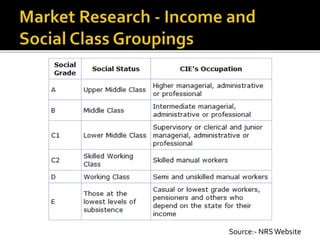
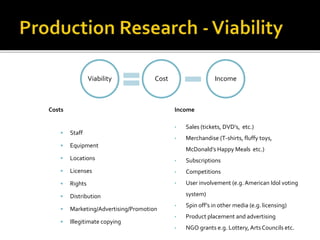
This document discusses research activities involved in planning and producing media products. It explains that market research and product research are important to understand audience needs and ensure commercial viability. Market research includes collecting statistical data on the audience, their awareness of and attitudes towards products. Product research involves developing content, assessing commercial potential, and planning production and post-production processes. Media companies often hire outside research agencies to conduct specialized research as it is more cost-effective than maintaining an in-house team. Careful research and planning of production costs and potential sources of income are necessary to determine a media product's viability.