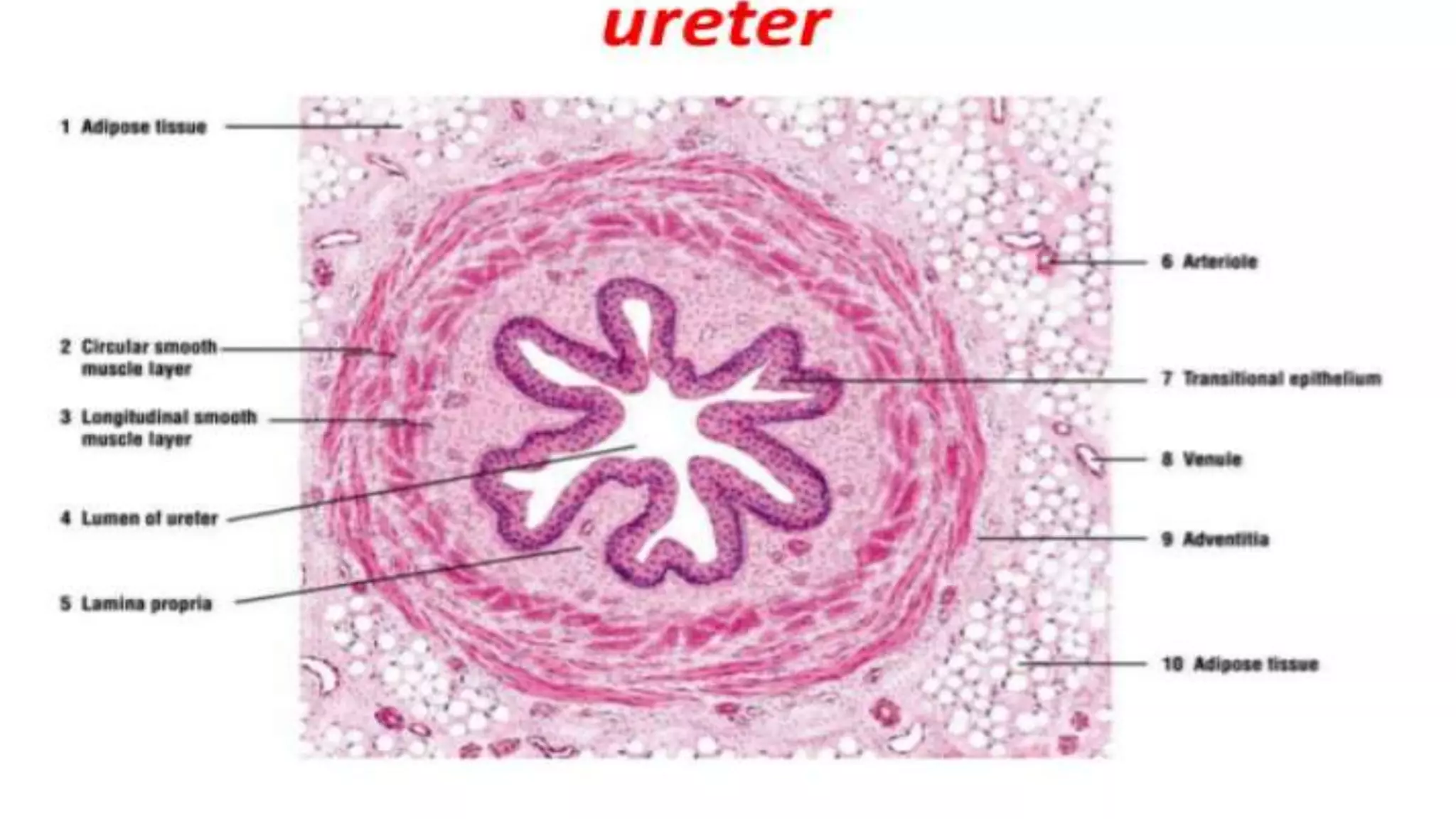
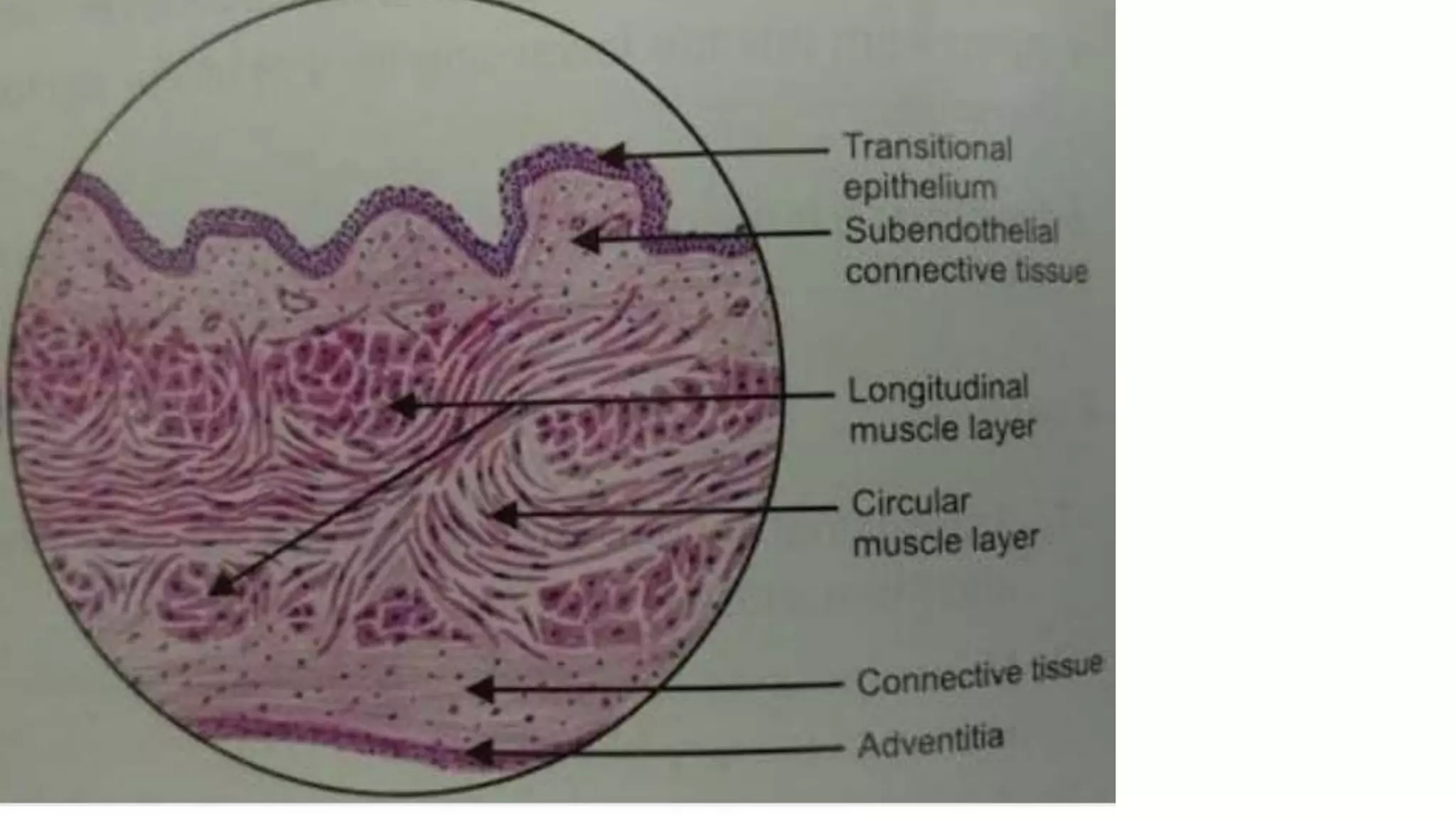
The document describes the anatomy and histology of the ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra. The ureter has three layers - mucosa, muscle layer, and adventitia. The urinary bladder also has these three layers with transitional epithelium lining the mucosa. The urethra acts as the passage for urine from the bladder to outside. It has mucosa, submucosa, and muscular layers. The male urethra is longer than the female urethra and has prostatic, membranous, and spongy regions.