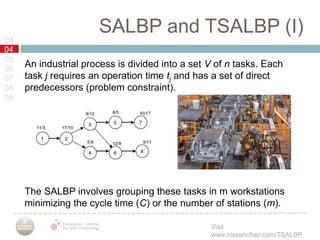
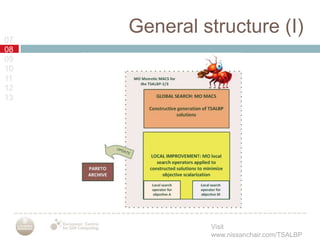
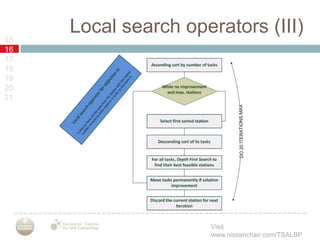
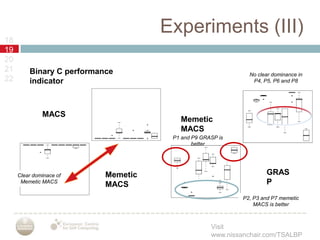
A multiobjective memetic ant colony optimization algorithm (MACS) is proposed to solve the time and space assembly line balancing problem (TSALBP) variant where the objectives are to minimize station area and number of stations. The algorithm combines a global search using MACS with two local search methods. It is compared against a GRASP algorithm on 9 problem instances, with no clear winner between the two approaches. Future work plans to design new evolutionary and memetic algorithms for the problem and add interactive preference methods.