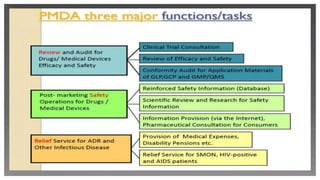
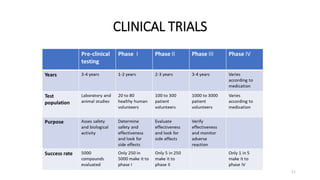
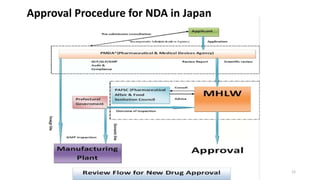
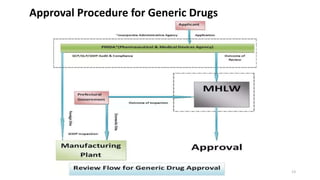
The document discusses regulatory requirements for the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (MHLW) in Japan. It describes the MHLW as the regulatory authority for pharmaceuticals that gives marketing approval and issues licenses. It also discusses the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA), an independent agency that works with the MHLW to scientifically review applications and ensure safety of drugs and devices. The PMDA was formed by merging several existing organizations. Finally, it notes that the MHLW and PMDA have improved drug approval processes in Japan but times still lag other countries.