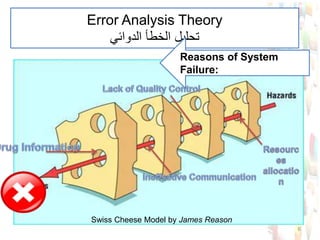
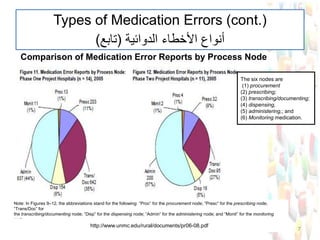
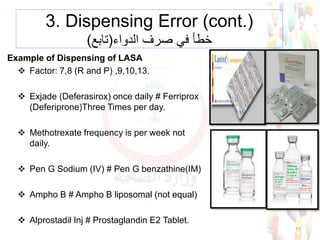
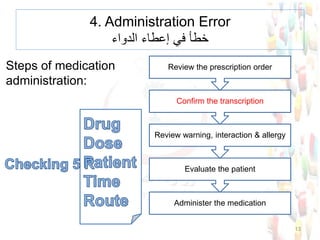
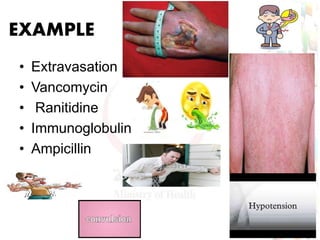
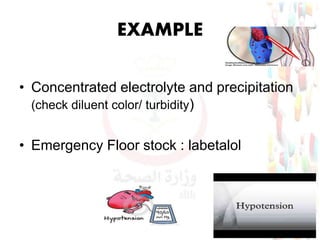
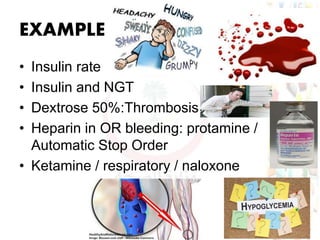
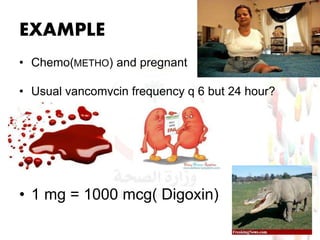
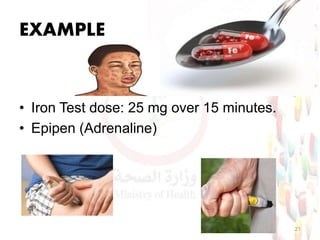
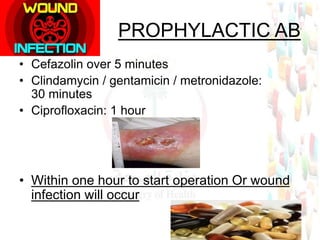
This document provides information about medication safety and errors. It discusses the extent of medication errors, where they occur in the medication use process, common error types, contributing factors and examples. The six main stages of the medication use process are procurement, prescribing, transcribing, dispensing, administering and monitoring. Transcription errors account for around 50% of medication errors. Administration errors are the cause of about 40% of medication errors. The severity of errors is also categorized. The goal is to prevent errors from occurring and recurring through understanding the medication use system and error analysis.