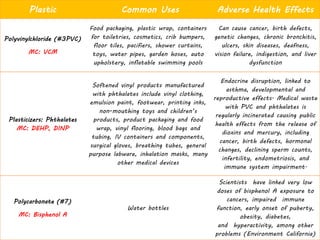
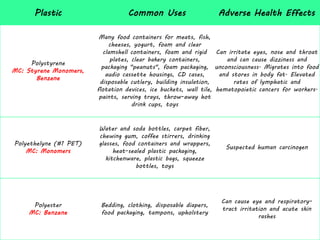
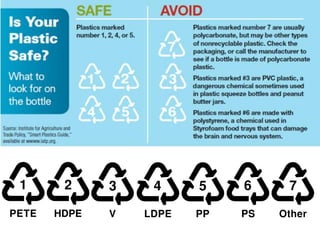
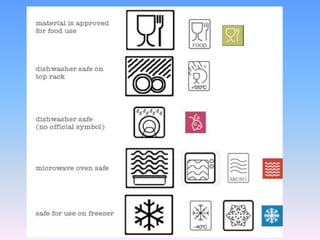
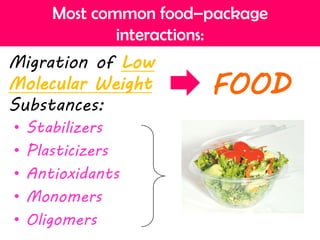
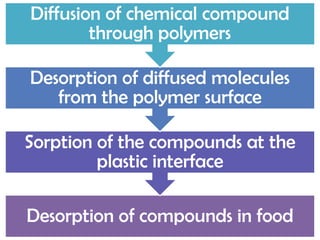
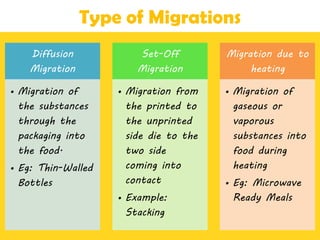
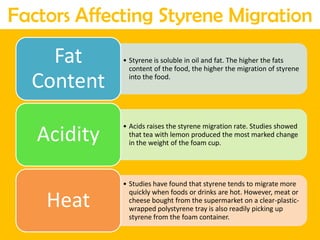
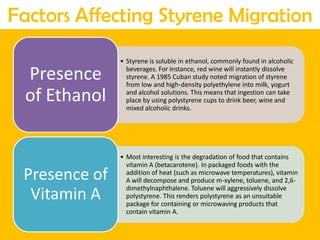
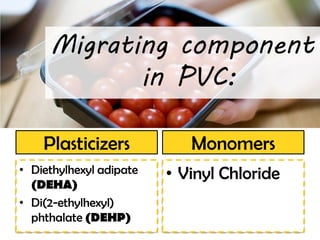
This document discusses issues related to the migration of monomers and other chemical compounds from plastic food packaging materials into foods. It provides examples of commonly used plastic materials like PVC, polycarbonate, polystyrene, polyethylene, polyester, and LDPE. Specific migrating components from each plastic like BPA, phthalates, styrene are mentioned. The document discusses factors affecting migration like heat, acidity, presence of ethanol or vitamin A. Potential health effects of migrating components include cancer, developmental and reproductive toxicity, obesity, and others. It emphasizes knowing which plastics are safest to use for different food applications.














![Effect of DEHP on Human Health
•Theacute toxicityof DEHP is low in animal models: 30g/kg in rats (oral) and 24g/kg in rabbits (dermal). Concerns instead focus on its potential as anendocrine disruptor.Toxicity
•Approximately 25% of US women have phthalate levels similar to those in the study.However, the study author cautioned that replication of these results are needed to strengthen any links between phthalates and adverse health outcomes. Development
•A study onCDCdata, "revealed that American men with abdominalobesityorinsulin resistance(a precursor todiabetes) were more likely to have high levels of [DEHP andDBP] metabolites in their urine than men without those problems. Obesity
•A clinically relevant dose and duration of exposure to DEHP has been shown to have a significant impact on the behavior ofcardiaccells in culture.
Cardiotoxicity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/migrationofmonomers-141210174638-conversion-gate02/85/Migration-of-monomers-21-320.jpg)