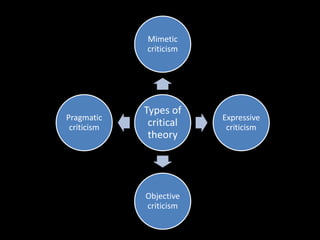
The document discusses different types of literary criticism:
1) Mimetic criticism focuses on how accurately a work depicts reality and judges its quality based on verisimilitude.
2) Pragmatic criticism views a work as constructed to achieve effects on the audience and judges its value by its success in doing so.
3) Practical criticism concerns itself with analyzing particular works and writers, often implicitly or when occasion demands, as seen in influential English and American works like Dryden's essays and Arnold's criticism.