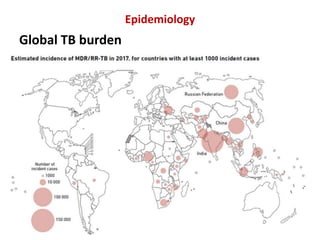
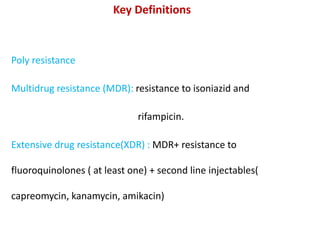
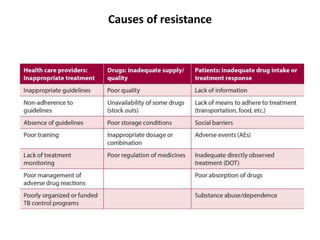
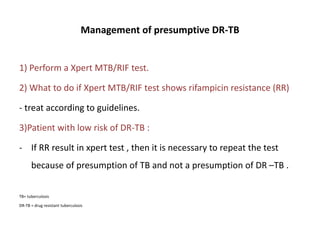
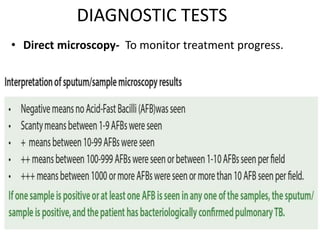
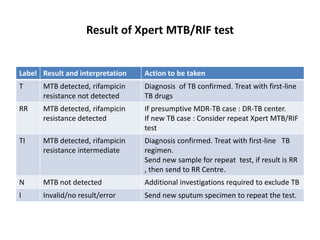
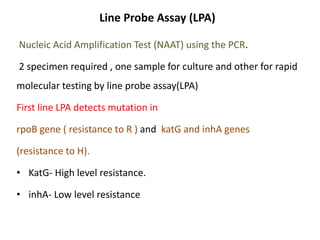
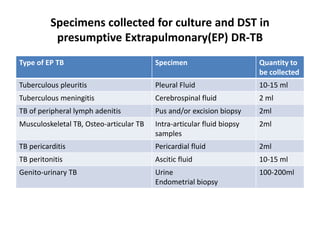
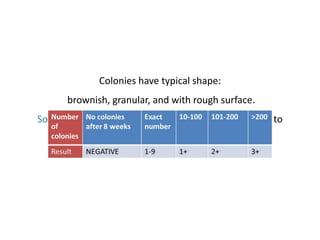
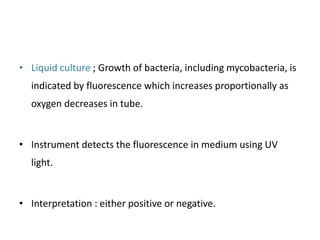
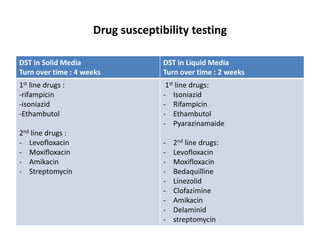
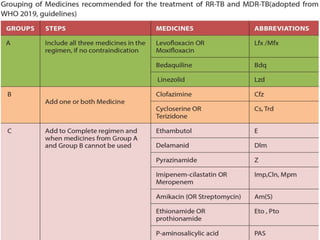
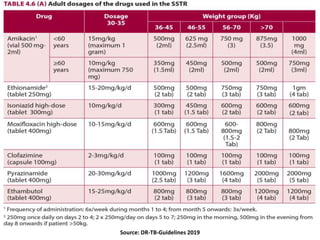
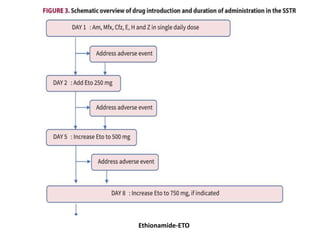
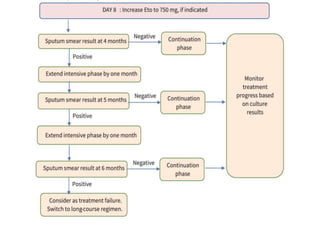
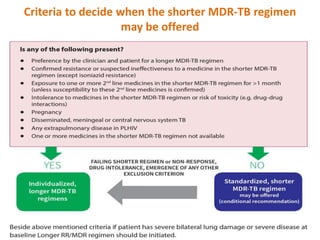
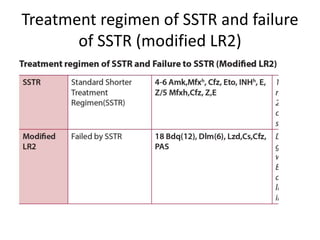
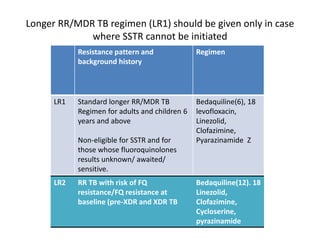
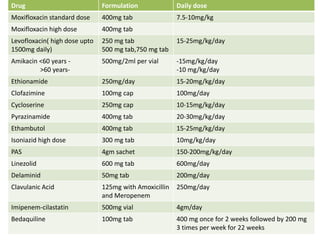
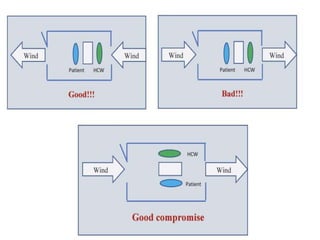
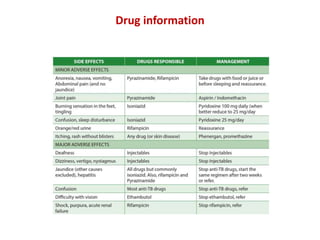
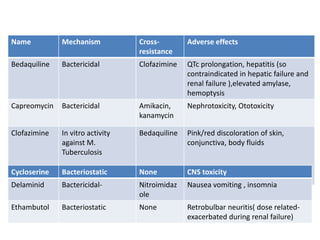
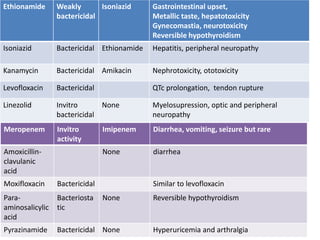
This document provides information on multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB). It discusses the epidemiology and definitions of drug-resistant TB. It describes how to diagnose DR-TB through tests like Xpert MTB/RIF, line probe assay, and culture and drug susceptibility testing. Treatment options for DR-TB are also outlined, including shorter standardized treatment regimens and longer regimens. Criteria for determining appropriate treatment regimens and defining treatment outcomes are also summarized.