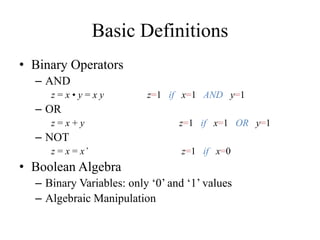
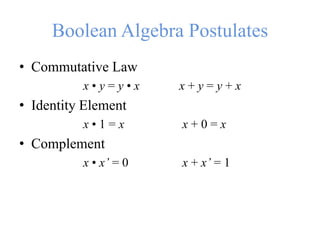
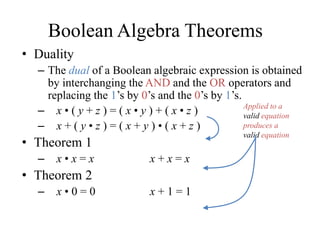
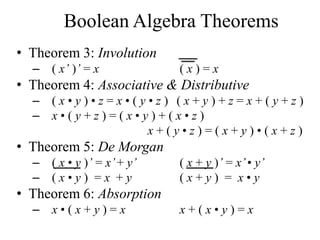
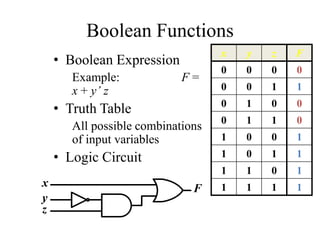
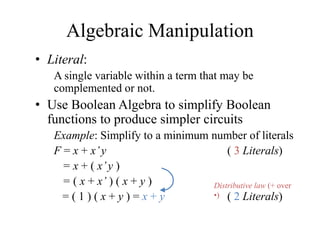
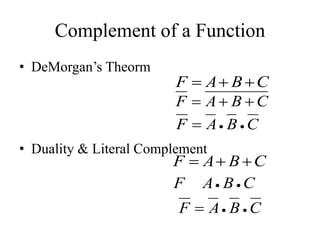
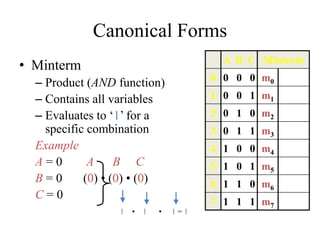
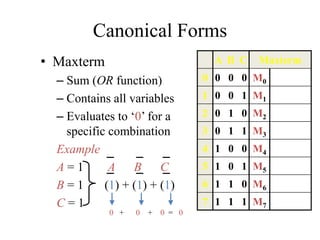
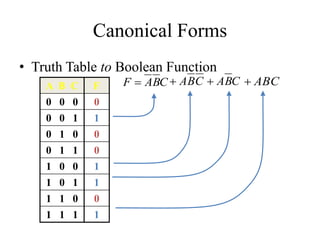
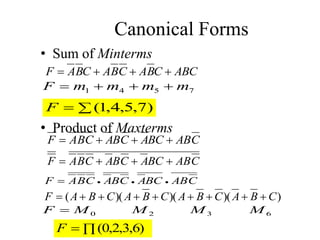
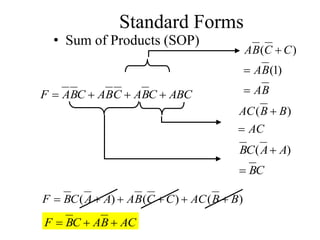
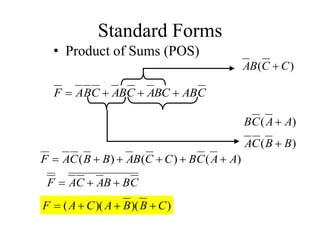
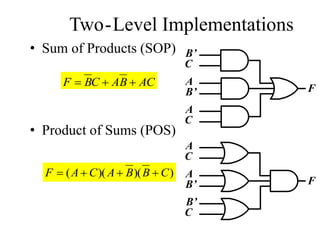
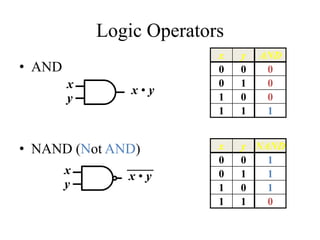
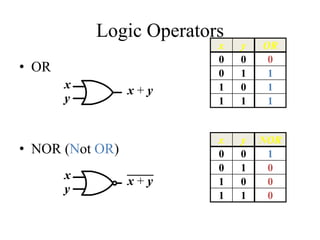
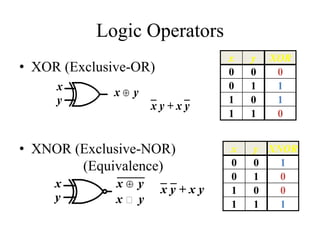
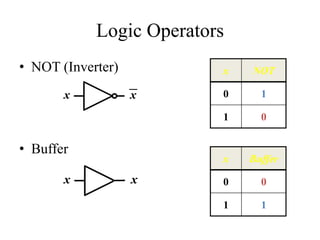
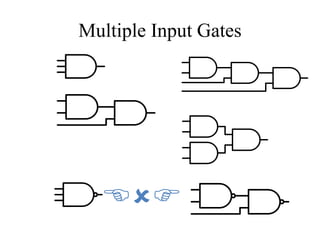
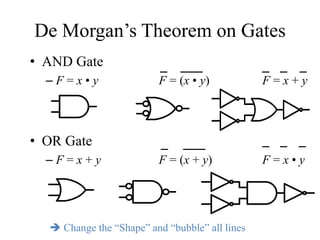
This document provides an overview of digital logic circuits and data representation. It defines basic Boolean algebra concepts like binary operators, truth tables, and theorems. It also covers standard forms for representing Boolean functions like sum of products and product of sums. Finally, it discusses logic gates, multiple input gates, and De Morgan's theorem as it applies to gate transformations.