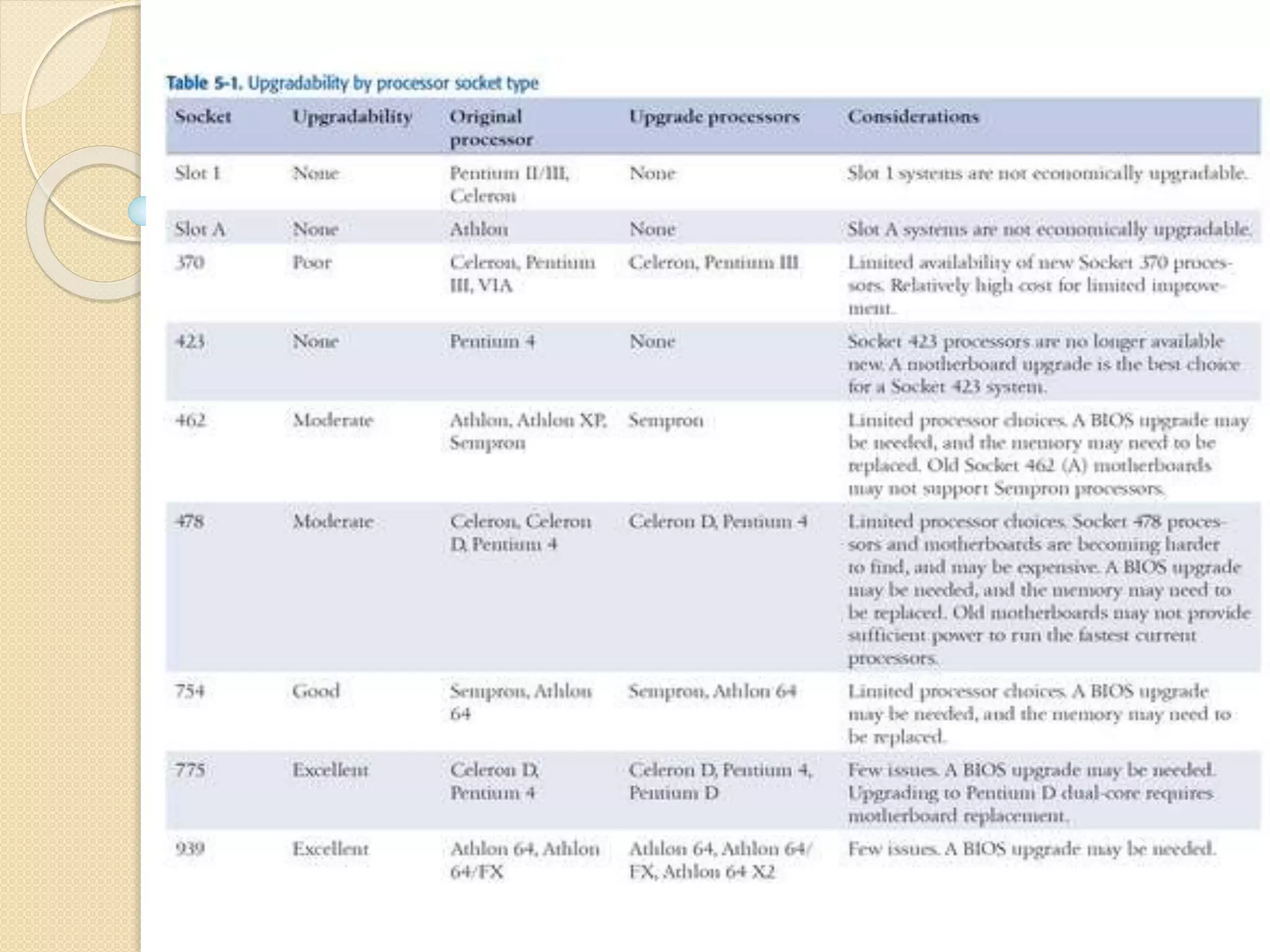
The document discusses processors, including their key characteristics and technologies. It describes:
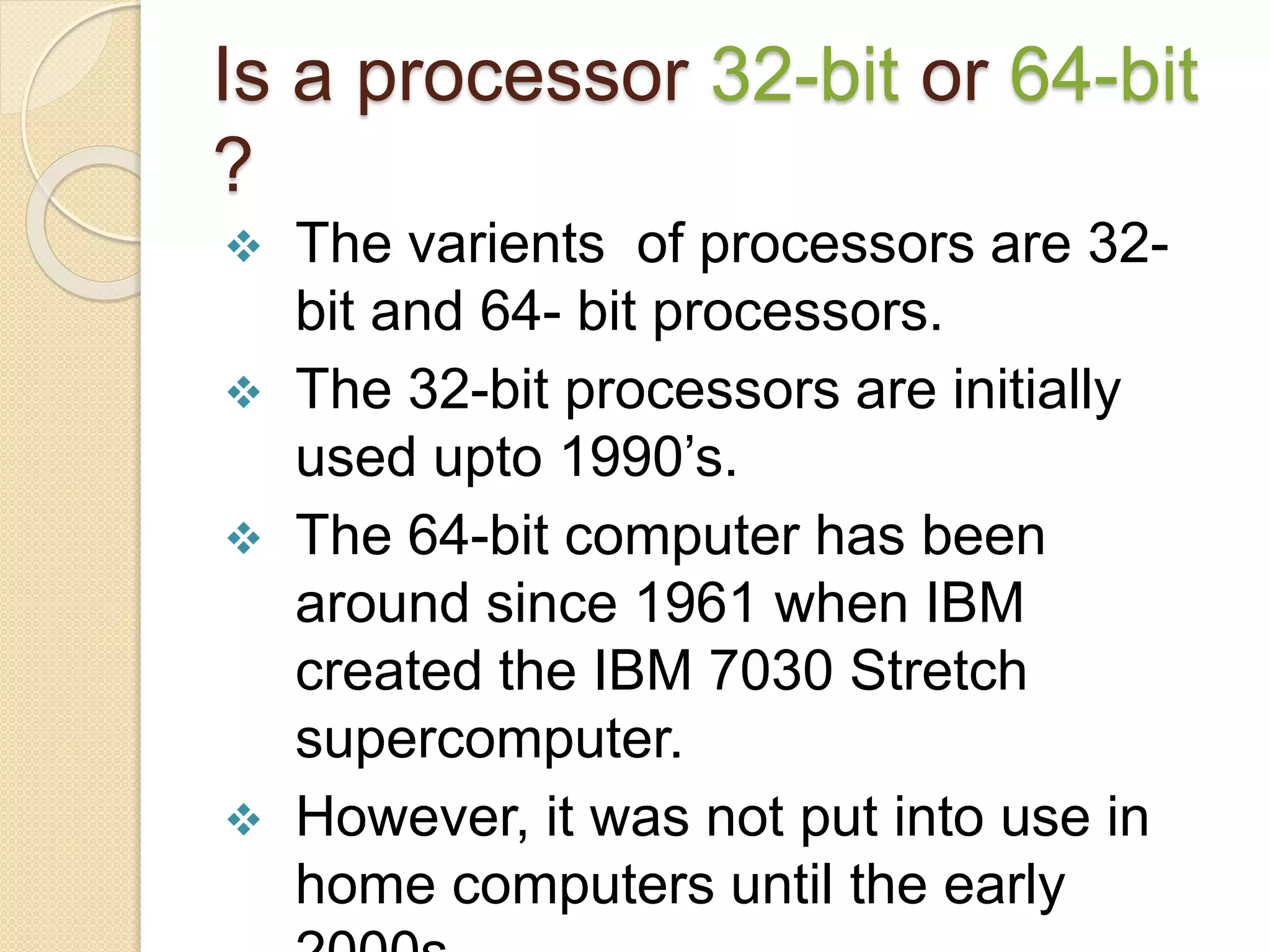
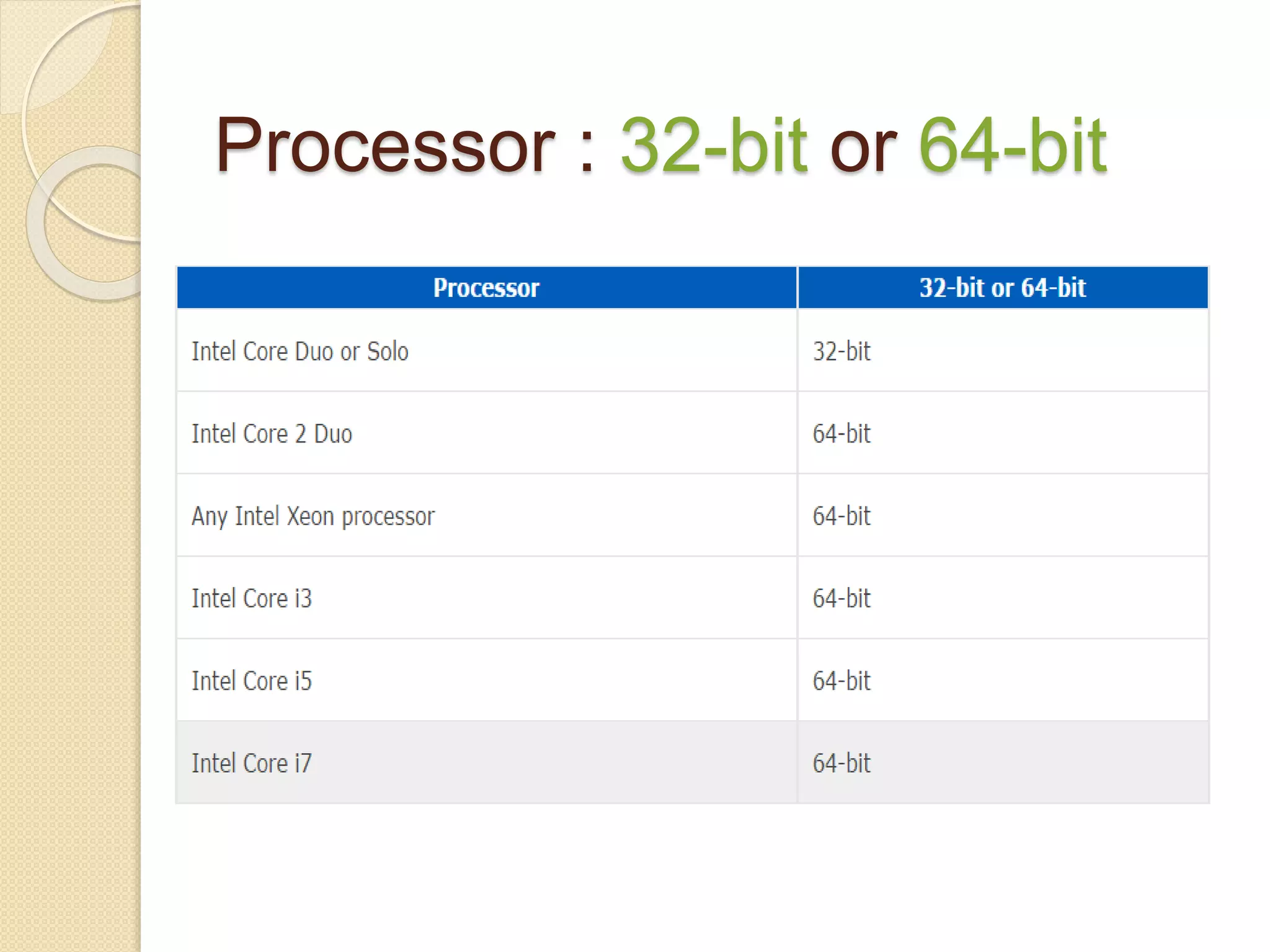
- Processors can be 32-bit or 64-bit, with 64-bit processors now commonly used in home computers.
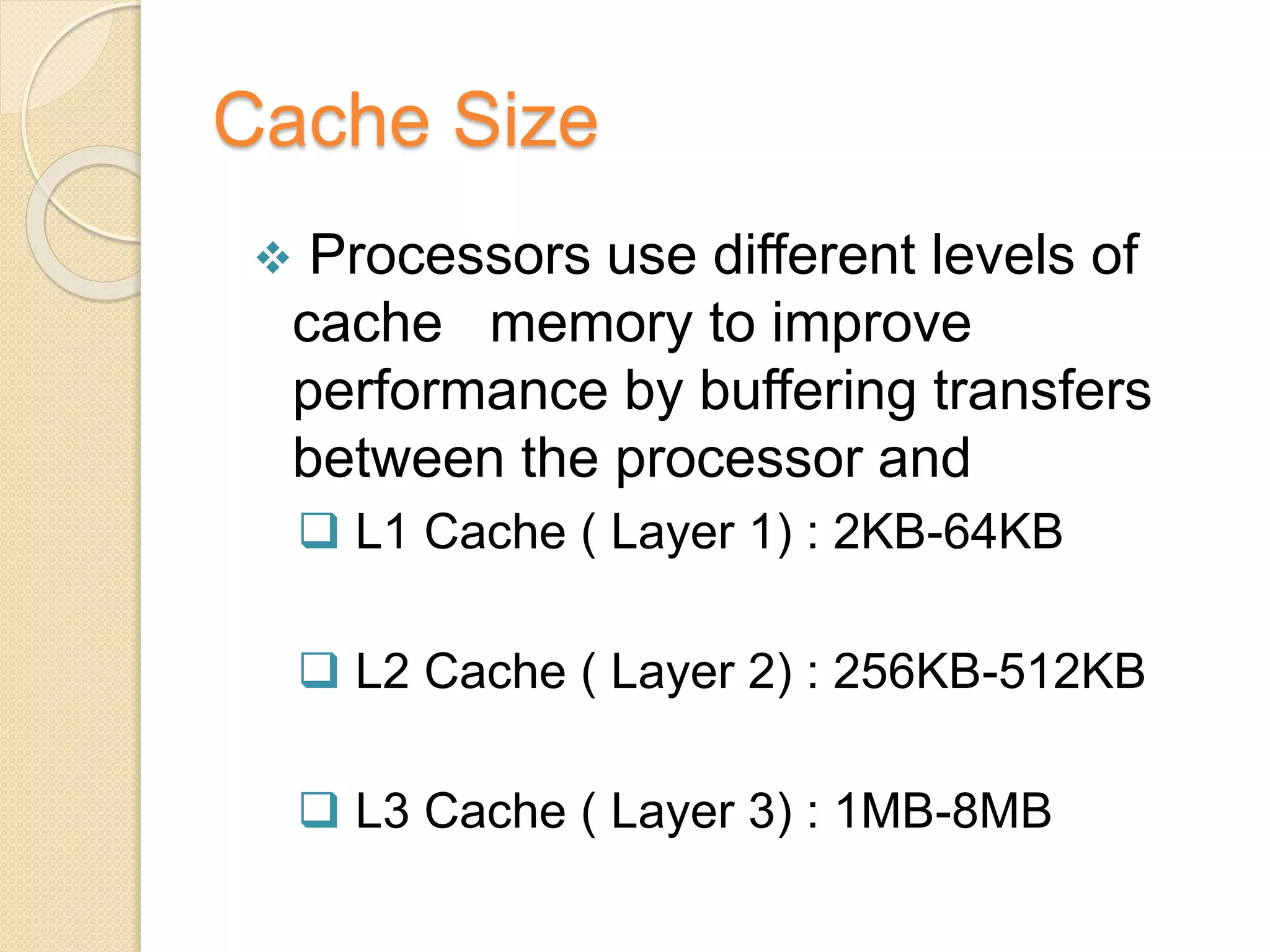
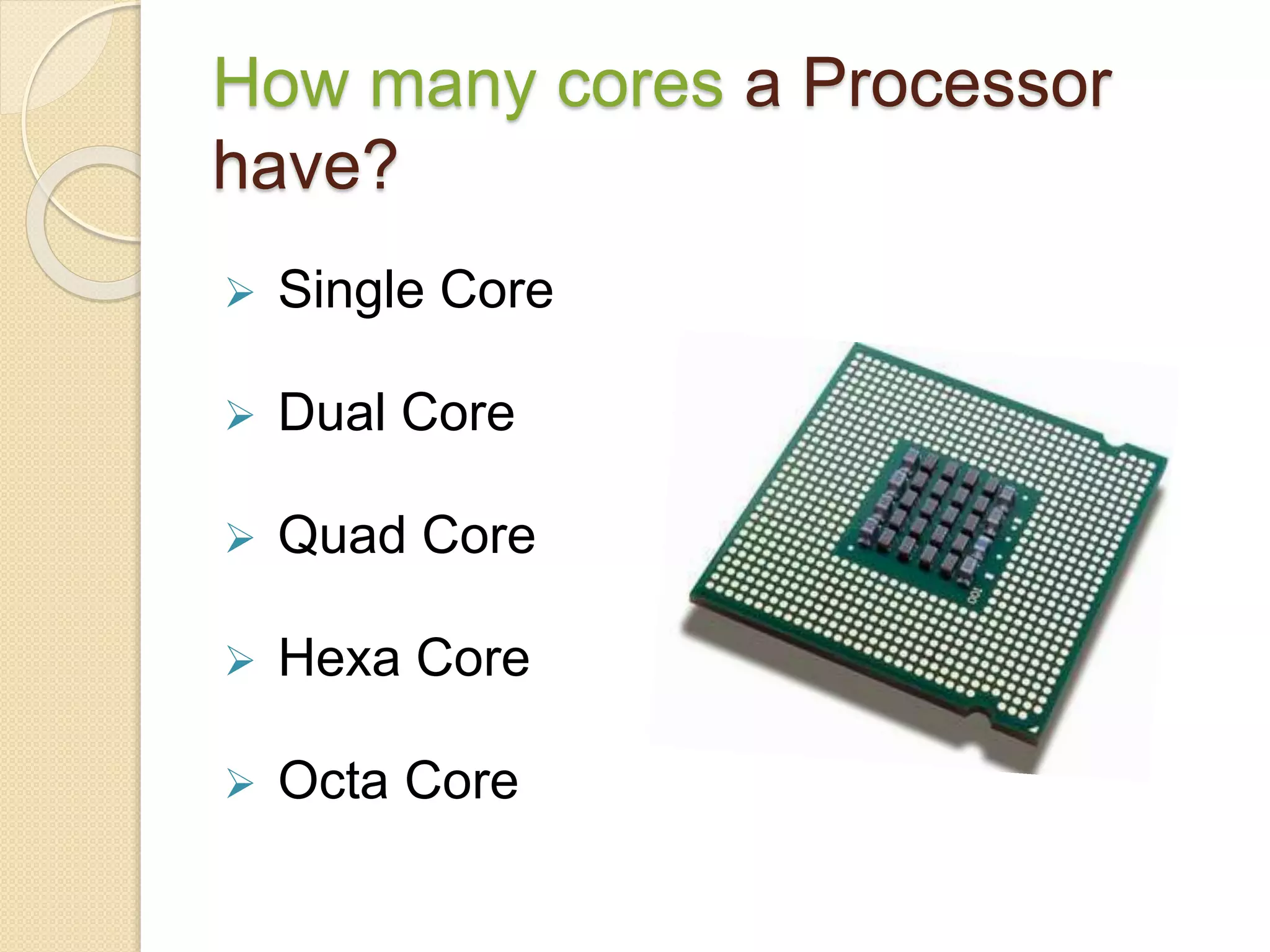
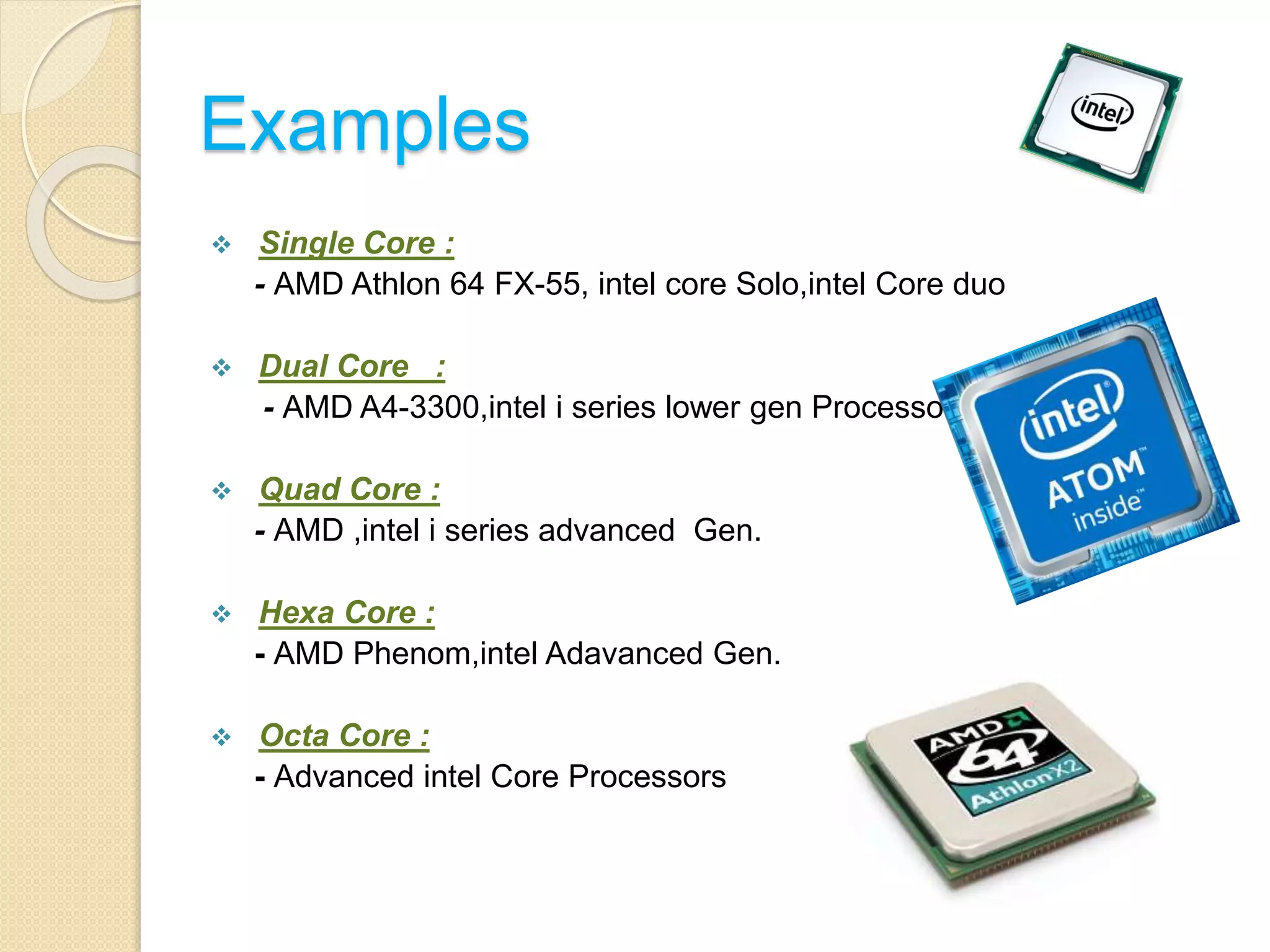
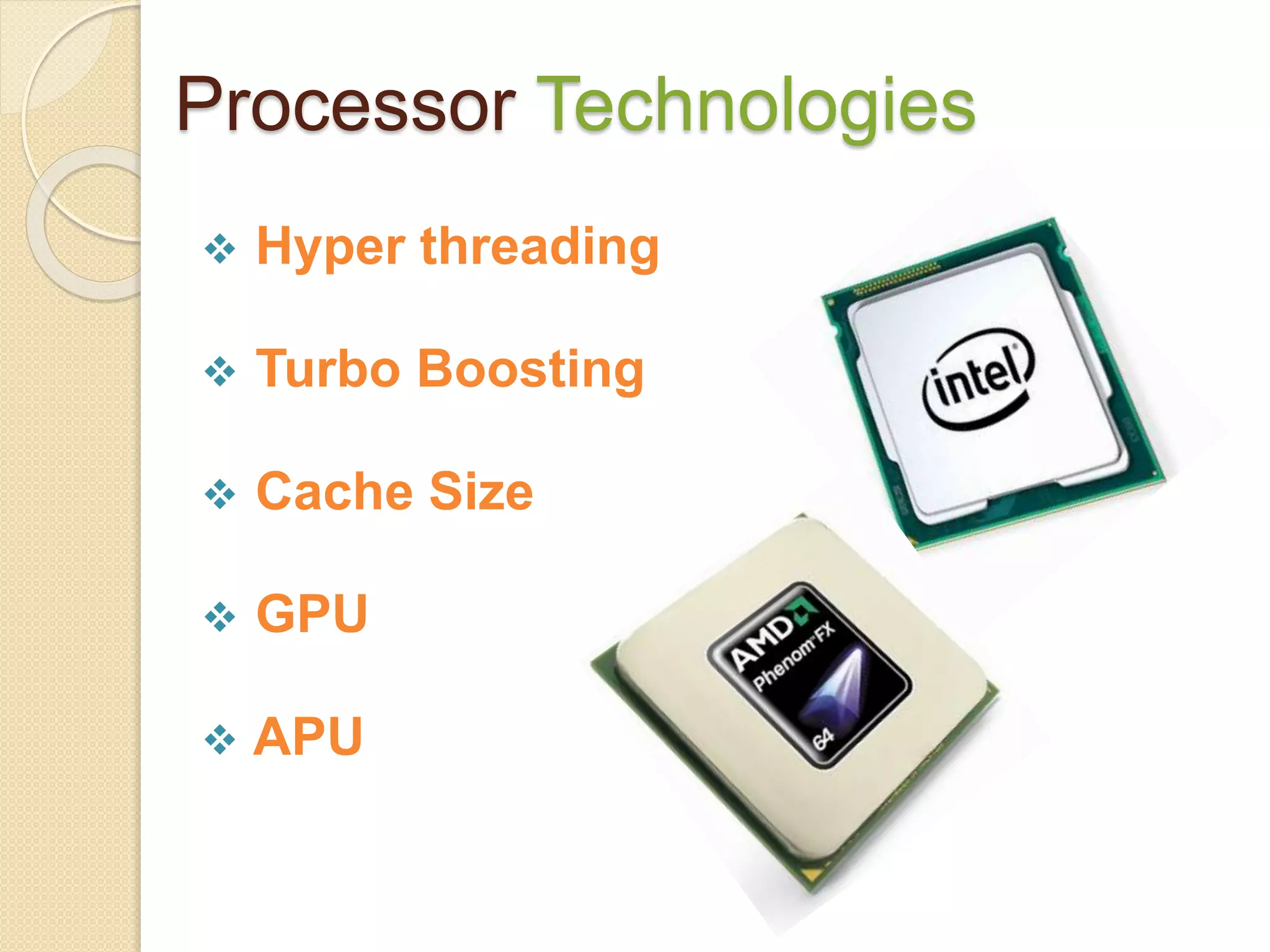
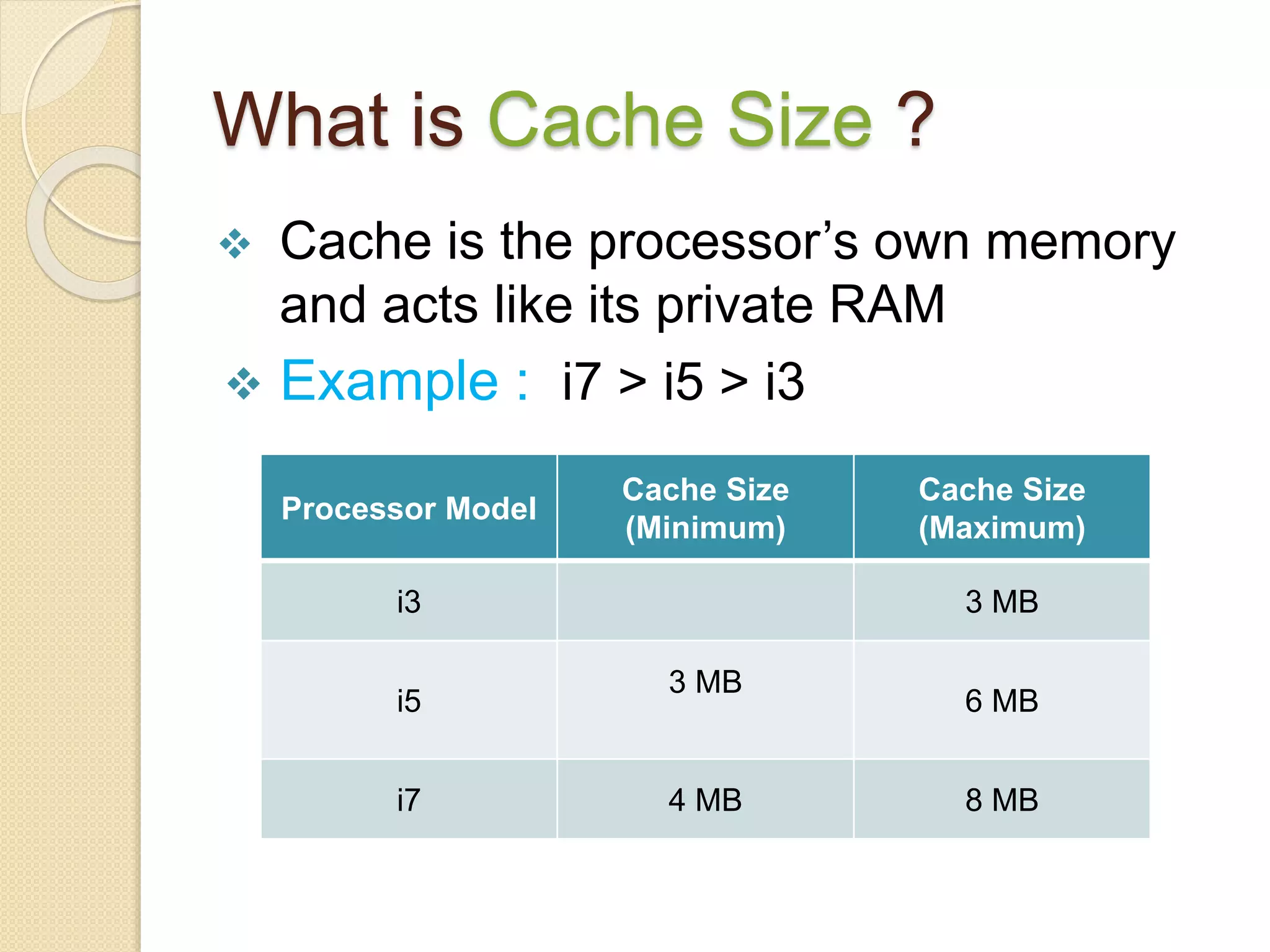
- Key processor characteristics that impact performance include clock speed, cache size, number of cores, and technologies like hyperthreading and turbo boosting.
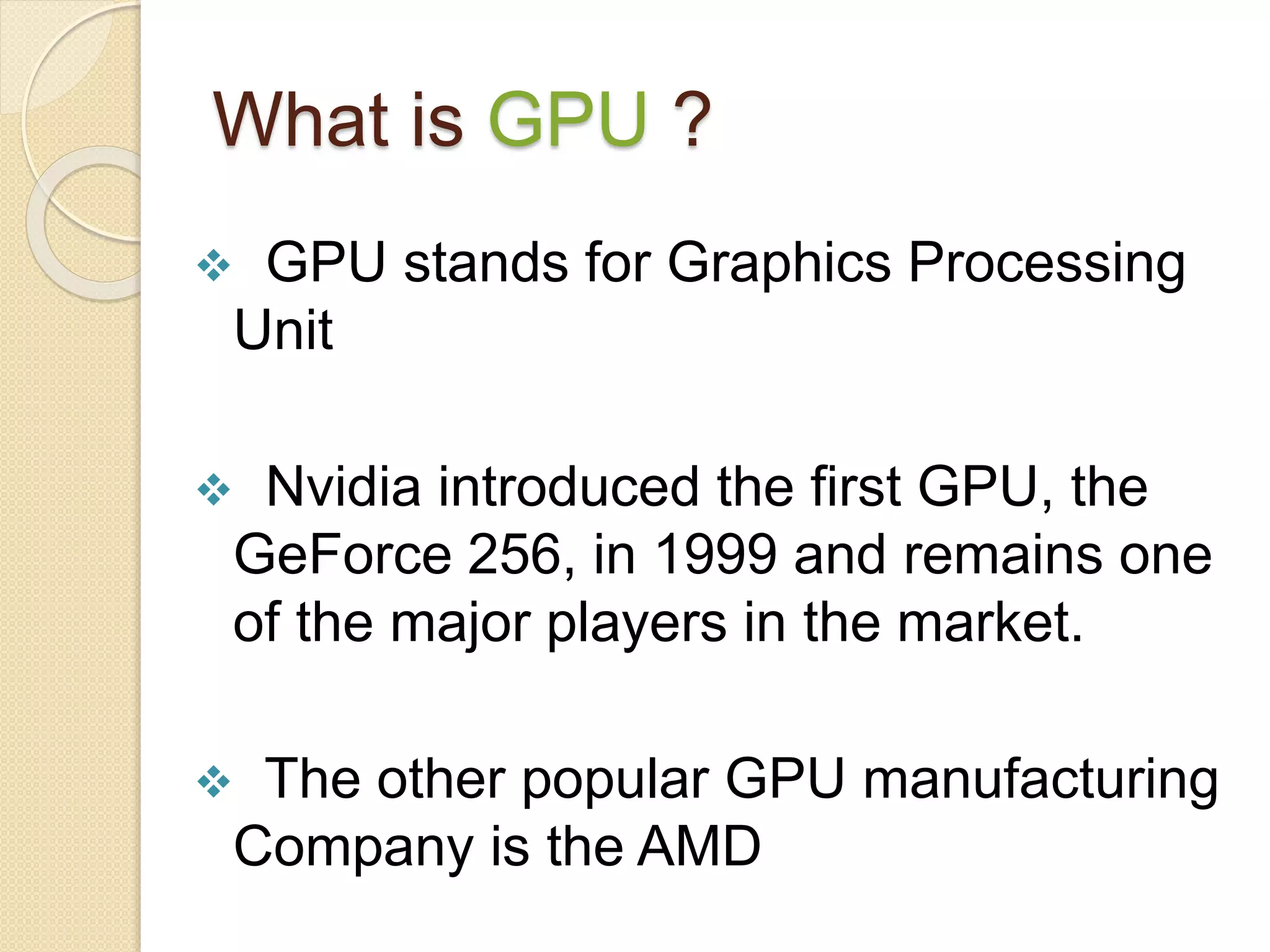
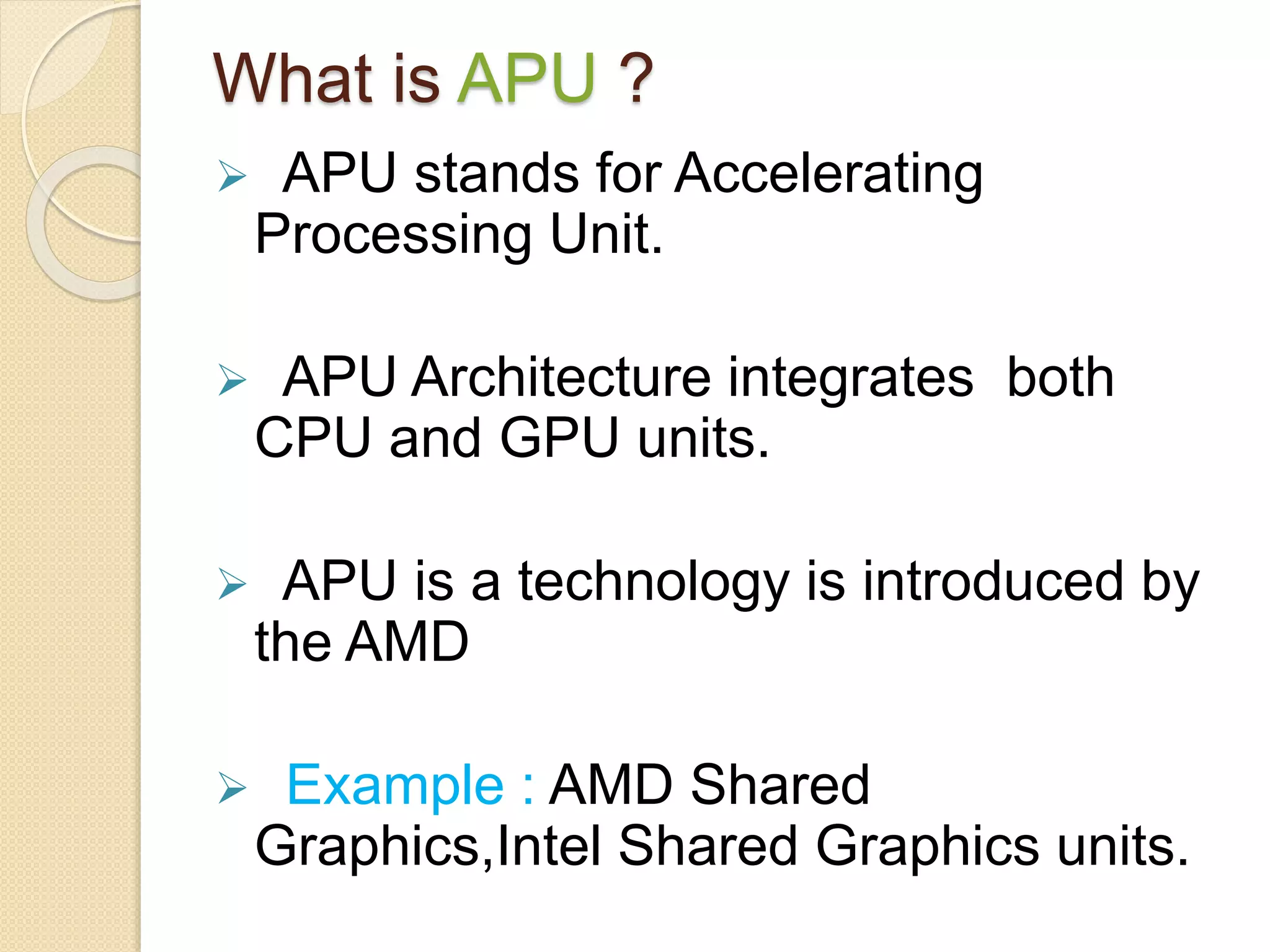
- Popular processor manufacturers include Intel and AMD. GPU manufacturers include AMD and Nvidia. APUs integrate both CPU and GPU functions.
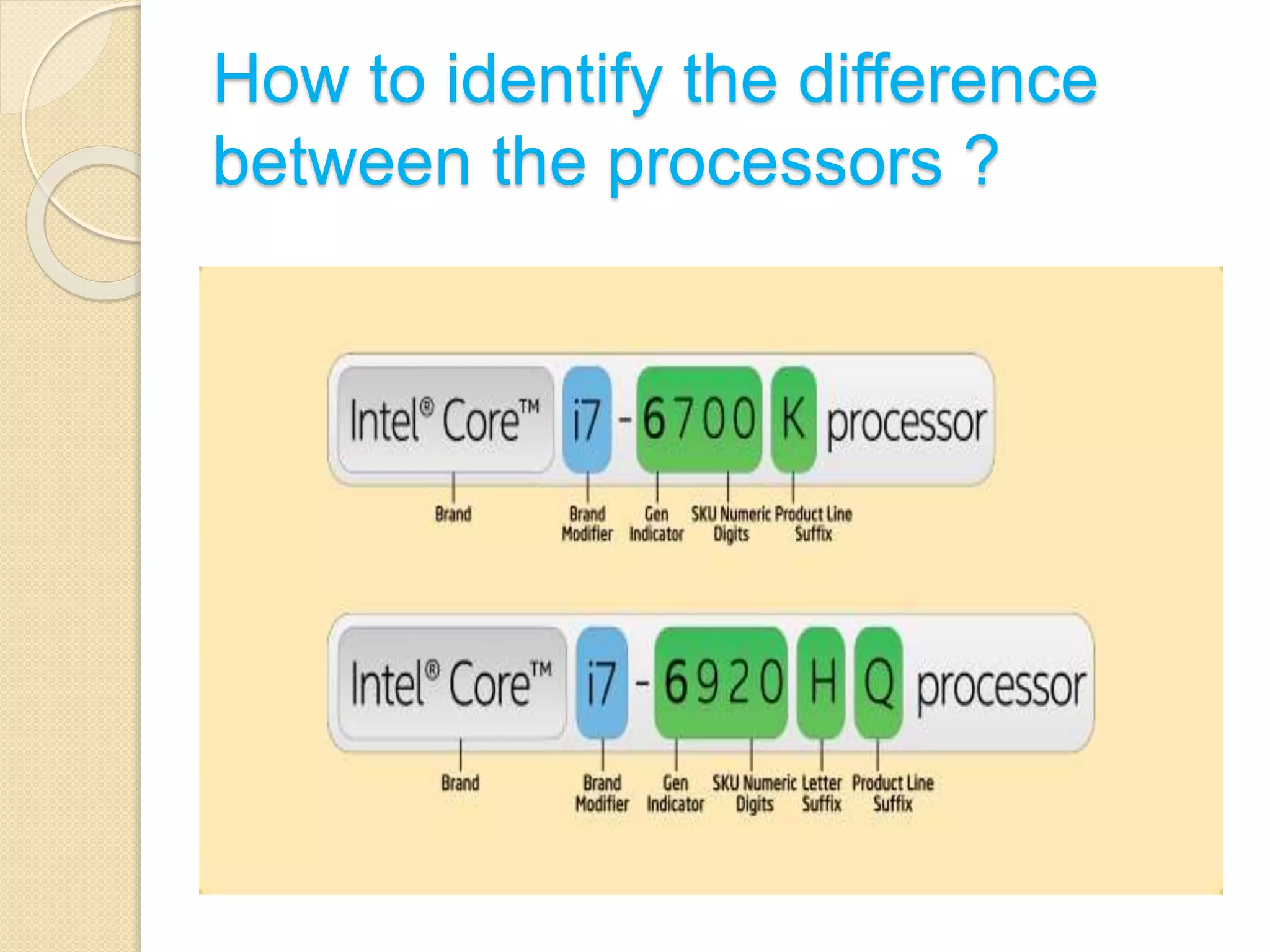
- Factors like power usage, graphics capability, and overclocking potential are denoted in processor model names/numbers. Understanding these specifications helps determine the best processor.