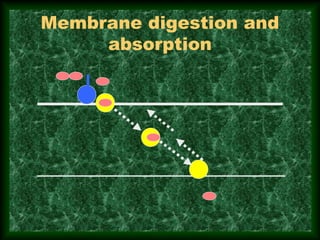
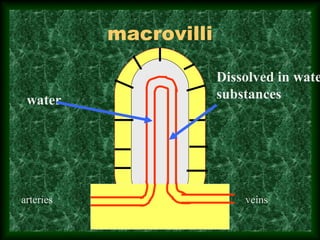
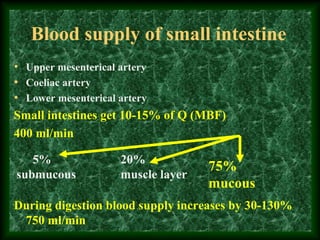
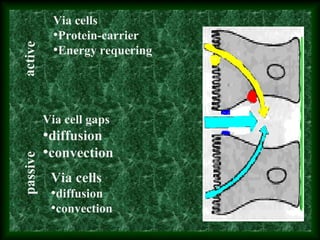
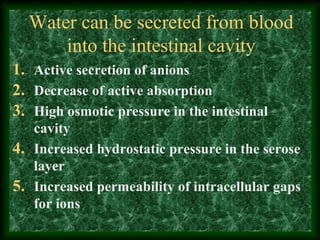
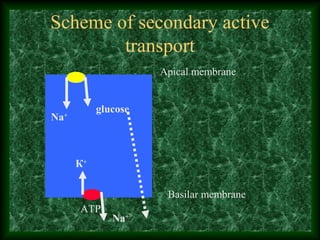
This document summarizes membrane digestion and absorption in the small intestine. It discusses how enzymes digest substrates in the mucus, glycocalyx, and on enterocyte membranes. Key points include the large surface area and efficiency of membrane digestion, as well as its close connection to absorption. Absorption involves both passive diffusion and active transport across enterocyte membranes and within microvilli. The major nutrients - proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins and minerals - are absorbed primarily in the duodenum and jejunum through these membrane transport processes.