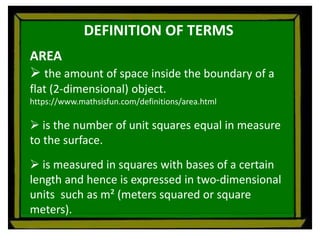
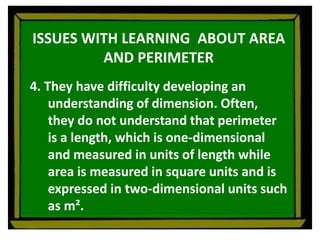
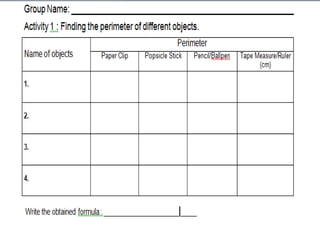
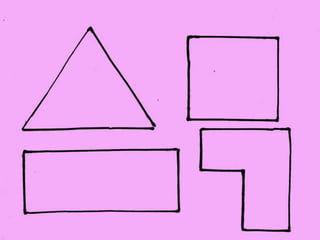
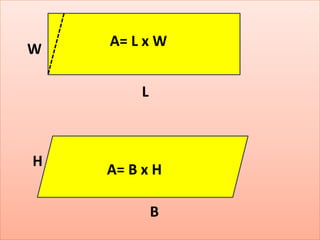
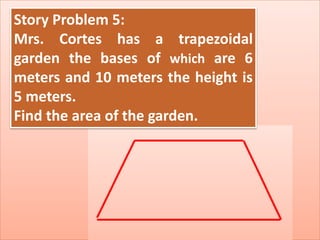
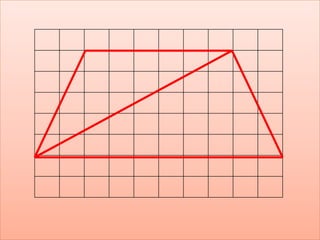
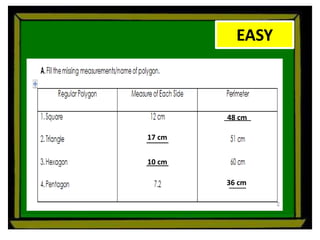
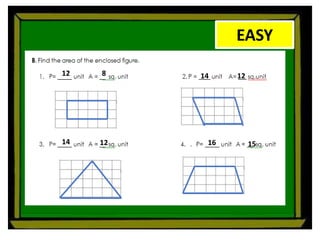
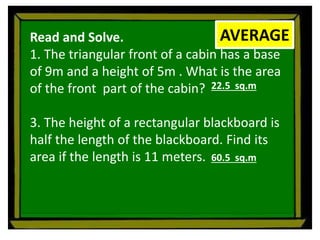
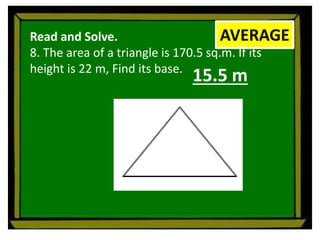
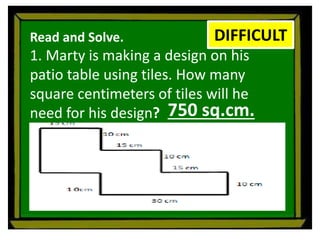
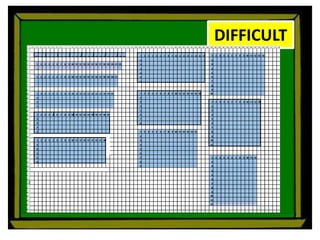
The document defines perimeter and area. Perimeter is a one-dimensional length measured in units like meters, while area is a two-dimensional measurement expressed in square units like square meters. Some issues students face in learning about area and perimeter are seeing them as just formulas, mixing up the concepts, not understanding standard units, and not linking mathematical concepts to real-world experiences. The document then describes activities to help students learn about perimeter and area through measuring real objects, finding perimeters and areas of shapes, decomposing complex figures, and solving word problems.