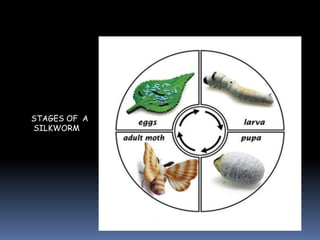
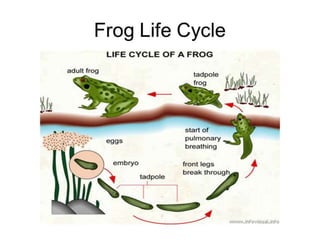
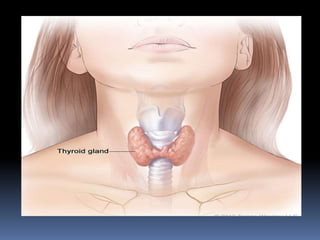
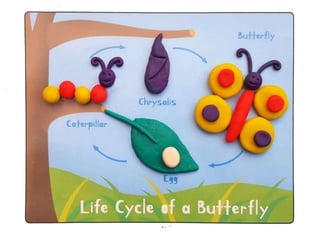
This document provides information about metamorphosis and frog development. It defines metamorphosis and describes the indirect development process that frogs undergo, starting as an egg laying tadpole and transforming through developmental stages into an adult frog. Key stages in a frog's life cycle are outlined, and the role of hormones like thyroxine in facilitating metamorphosis is explained. The document aims to teach students about these concepts through text, videos and a suggested hands-on art activity using modeling or mosaics.