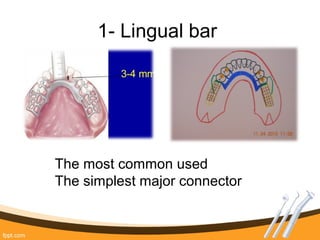
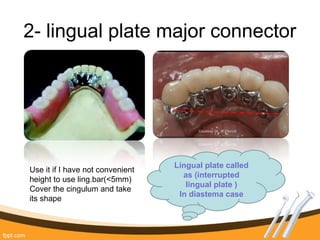
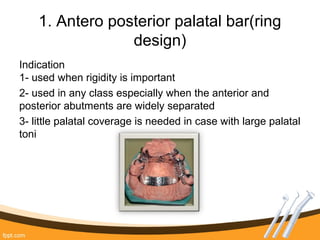
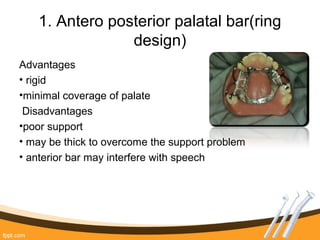
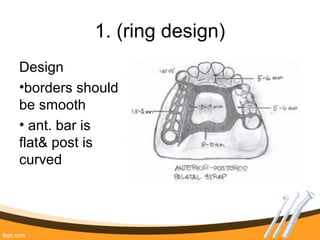
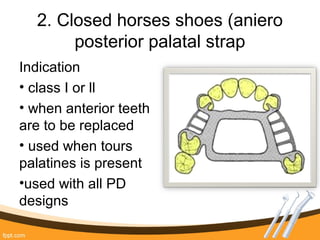
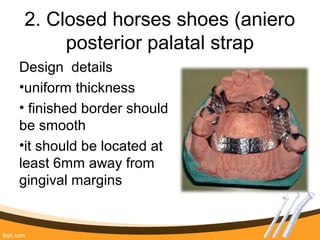
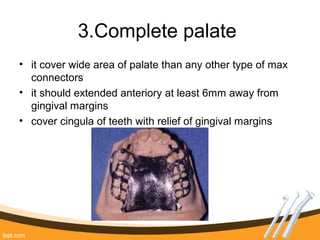
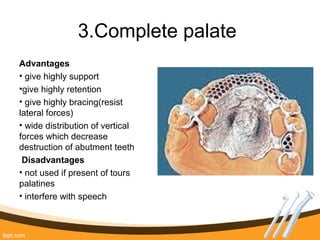
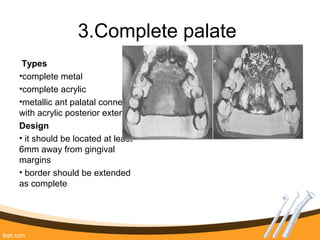
The document outlines the definition, functions, and requirements of major connectors used in removable partial dentures (RPD), including types for both mandibular and maxillary applications. It discusses various designs such as the lingual bar, lingual plate, and antero-posterior palatal bar, along with their indications, advantages, and disadvantages. The emphasis is on achieving rigidity, comfort for patients, and proper positioning to avoid interference with gingival margins and soft tissues.