The document discusses methods for flood control, including:
1. Controlling water levels through dams, check dams, and reservoirs to store flood waters.
2. Building barriers like levees and embankments to restrict flood waters to river channels.
3. Altering river channels by straightening, widening, and deepening them to increase capacity.
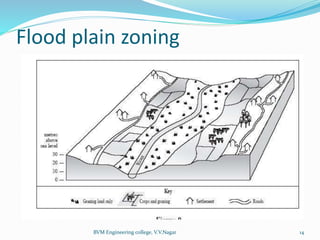
4. Controlling land use near rivers through zoning to reduce impervious surfaces and flooding.
5. Using floodways to divert flood waters into low-lying areas or other pathways.