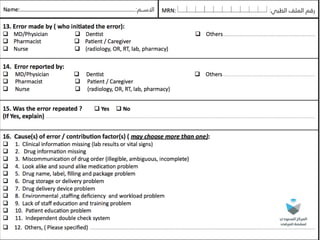
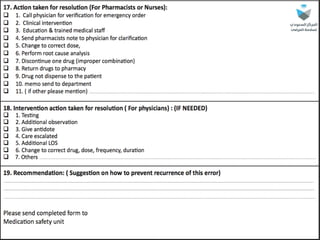
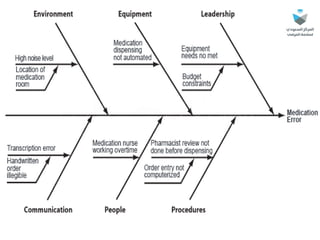
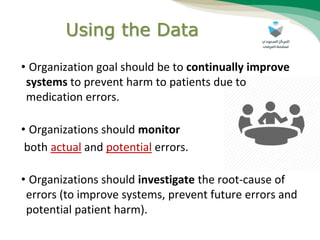
The document outlines a medication error reporting system, emphasizing effective detection and reporting processes. It details characteristics of successful reporting systems and discusses barriers to reporting, such as a culture of blame. The text concludes with the importance of continuous improvement in medication safety and the role of all healthcare professionals in it.