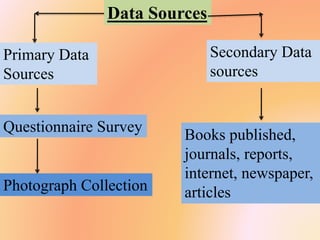
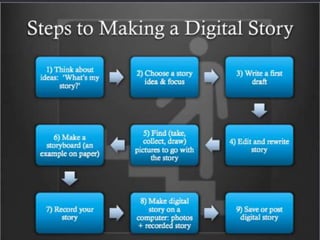
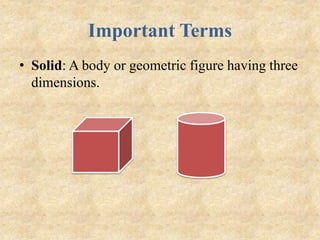
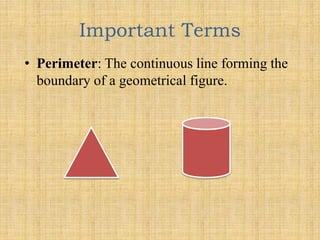
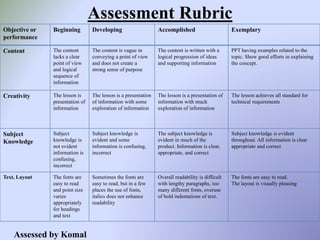
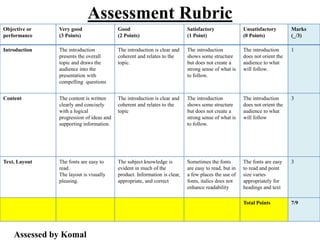
The document outlines a B.Ed. project by Swati Ghansela, focusing on the integration of ICT in education through a multimedia lesson plan on mensuration for sixth graders. It includes data analysis, lesson objectives, teaching methods, and assessments, showcasing the importance of technology in enhancing teaching and learning processes. Additionally, it discusses the creation of online discussion forums and blogs to foster community and sharing among educators and students.