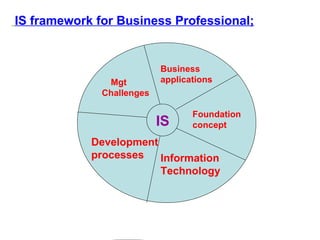
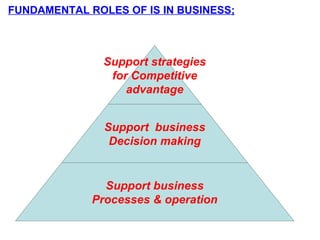
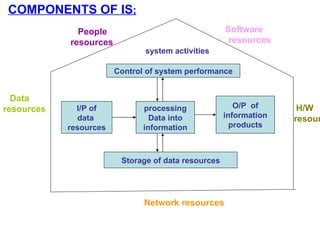
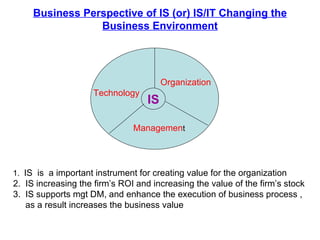
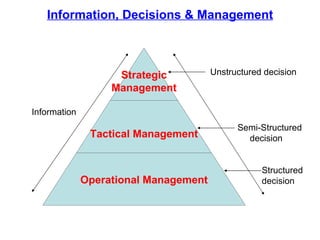
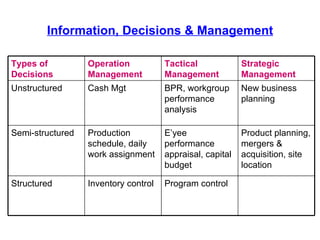
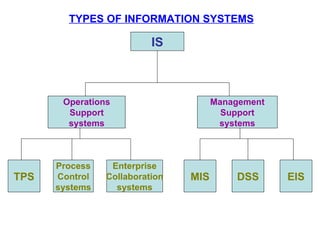
An information system is a set of people, procedures, and resources that collects, transforms, and disseminates information in an organization. It accepts data as input, processes it into information, and outputs that information. Information systems use a combination of people, hardware, software, networks, and data resources to store, retrieve, transform, and disseminate information within an organization. Information technology plays a vital role in business by helping to improve efficiency, effectiveness, decision making, and collaboration, strengthening competitive positions. There are four main stages in the process of an information system: entering data, changing and manipulating data, getting information out, and storing information and data.