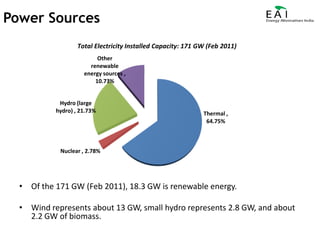
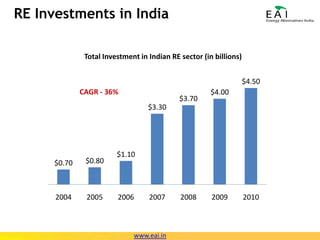
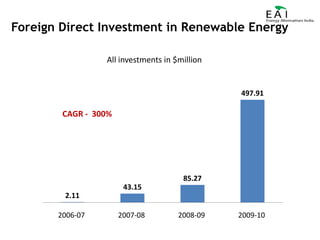
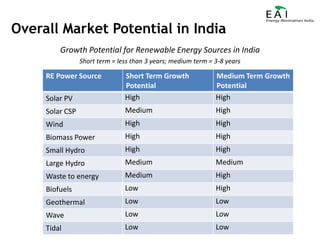
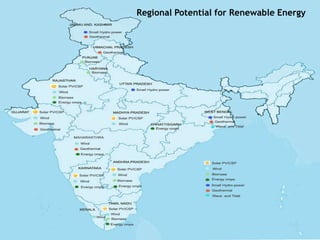
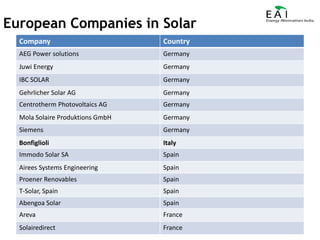
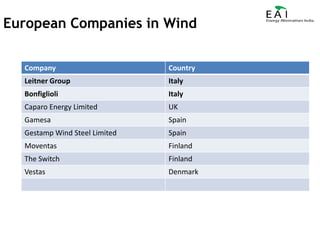
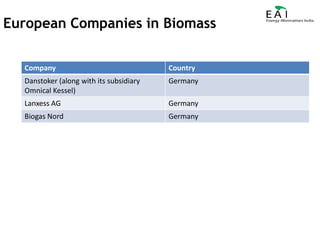
This document summarizes the potential and opportunities in Indian renewable energy. It outlines why India and renewable energy in India present opportunities, including fast economic growth, rising energy needs, and supportive government policies. It provides an overview of the status and growth potential of various renewable technologies in India like solar, wind, biomass, and waste-to-energy. Finally, it discusses attractive opportunities for foreign companies across the renewable energy value chain, particularly for European companies in equipment, manufacturing, and developing renewable energy projects in India.