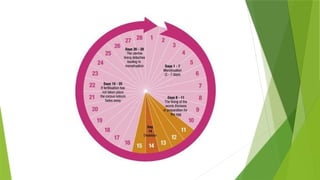
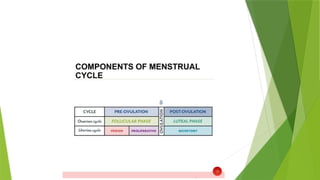
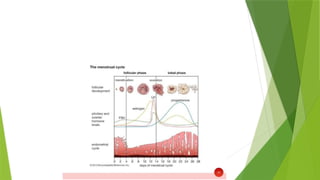
It's about the normal menstrual cycle of female and the change that happens in hormones including follicular stimulating hormone, luteinising hormone, estrogen and progesterone
It describes it in different phases and make it easy for understanding we have two phase depending upon the changes one a uterine phase which include changes in uterus and the other is ovarian phase which include changes in ovaries