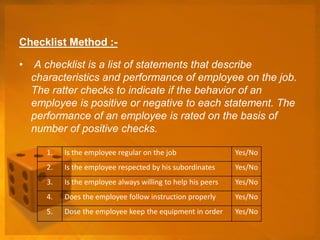
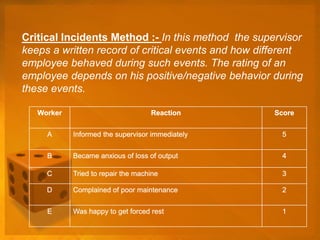
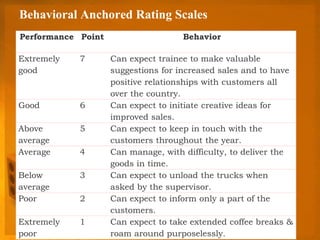
This document discusses various methods for performance appraisal and merit rating. It outlines traditional methods like confidential reports, essays, rankings and checklists. Modern methods discussed include assessment centers, human resource accounting, behaviorally anchored rating scales, and appraisal through management by objectives (MBO). The document also defines key terms like job analysis, job design, and job evaluation which are components for defining jobs and determining merit ratings. Factors for merit ratings beyond job performance are also listed.