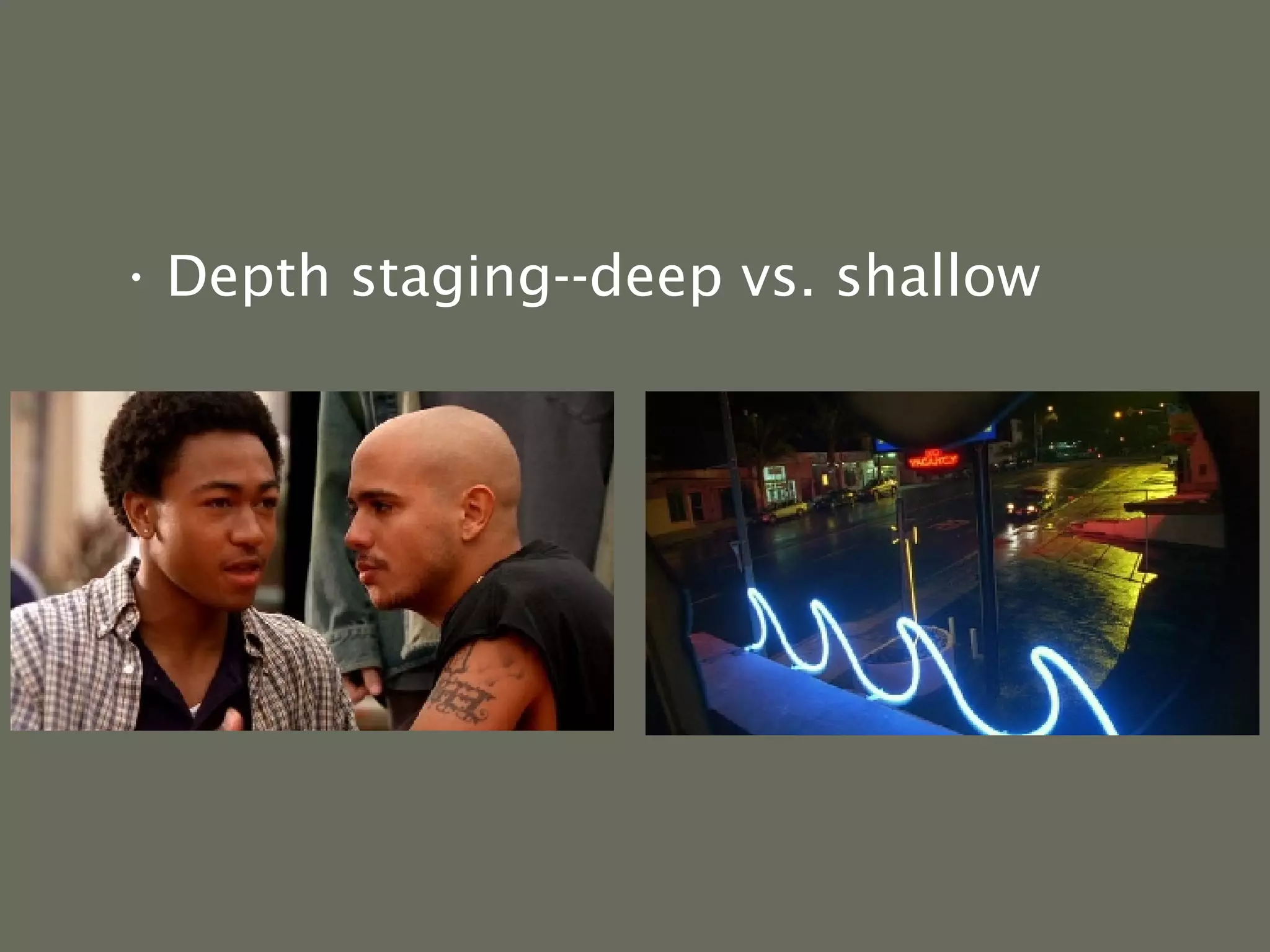
This document provides an overview of key concepts for analyzing media texts, specifically moving images. It defines a text as any media product that can be analyzed for its meanings, such as films, TV shows, magazines, and websites. Textual analysis involves breaking down a text into its component parts and arrangements to understand why creators chose those elements. For moving images, this includes analyzing the narrative or non-narrative form, visual style through techniques like mise-en-scène, cinematography, and editing, as well as sound elements.