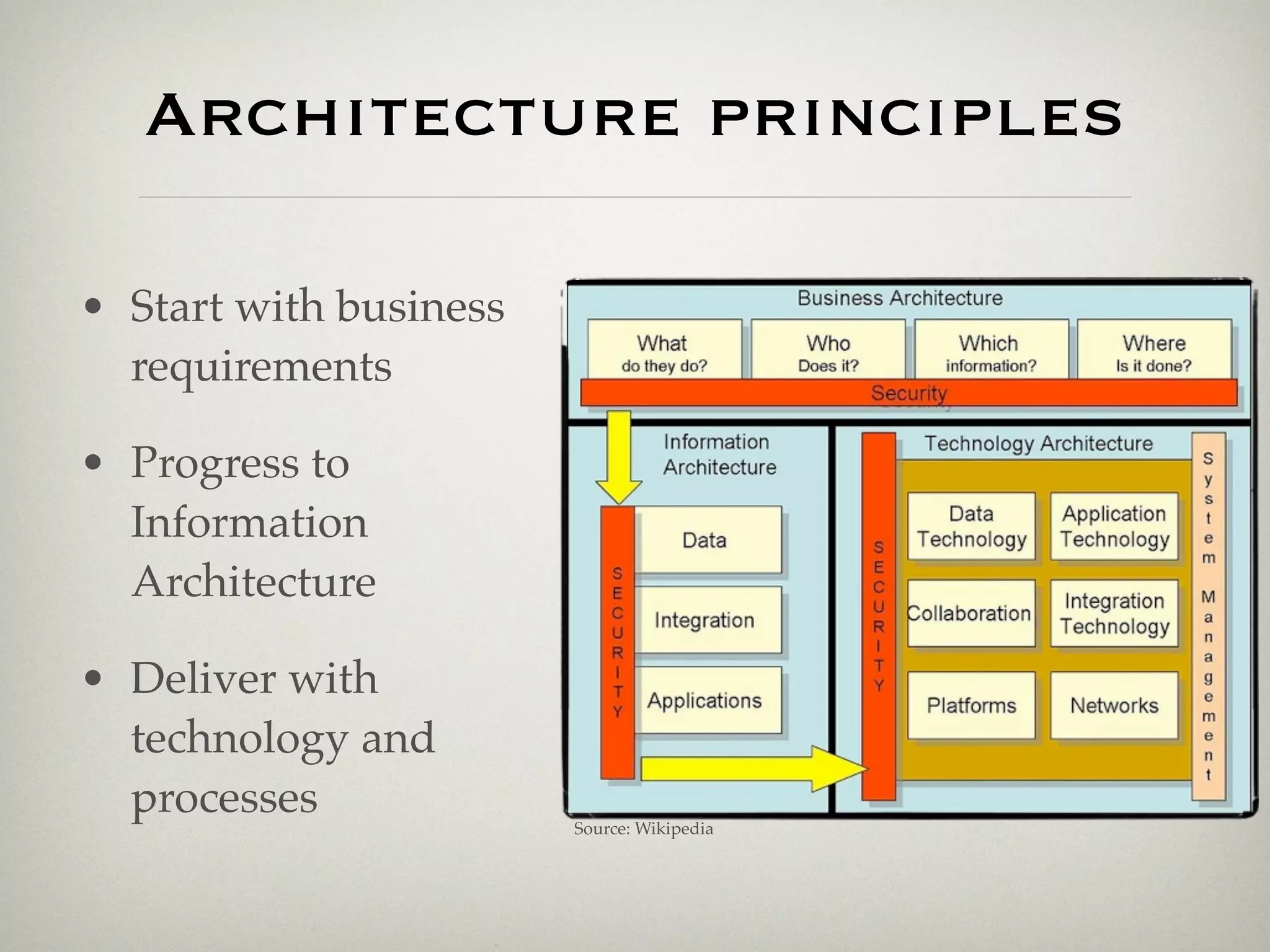
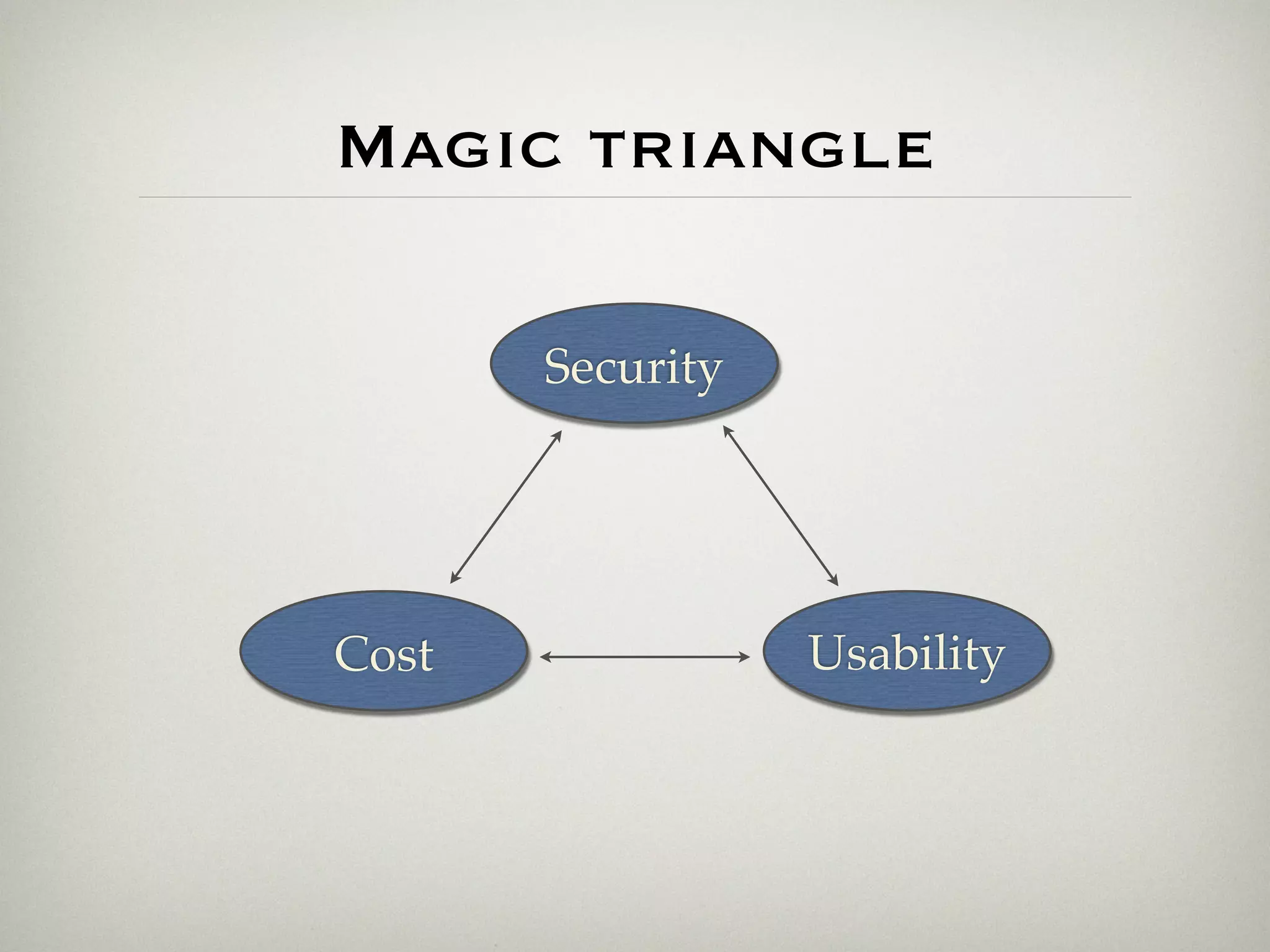
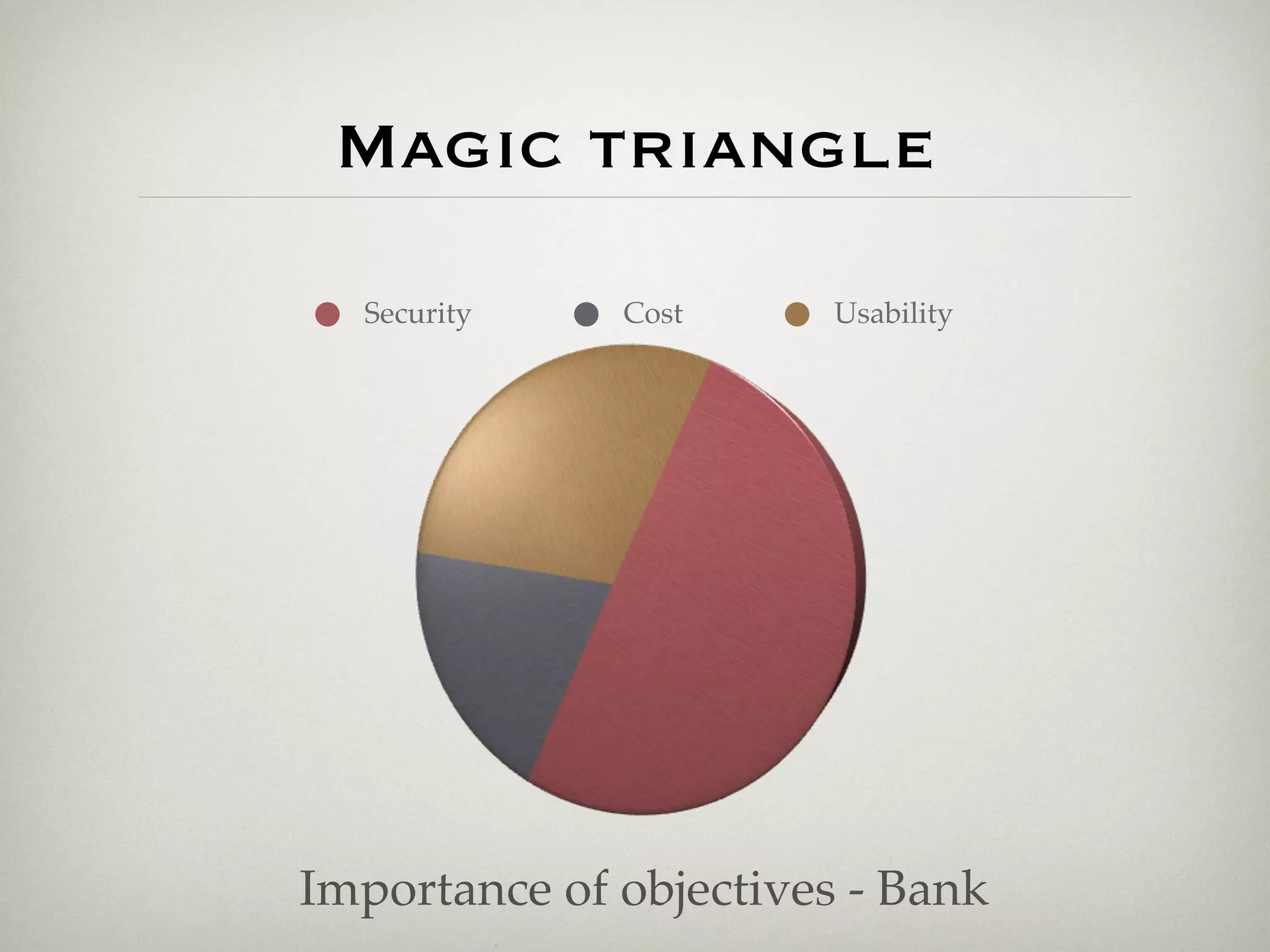
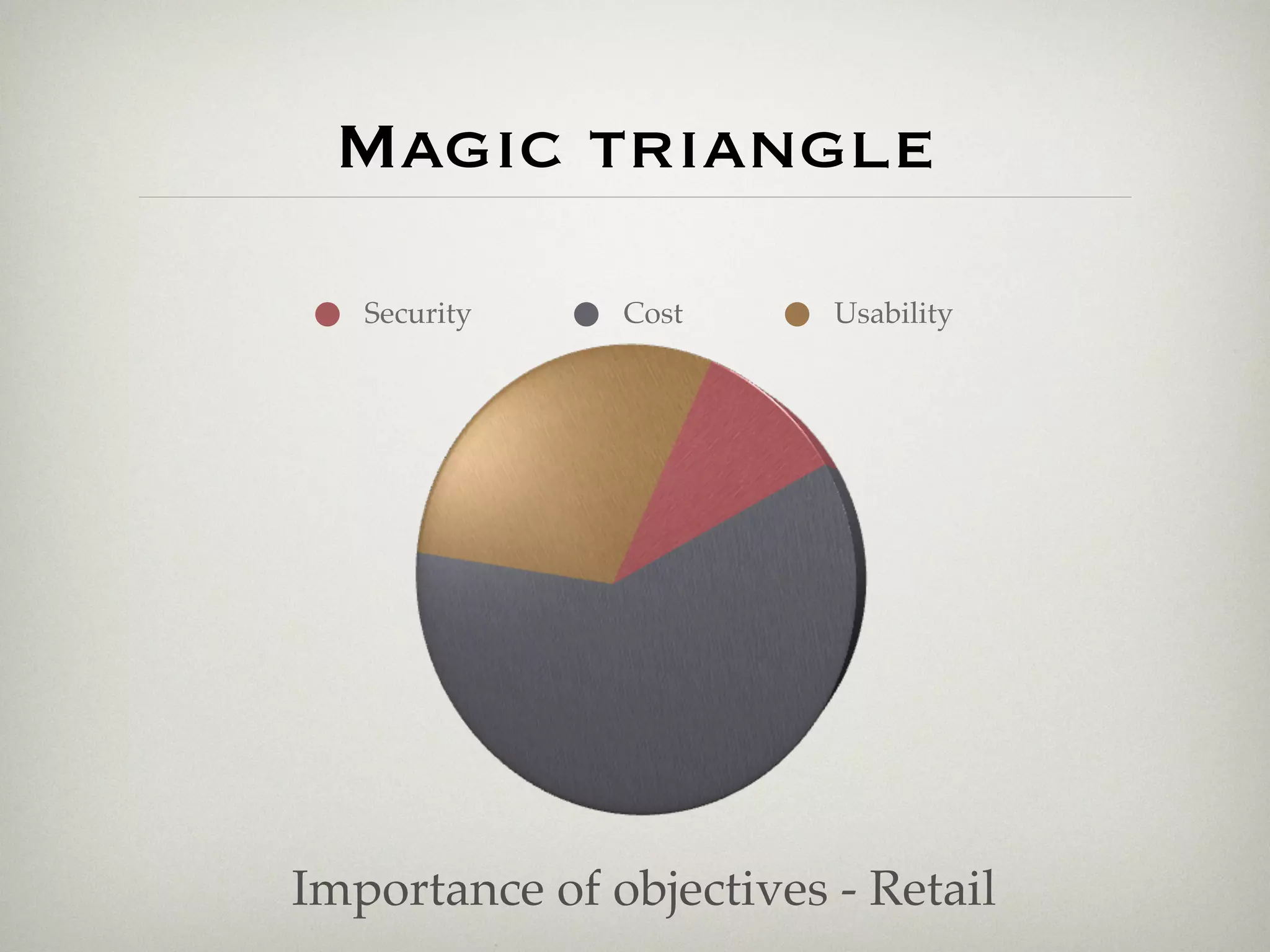
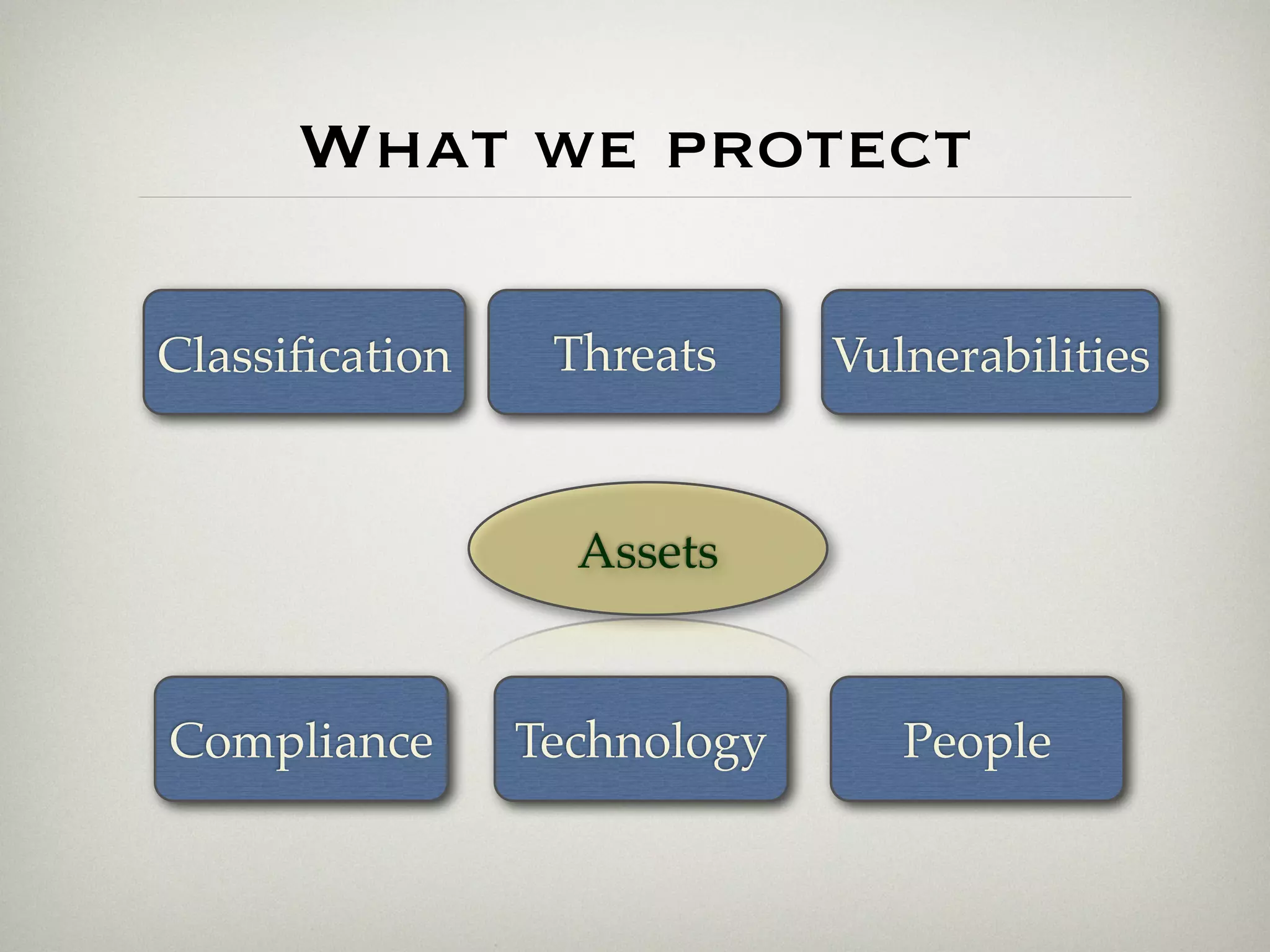
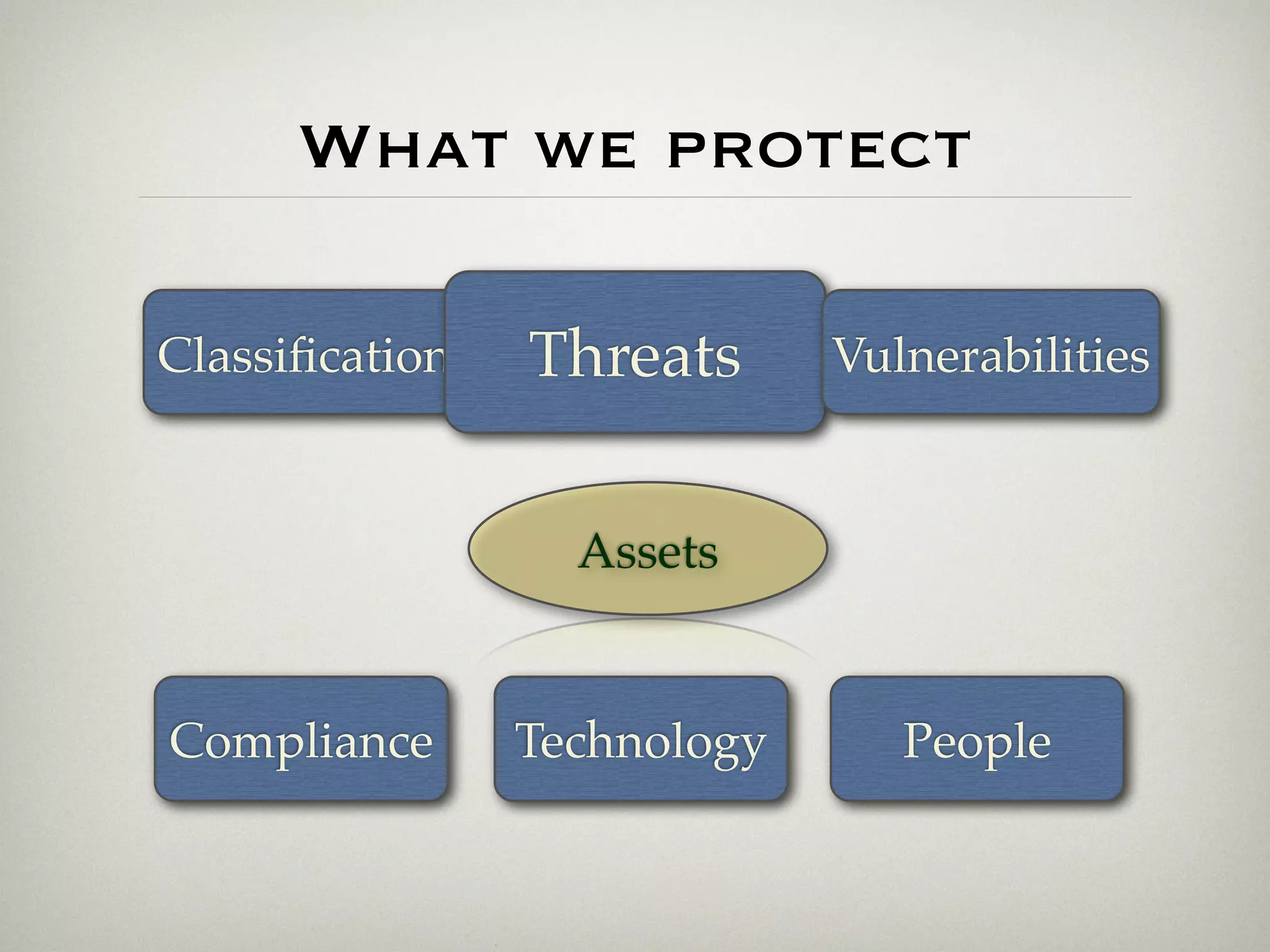
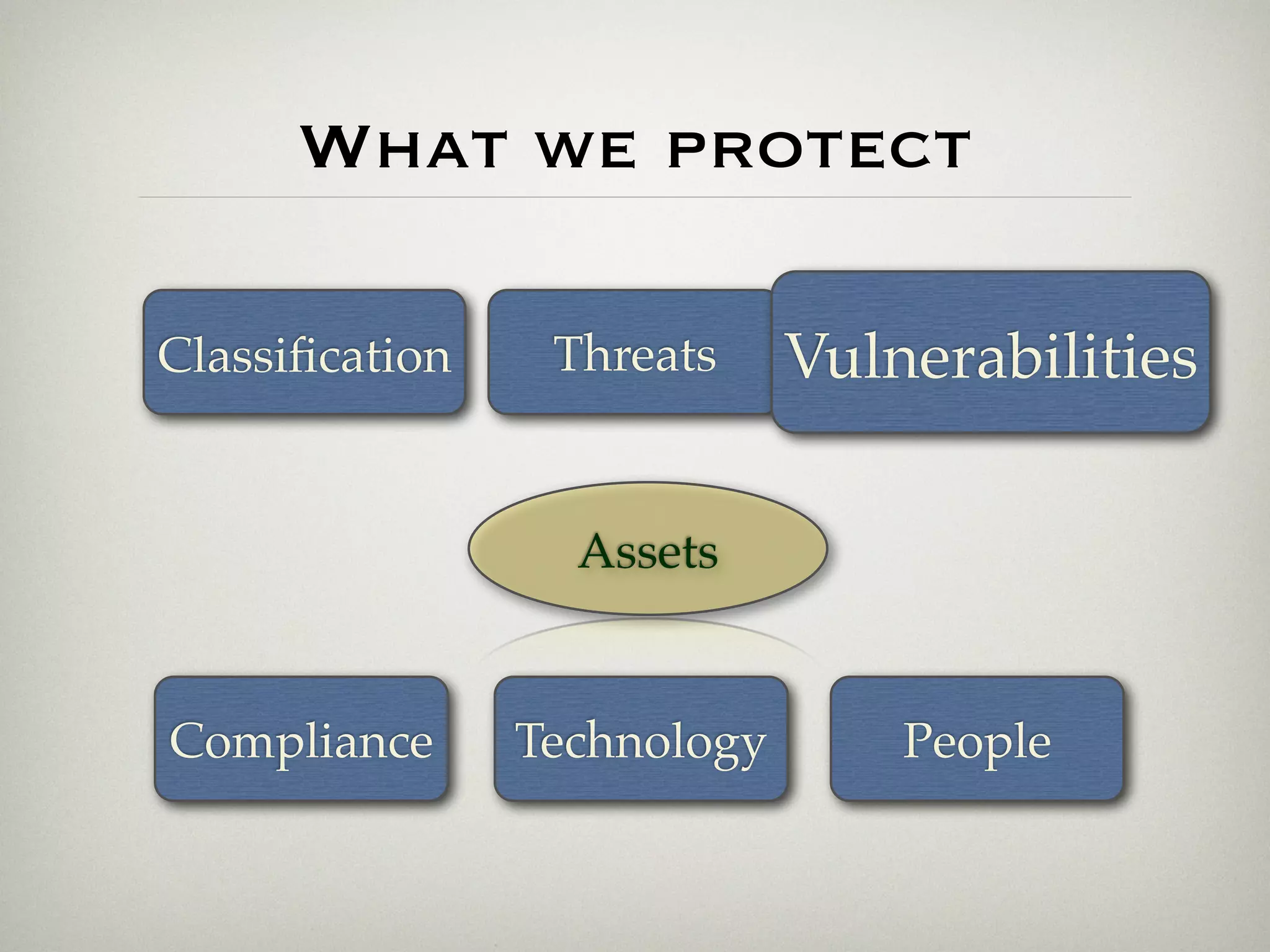
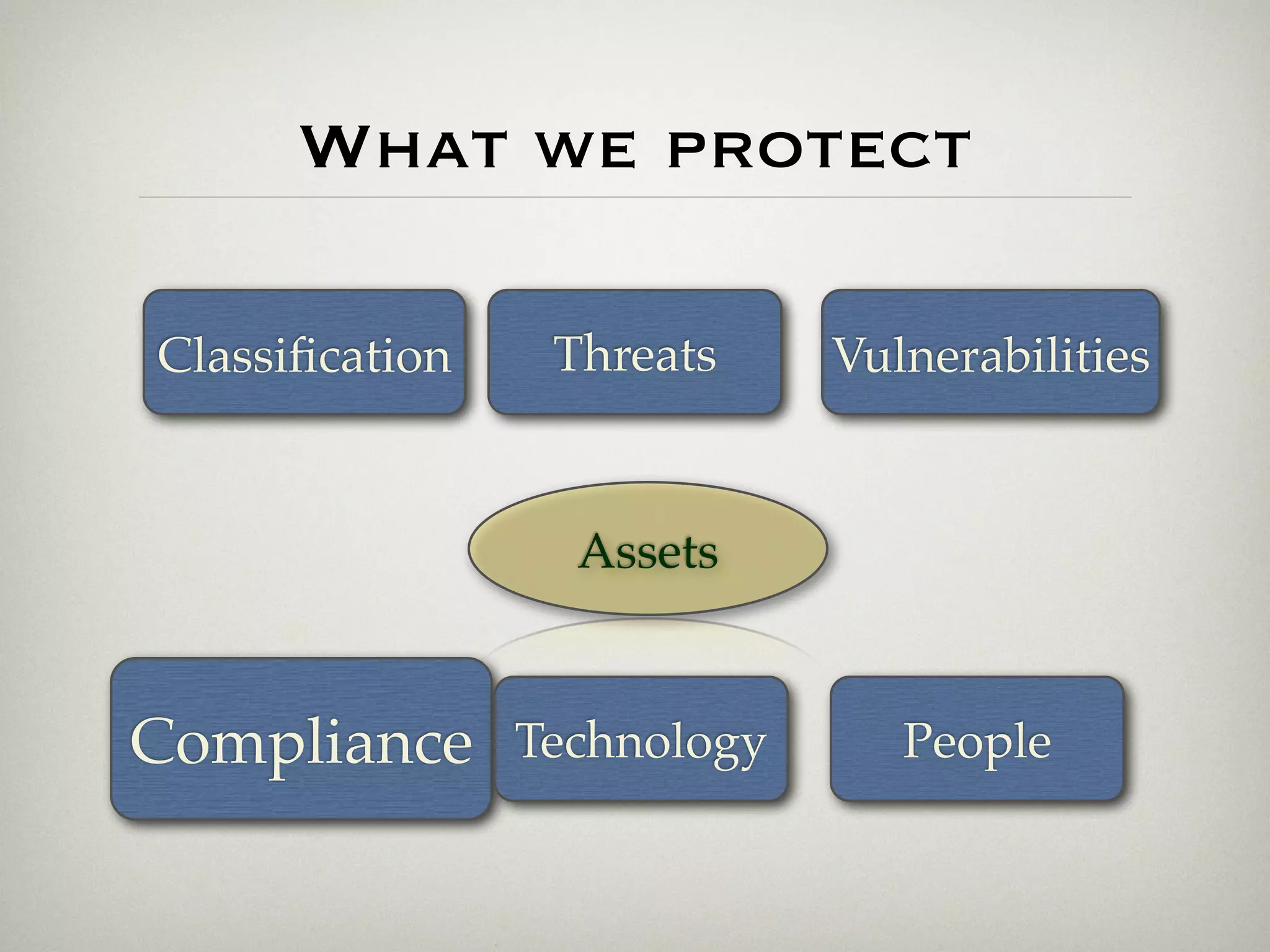
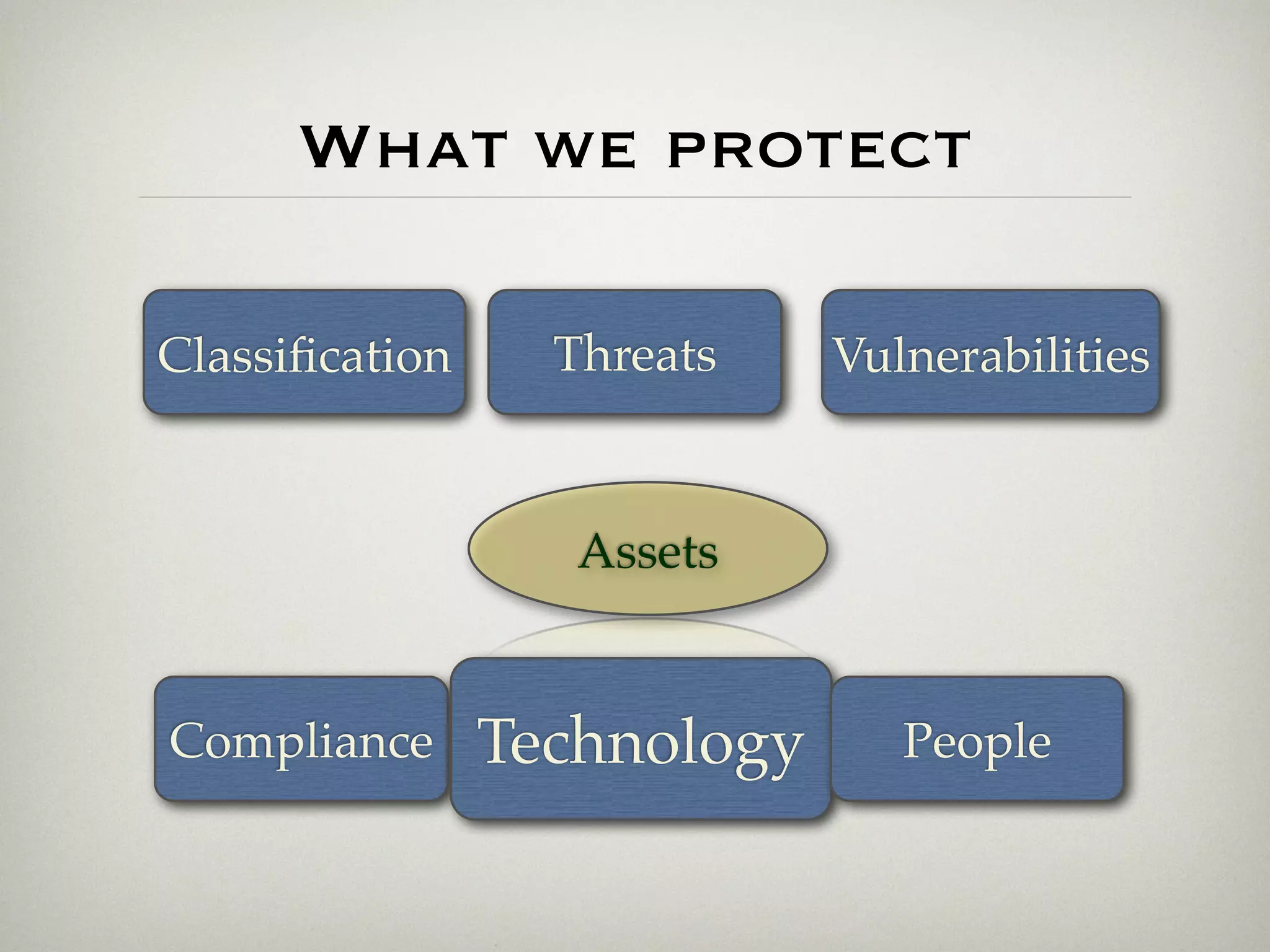
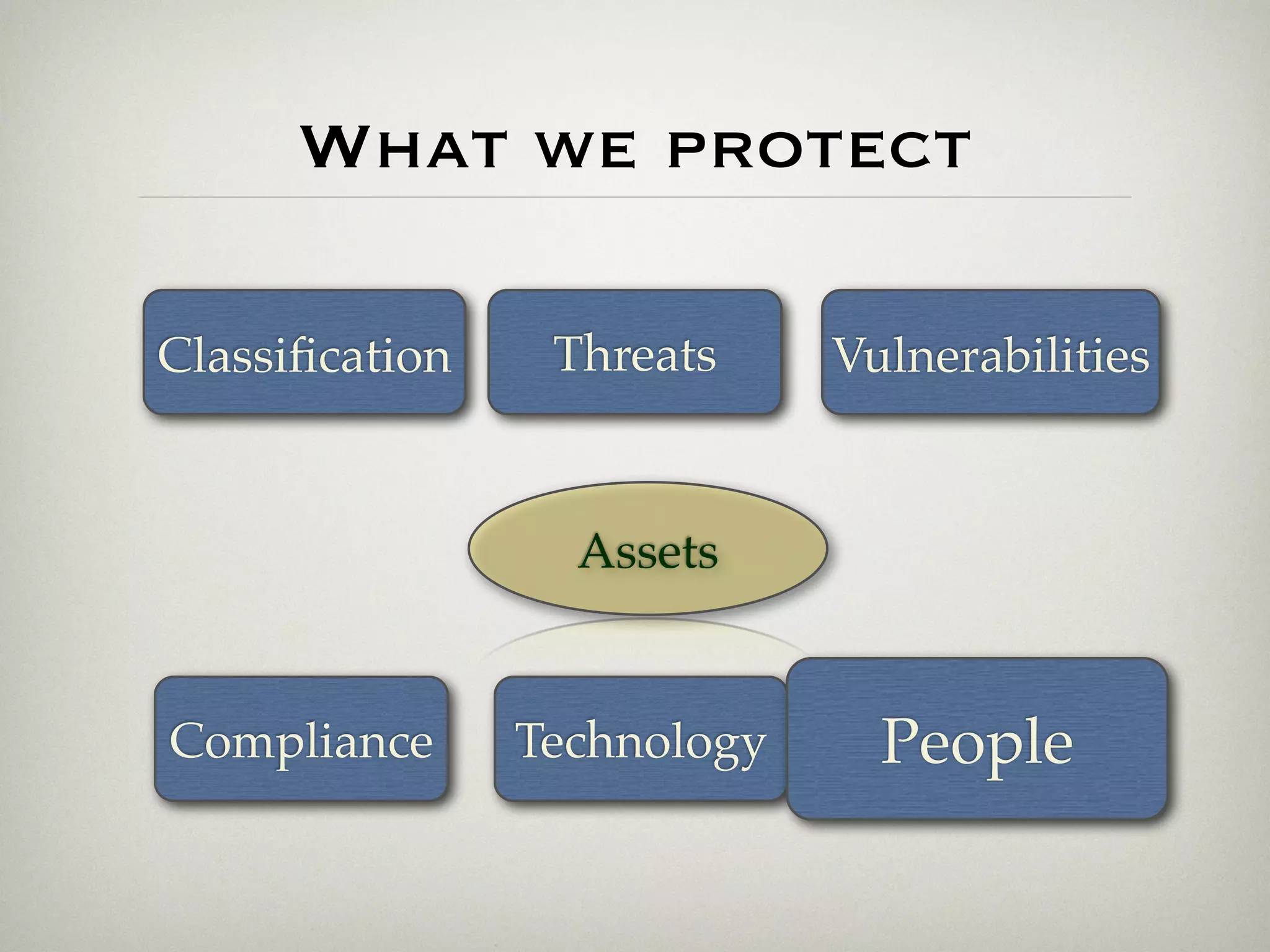
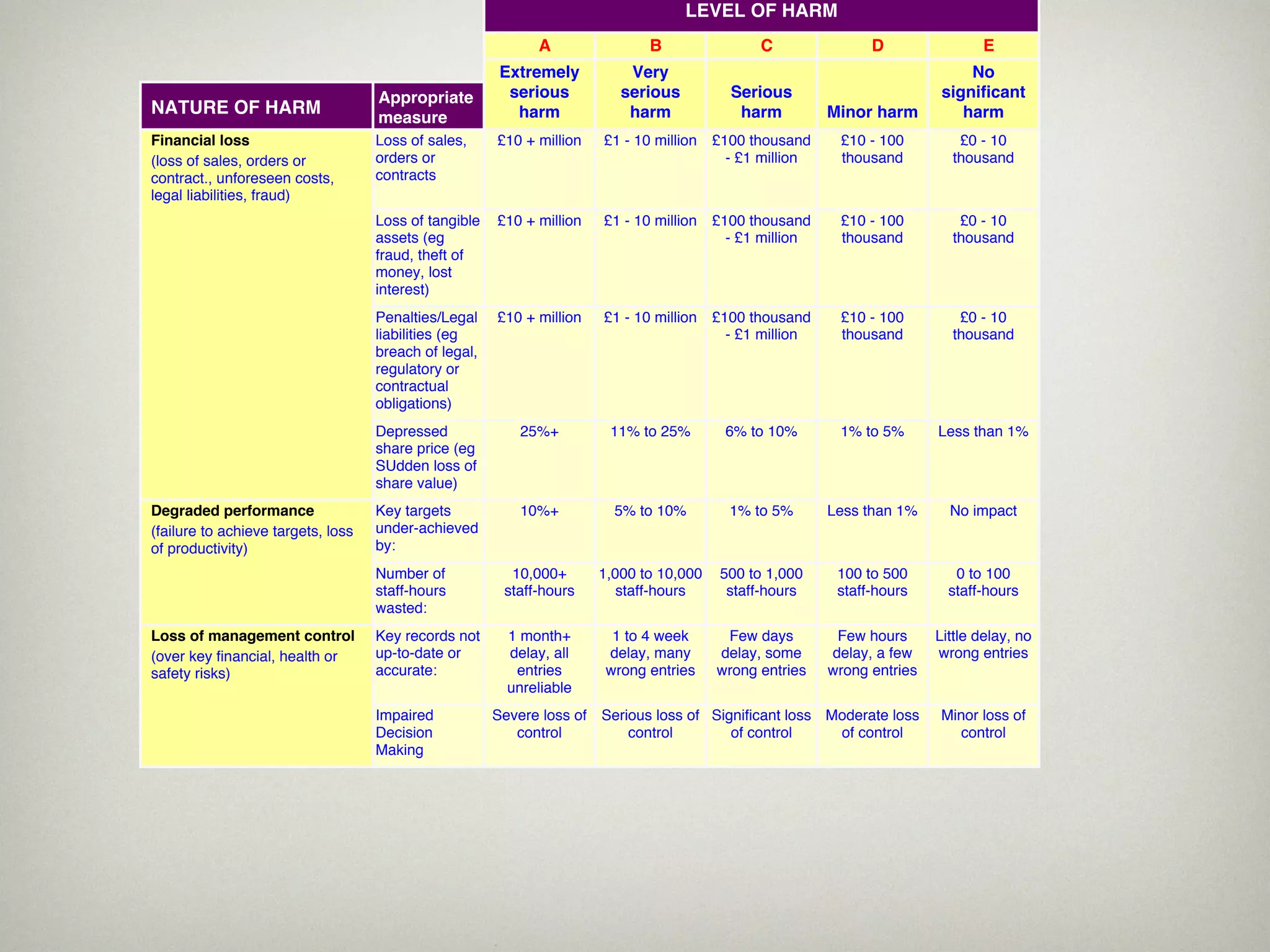
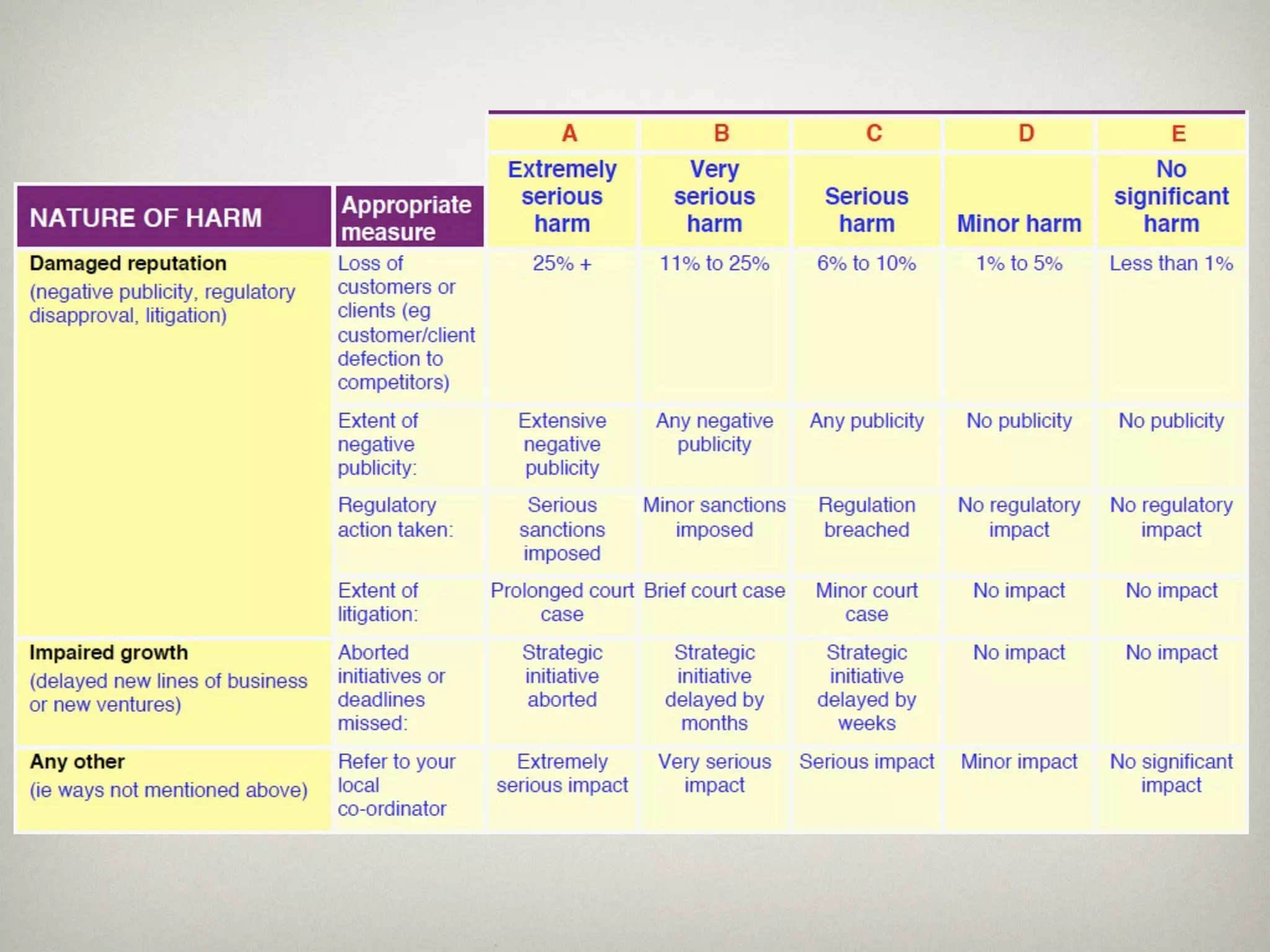
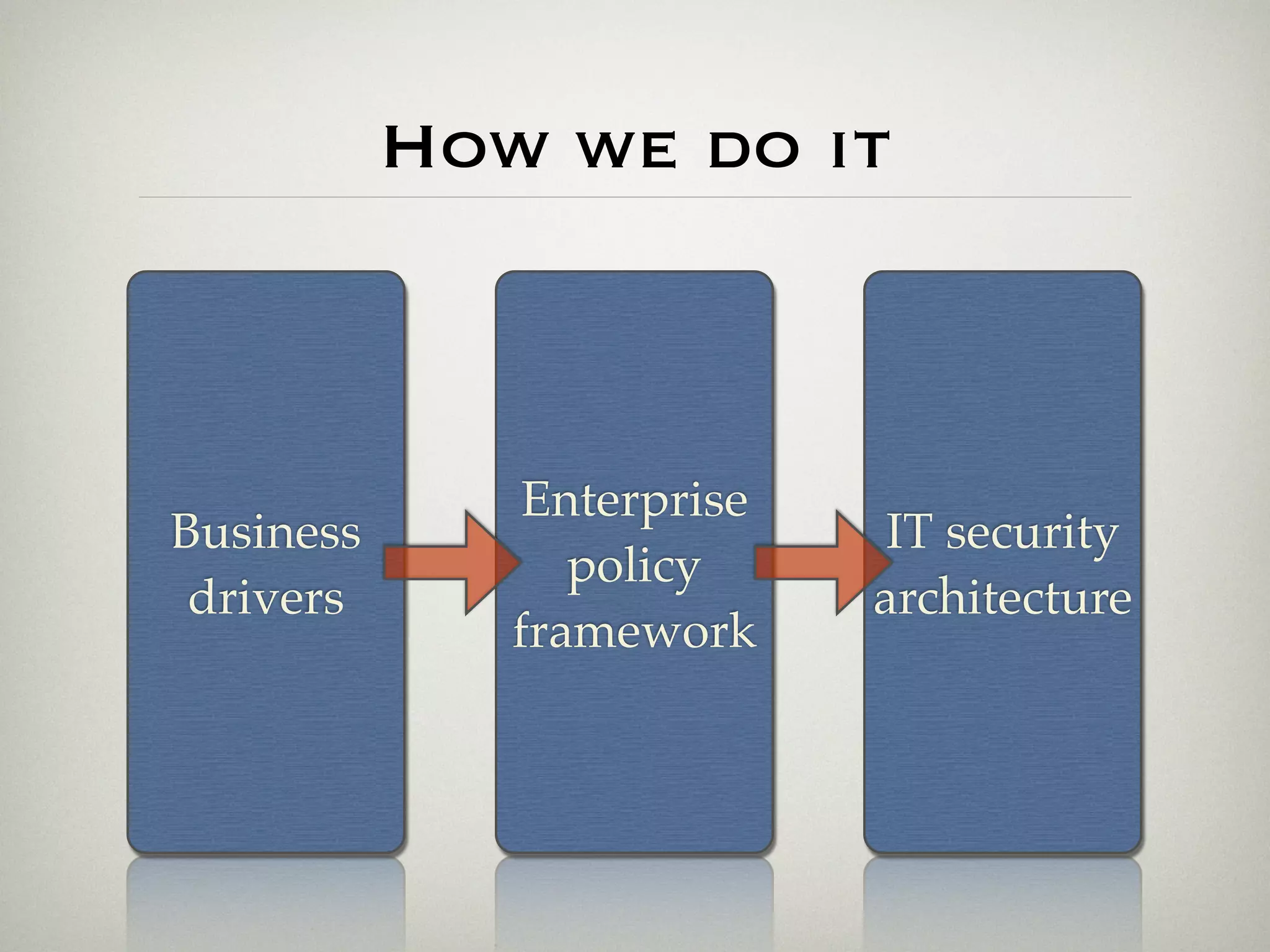
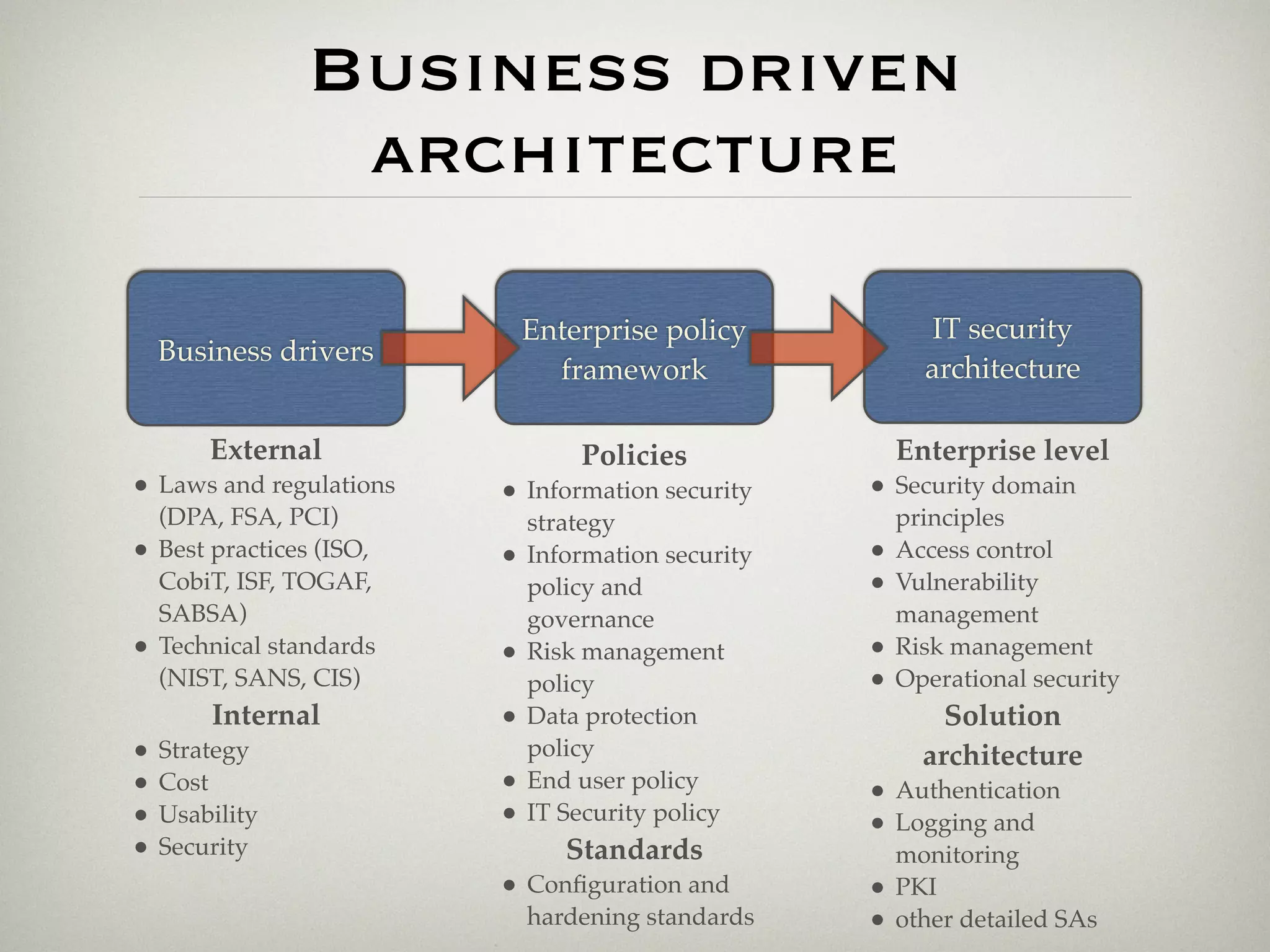
This document is a presentation about the role of security architecture in managing information risk in large retail enterprises. It discusses what security architecture is, the business benefits it provides, and practical examples from a retail organization. The presentation covers topics like principles of security architecture, protecting assets from threats and vulnerabilities, examples of real security issues faced by banks and telecom companies, and using a layered "onion" approach to security rather than just relying on outer defenses. It proposes taking a business-driven approach to security architecture aligned with enterprise policies and frameworks.