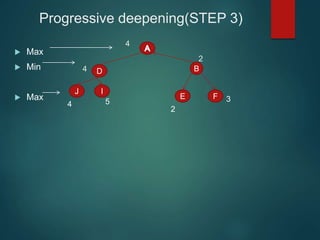
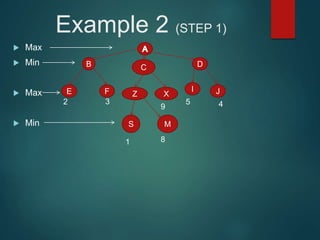
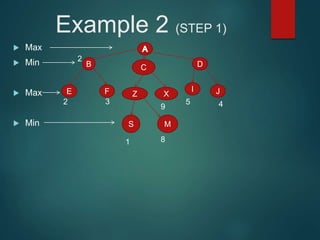
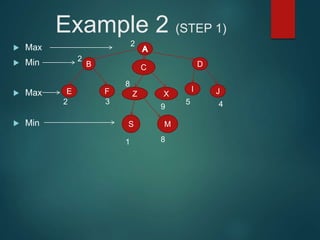
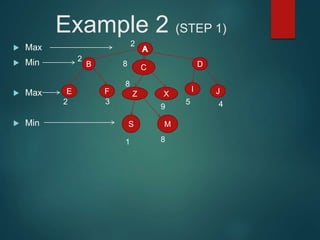
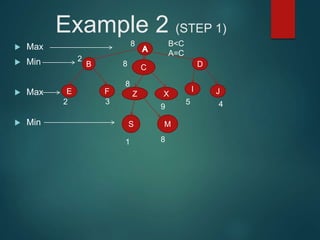
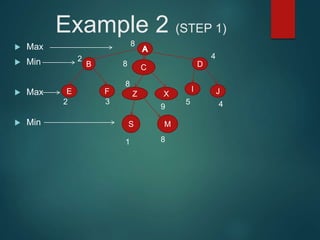
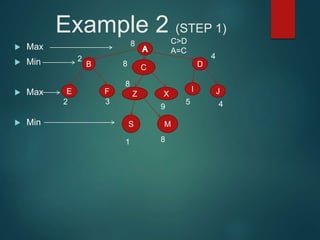
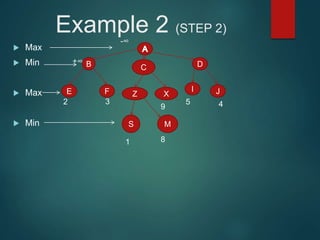
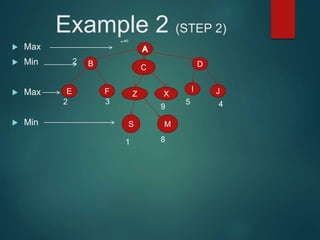
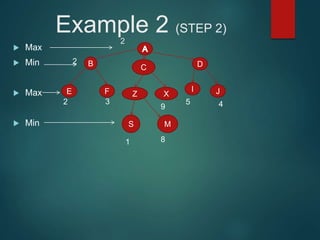
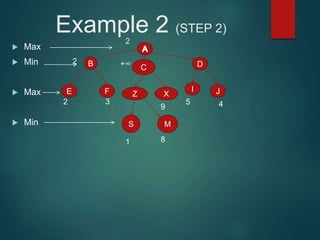
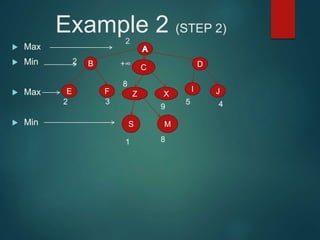
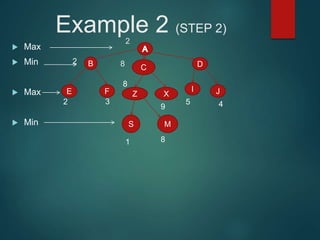
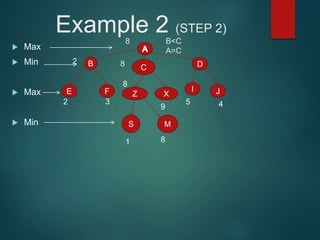
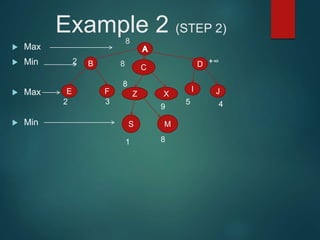
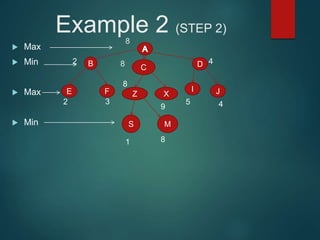
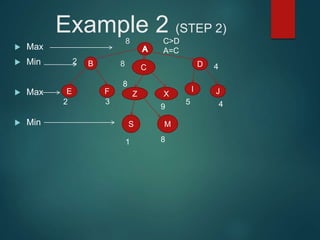
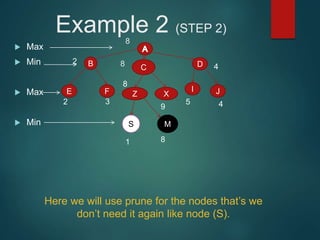
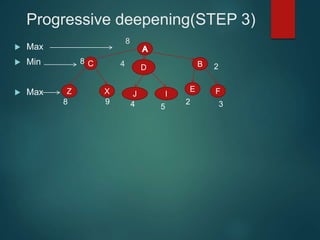
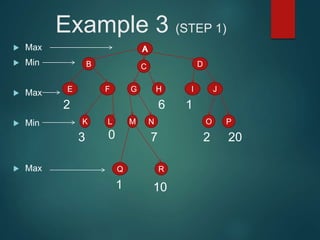
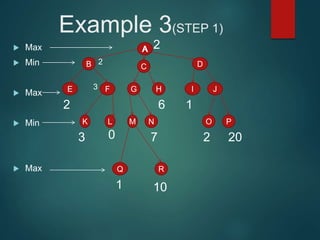
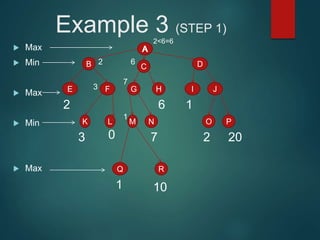
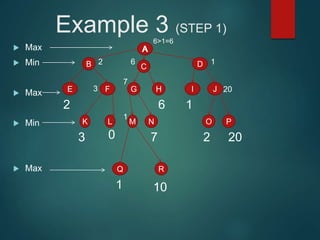
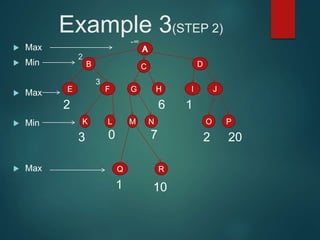
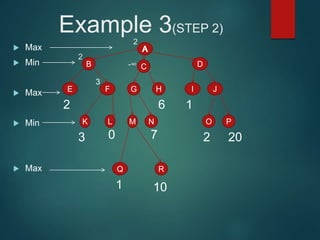
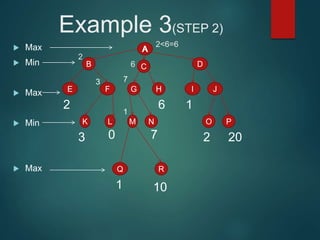
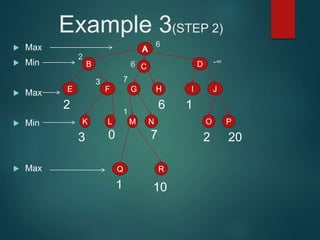
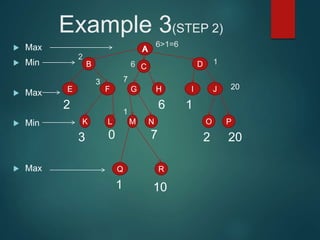
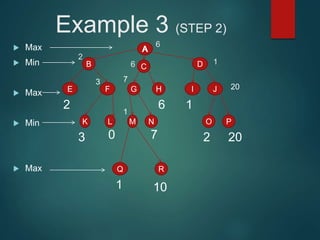
The minimax algorithm is used to determine the best possible move for a player in two-player zero-sum games like chess. It works by having each player assume their opponent will make the best counter-move. The algorithm searches the game tree by alternately maximizing and minimizing at each level to assign a value to leaf nodes, then backing up values towards the root. This process determines the move with the highest minimum value from the player's perspective.