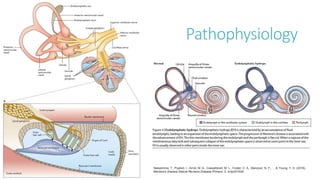
Meniere's disease is a disorder of the inner ear that causes episodes of vertigo, hearing loss, and tinnitus. It affects around 190 per 100,000 people in the US, most commonly between ages 40-60. The pathophysiology is not fully understood. Diagnosis involves ruling out other conditions and observing characteristic symptoms over time. Treatment aims to relieve acute symptoms, prevent recurrences, and stop progression, using medications, injections, or rarely surgery.