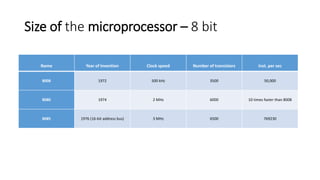
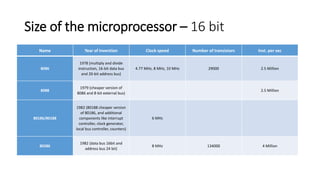
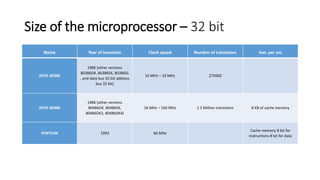
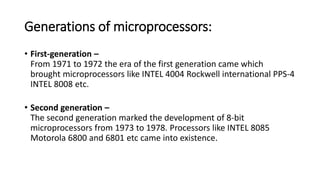
The evolution of microprocessors began in 1971 with Intel's 4004, one of the first microprocessors containing 2300 transistors and able to perform 60,000 instructions per second. Subsequent microprocessors increased processing capabilities through higher clock speeds, more transistors, and larger data buses. Key developments included the 8-bit 8008 in 1972, 16-bit 8086 in 1978, 32-bit 80386 in 1986, and 64-bit Pentium in 1993. Modern multi-core processors like Intel Core 2 from 2006 can have over 291 million transistors and perform billions of instructions per second.