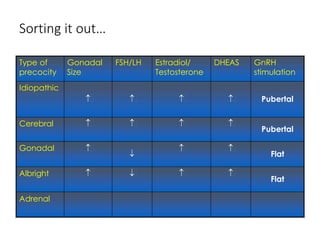
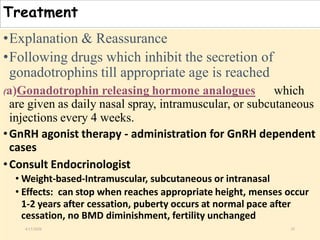
The document discusses puberty as a physiological phase characterized by the maturation of genital organs and changes influenced by factors such as nutrition, genetics, and hormonal activity. It details the manifestations of puberty in females, the causes of precocious and delayed puberty, and the management and treatment options for abnormalities. The document also covers changes in genital organs, breast development, and presents a classification system for assessing puberty-related disorders.