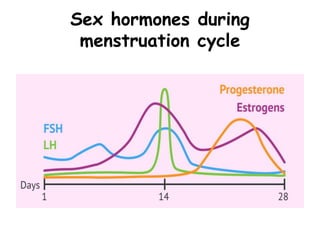
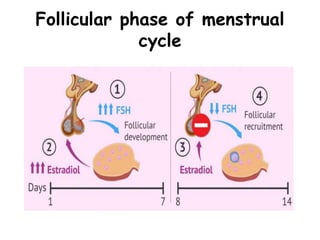
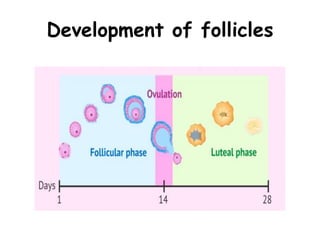
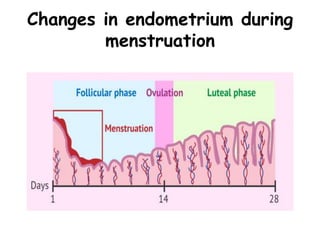
The menstrual cycle occurs roughly every 28 days in fertile women and involves changes controlled by hormones. It includes menstruation where the uterine lining sheds, the follicular phase where an egg develops and estrogen rises, ovulation where an egg is released, and the luteal phase where progesterone rises in preparation for potential pregnancy. These precise hormonal changes are necessary for reproduction and involve the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, ovaries, and uterus.