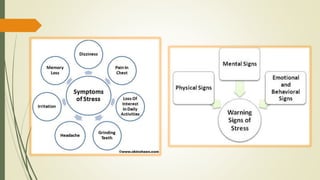
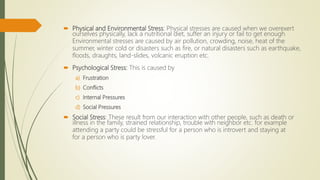
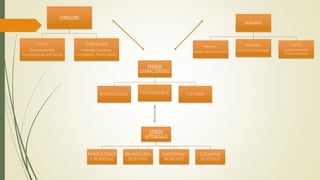
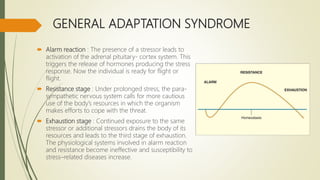
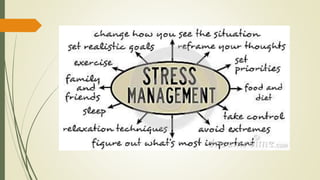
The document discusses stress, its nature, types, sources and effects. It describes the General Adaptation Syndrome which outlines the body's three stages in response to stress - alarm, resistance, and exhaustion. Stress can have emotional, physiological, cognitive, and behavioral effects and weaken the immune system. Coping strategies discussed include task-oriented, emotion-oriented, and avoidance-oriented approaches as well as relaxation techniques, meditation, biofeedback, exercise, assertiveness, time management, and rational thinking. Prolonged or high levels of stress can lead to illness.