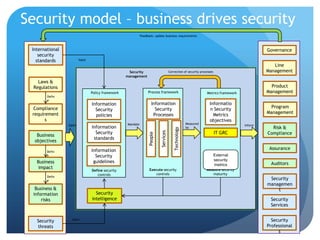
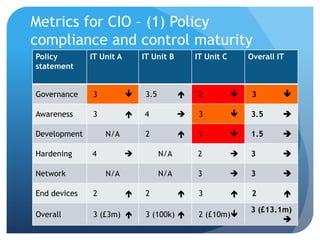
This document discusses meaningful security metrics for various stakeholders. It recommends metrics that measure policy compliance, control maturity, and value at risk for CIOs. For operations managers, it suggests metrics that track systems outside of SLAs and security incidents breaching SLAs. For CISOs, suggested metrics include value at risk, compliance, and annual risk reduction compared to spending. For CEOs and boards, total exposure and unmanaged risk are recommended metrics. It also provides characteristics for effective security metrics and metrics for evaluating the metrics themselves.