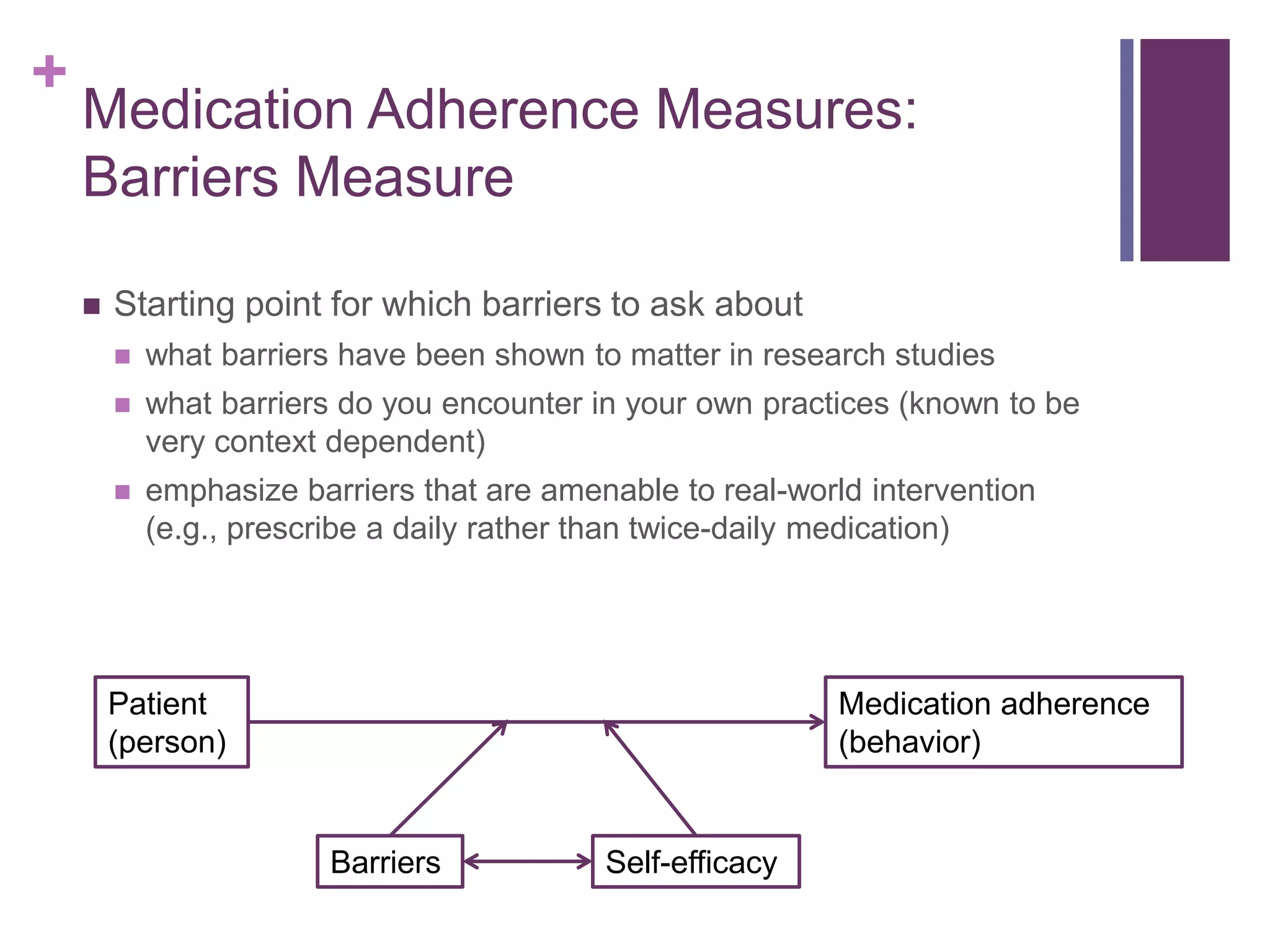
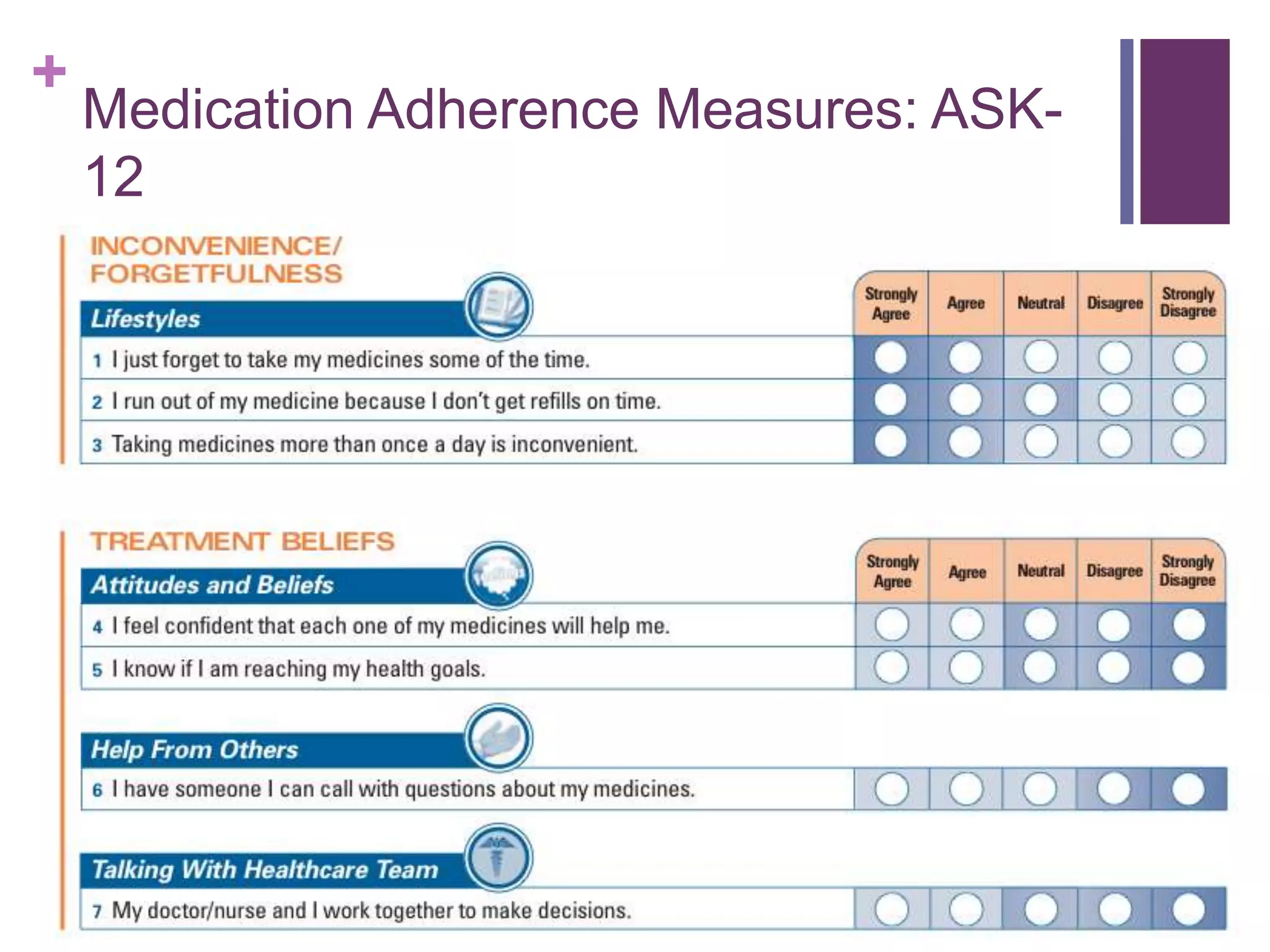
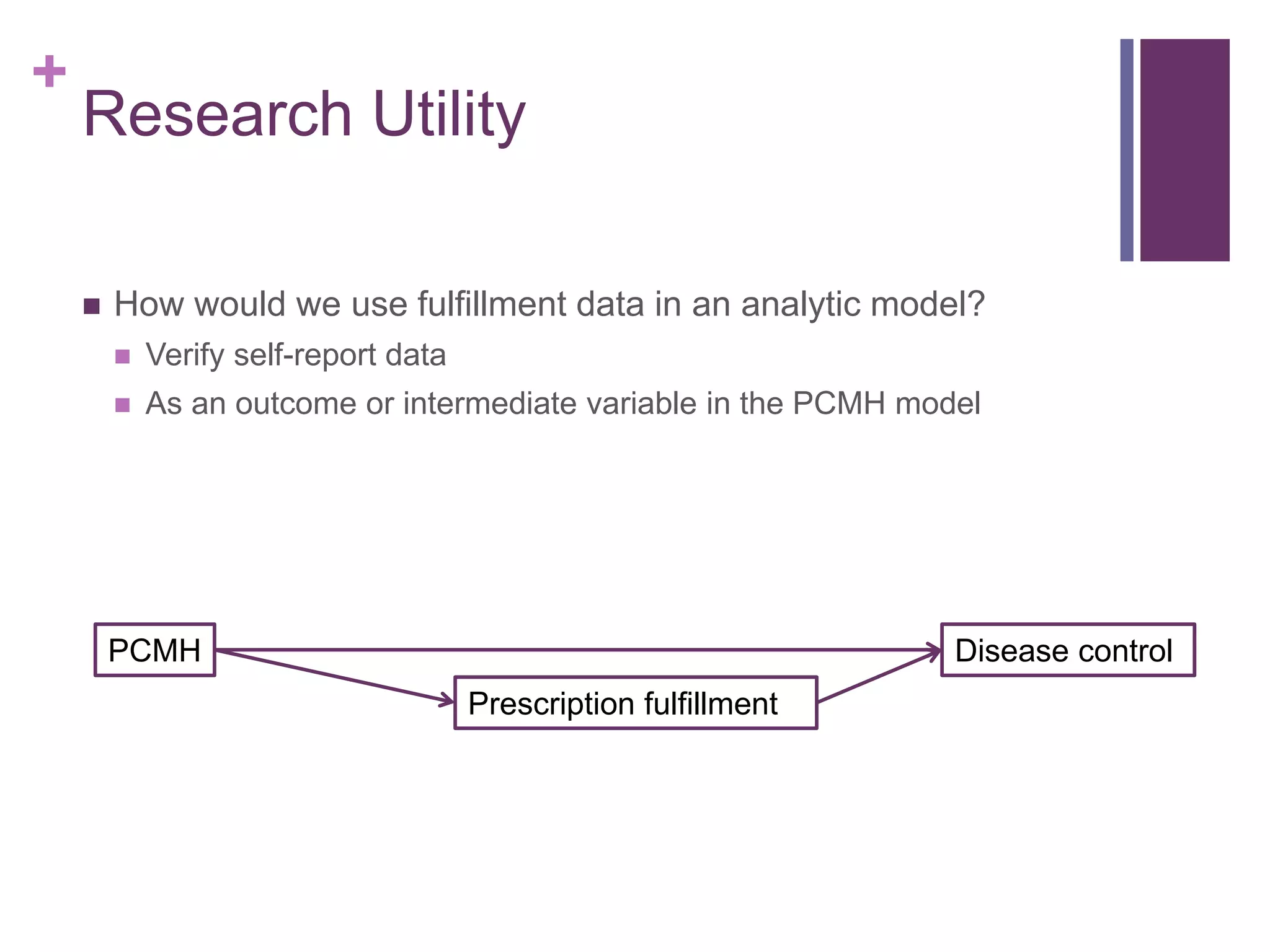
The document provides a comprehensive overview of medication adherence, focusing on what domains should be measured, barriers patients face, and the self-efficacy of patients regarding their medication regimens. It discusses various methods for measuring adherence, including self-report questionnaires and prescription fulfillment data, and reviews existing measures for their effectiveness and validation. It emphasizes the importance of addressing barriers to adherence and suggests practical approaches for clinical settings to implement these measures in routine practice.











![+
Scale
[Ref #] Scale type Time period Sample size Population
Validated
against
Validity
Results
Adherence
Self Report
Questionnair
e (ASRQ)
[25-27] Likert
None
Specified 245
Patients from
GP practice
taking
antihyperten
sives MEMS
Significant
association
(p=0.0004)
216
Patients from
GP Practices
taking
antihyperten
sives MEMS
Sensitivity=
46%;
Specificity=6
6%
Gehi [41] Likert
Previous
month 1015
Outpatients
with
documented
chronic heart
disease
Develop-
ment of CV
events
Significant
association
(p=0.03)
bivariate
analysis,
0.06
multivariate
analysis)
Inui [46] Dichotomous
Previous 2
months 241
Patients with
HTN Pill count
Sensitivity =
55%;
Specificity =
88%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/medadherenceandselfefficacy-150710054107-lva1-app6892/75/Med-adherence-and-self-efficacy-12-2048.jpg)
![+
Scale
[Ref #] Scale type Time period Sample size Population
Validated
against
Validity
Results
Medical
Outcomes
Study
Adherence
question [57] Likert
Previous 4
weeks 139
Patients >18
with HTN,
DM, hyper-
cholesterole
mia, hypo-
thyroidism or
requiring
HRT
Pharmacy
refill records
Spearman
Rho=
0.261(p=0.05
)
Visual
Analogue
Scale (VAS)
six month
version [89]
Continuous
(visual
analogue)
Previous 6
months 1985
Patients >18
with DM MEMS
VAS higher
than MEMS
adherence
mean
difference
15% (p value
not reported)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/medadherenceandselfefficacy-150710054107-lva1-app6892/75/Med-adherence-and-self-efficacy-13-2048.jpg)