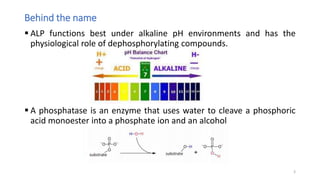
The document provides an overview of alkaline phosphatase (ALP), covering its name origin, physiological role, and isozymes found in humans, including its increase in blood levels during pregnancy due to placental production. Elevated ALP levels can indicate various medical conditions such as biliary obstruction and osteoblastic bone tumors, while low levels may result from specific health issues like hypophosphatasia and malnutrition. Key tissues containing ALP include the liver, bone, and kidneys.