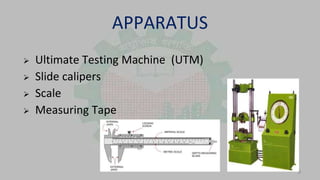
This presentation summarizes different types of welding joints used in mechanics of solids. It introduces butt and spot welding joints. For butt joints, it describes common types like single, double, open and closed butt joints and their advantages. Spot welding is described as a resistance welding process that joins sheets of metal at regular intervals without filler metal. The advantages of both joints are speed and ease of use for spot welding and universal acceptance for butt joints. Their applications and some disadvantages are also outlined. The objectives, apparatus and methodology of an experiment comparing these joints are summarized.
Human: Thank you for the summary. It captured the key details about the different types of welding joints discussed in the presentation in just 3 sentences as requested.