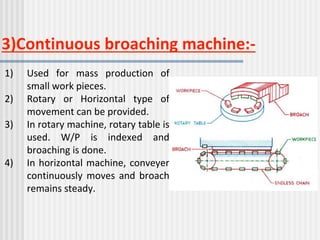
Broaching is a machining process involving a broach tool with cutting teeth that removes material in one stroke, applicable to both internal and external surfaces. The operation entails selecting the appropriate broach and machine, mounting the broach, and conducting the machining process, with various machine types categorized by direction, operation method, drive, and type. Advantages include high production rates and precision finishing, while disadvantages involve high tool costs and specific fixture requirements.