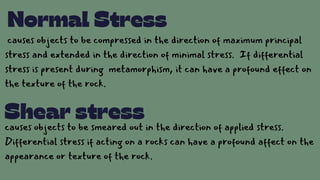
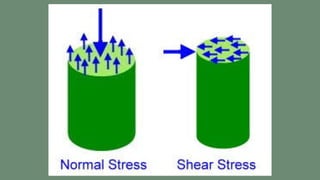
Metamorphism is the process by which solid rocks undergo changes to their mineralogy and texture due to changes in temperature, pressure, and fluids at depth in the Earth. During metamorphism, the original rock, called the protolith, undergoes changes without melting as a result of increased temperature and pressure from burial or intrusion. These changes result in new mineral assemblages and textures. There are three main types of metamorphism that occur depending on the relative effects of mechanical and chemical changes: contact metamorphism near igneous intrusions, regional metamorphism at deeper burial depths, and dynamic metamorphism from tectonic forces.