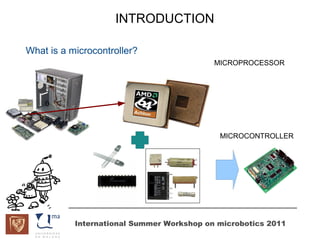
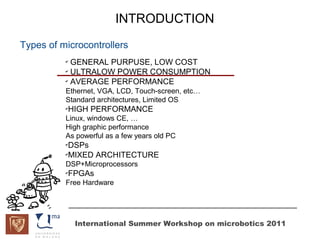
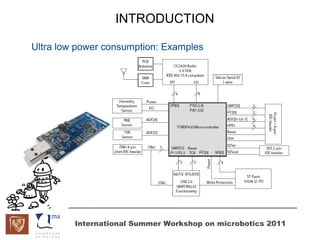
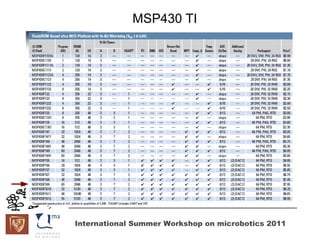
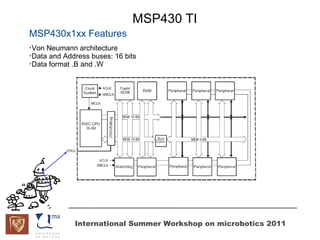
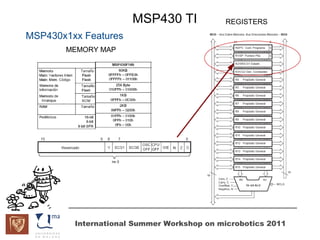
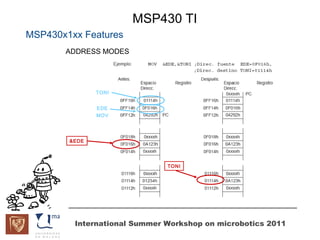
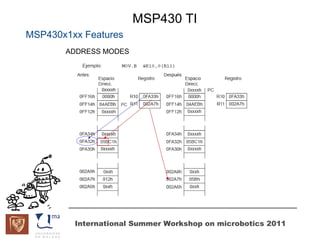
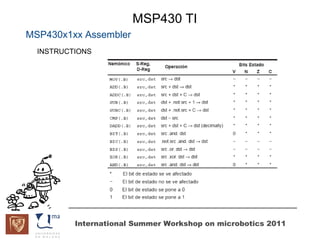
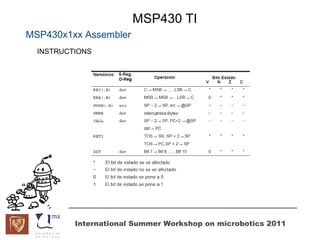
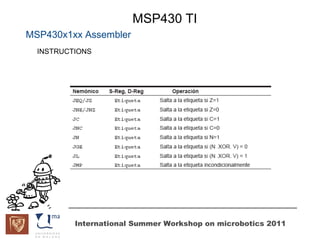
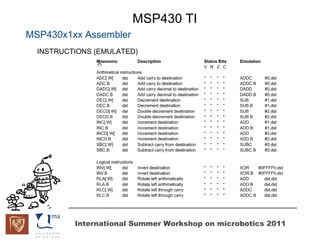
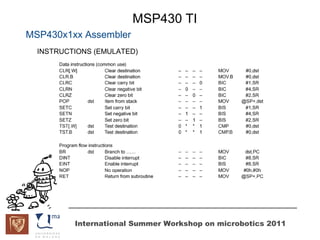
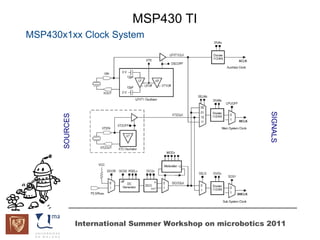
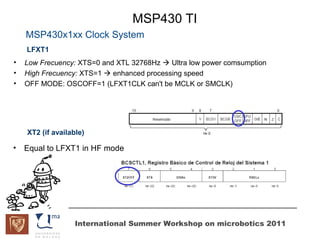
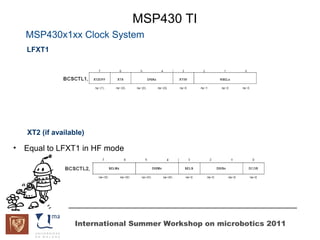
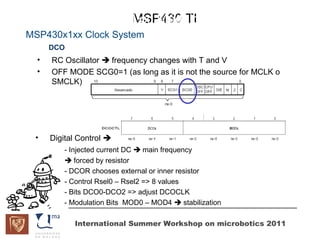
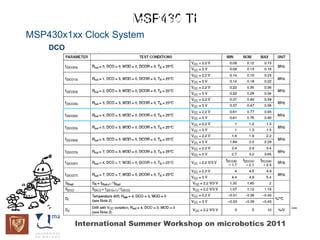
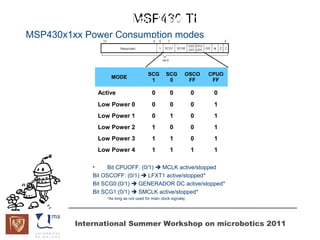
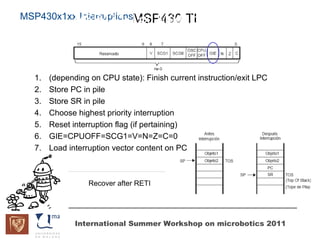
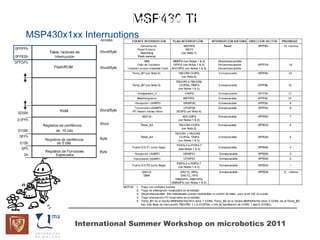
The document discusses microcontrollers and the MSP430 microcontroller. It begins by defining a microcontroller and comparing it to a microprocessor. It then describes the different types of microcontrollers and provides examples of their uses. The remainder of the document focuses specifically on the MSP430 microcontroller from Texas Instruments, describing its features such as low power consumption, peripherals, memory architecture, and clock system. It also discusses the MSP430's assembly language and interrupt handling capabilities.