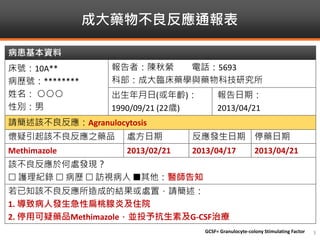
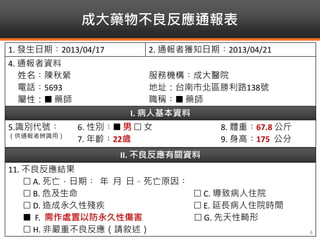
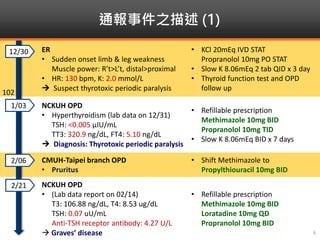
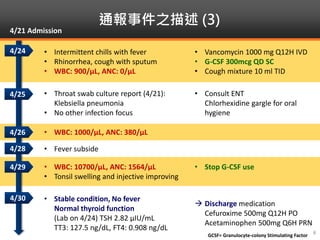
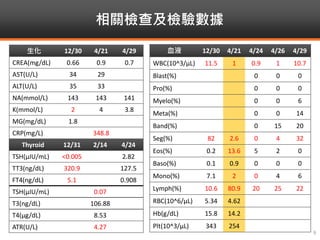
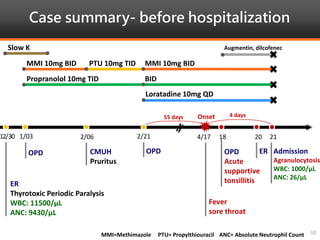
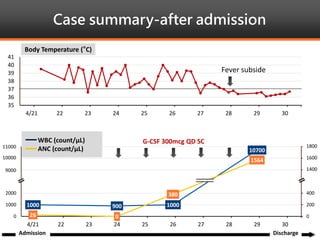
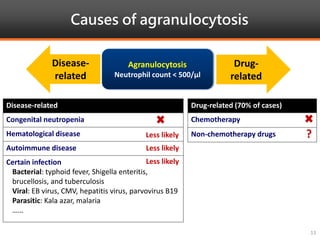
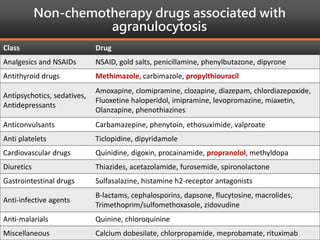
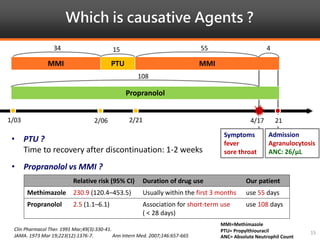
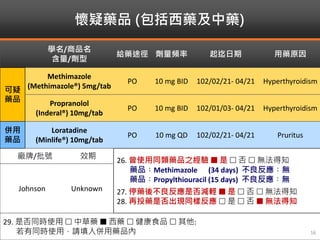
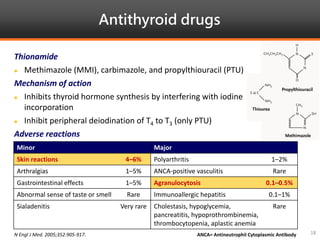
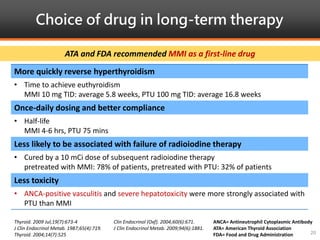
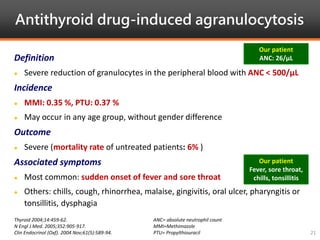
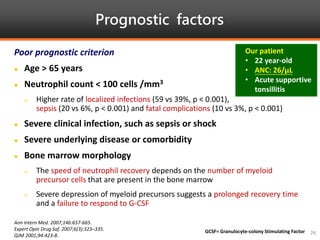
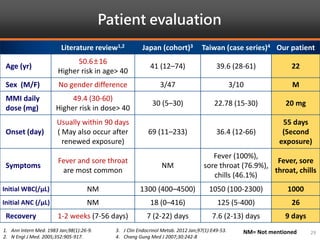
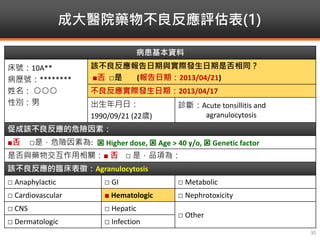
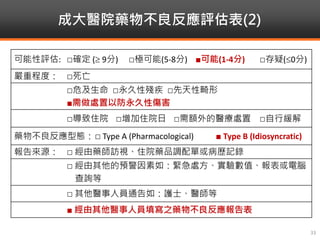
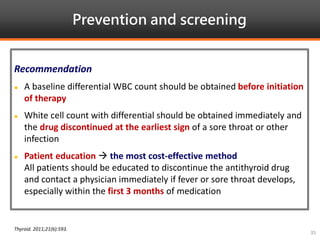
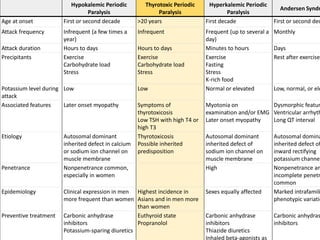
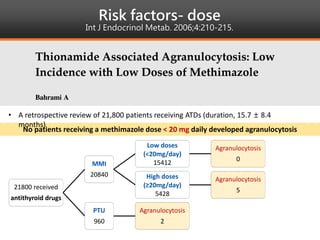
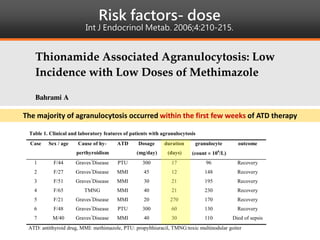
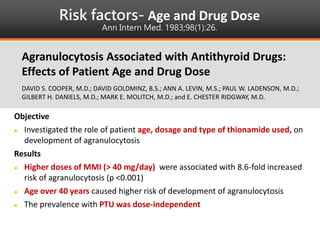
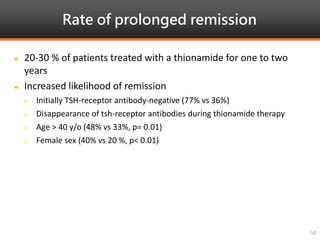
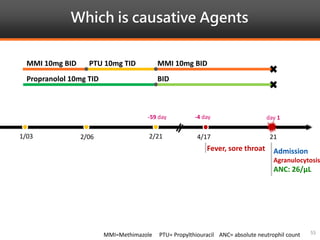
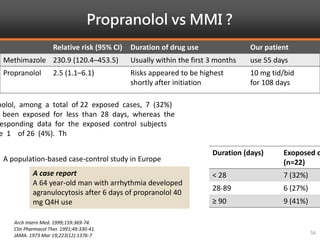
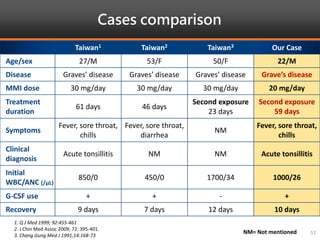
Methimazole was suspected to have caused agranulocytosis in a 22-year-old male being treated for Graves' disease. He developed fever and sore throat and was found to have a very low absolute neutrophil count of 26/uL. He was hospitalized and treated with antibiotics, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, and discontinuation of methimazole. His white blood cell count and symptoms improved after treatment. Methimazole has been known to cause agranulocytosis, especially within the first 3 months of use, and is the most likely causative agent given the patient's clinical course and timeline of methimazole therapy.