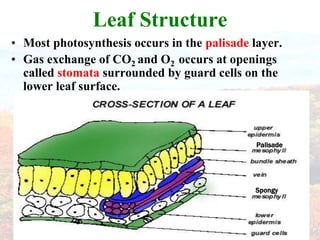
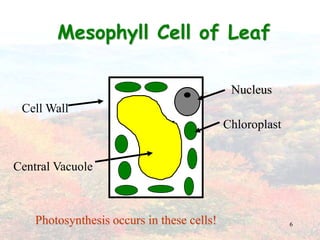
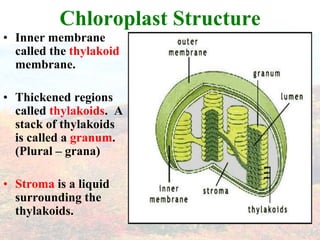
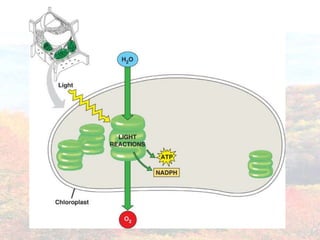
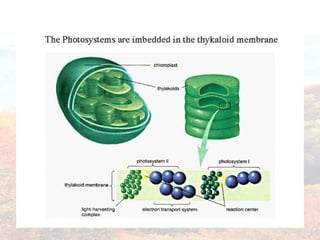
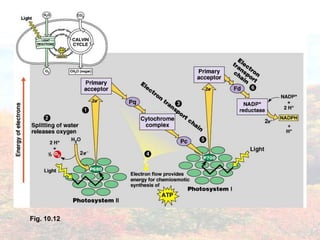
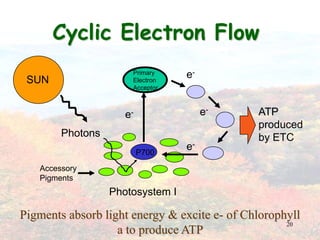
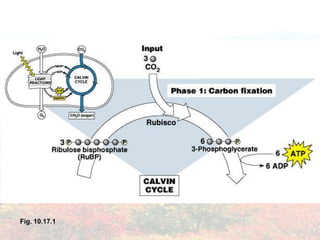
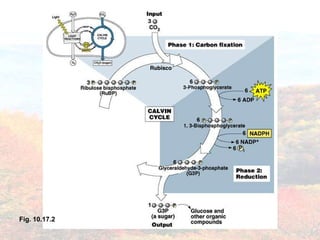
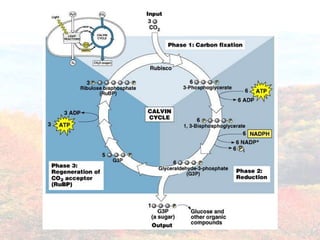
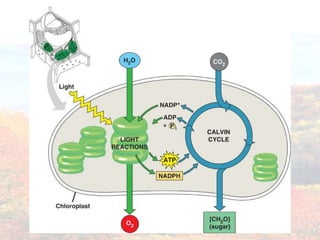
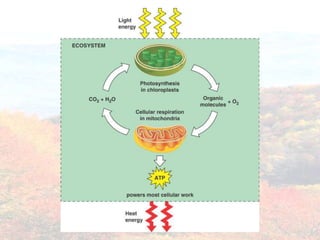
Photosynthesis occurs in plant leaves and involves two main phases: the light reactions and the dark reactions. In the light reactions, which take place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and used to convert water to oxygen and produce ATP and NADPH. In the dark reactions, also called the Calvin cycle, the ATP and NADPH produced in the light reactions are used to convert carbon dioxide into glucose in three main steps: carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration. Photosynthesis provides the basic energy source for essentially all life on Earth.