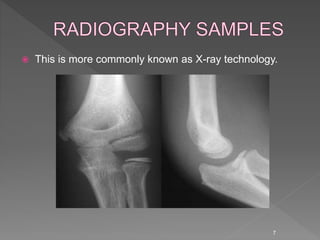
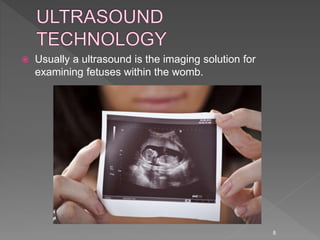
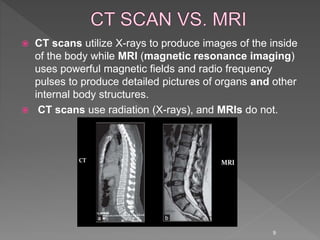
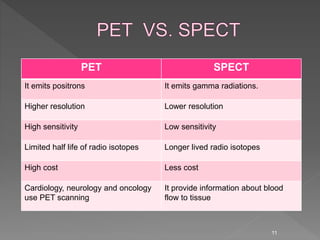
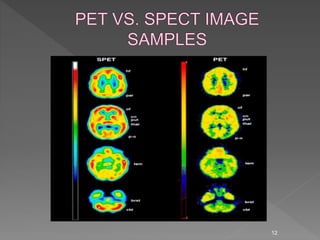
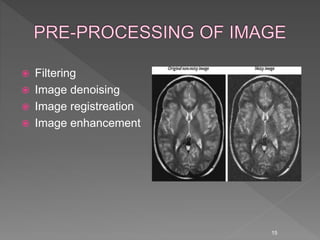
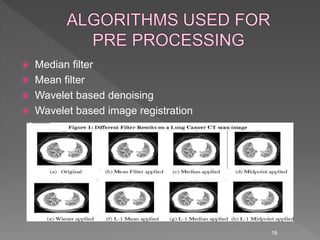
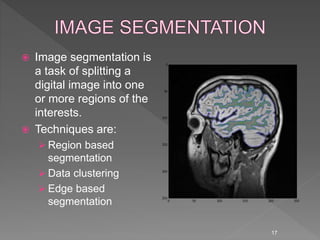
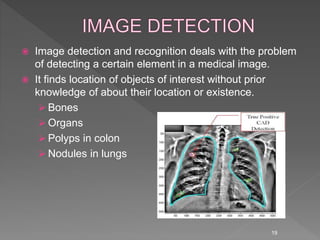
Medical image processing involves acquiring medical images through modalities like X-rays, CT, MRI, using techniques like ultrasound. The images are then preprocessed, segmented, analyzed and classified to diagnose diseases or detect abnormalities. Key applications include tumor detection, monitoring bone strength, and medical image fusion to enable accurate analysis and remote sharing of data to enhance diagnosis and treatment.