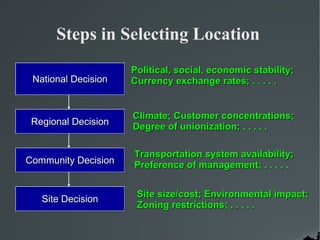
The document discusses factors that affect the selection of an optimal plant location, including availability of raw materials, proximity to markets, transportation infrastructure, climate conditions, government policies, and cost considerations. It outlines quantitative approaches like break-even analysis and qualitative approaches such as factor rating methods that are used to evaluate competing location sites. Key location selection factors are analyzed at the regional, community, and specific site levels. Recent industry trends toward suburban and backward areas are also noted.