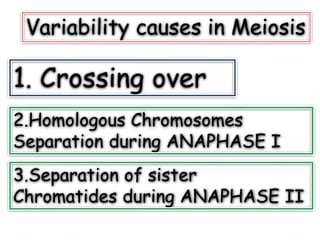
1. Meiosis involves two divisions that reduce the number of chromosomes by half, leading to genetic variability. The key events are crossing over, separation of homologous chromosomes, and separation of sister chromatids.
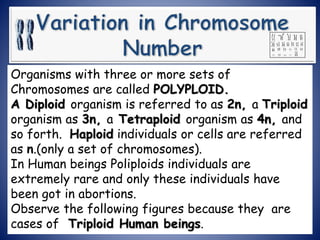
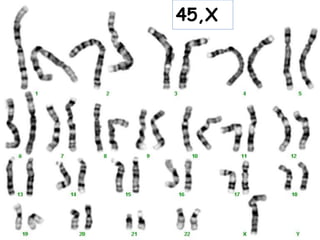
2. Chromosomes are classified based on centromere location as metacentric, submetacentric, or telocentric. Aneuploidy occurs when the number of a particular chromosome is altered.
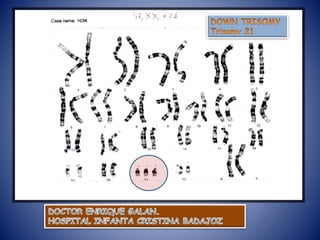
3. Nondisjunction of homologous chromosomes during meiosis can result in trisomy disorders like Down syndrome, where a third chromosome 21 is present.