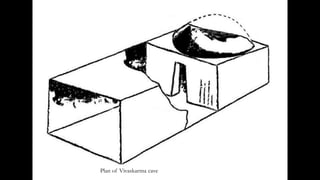
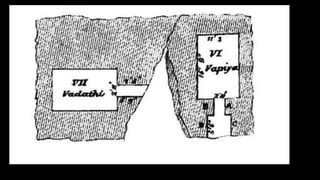
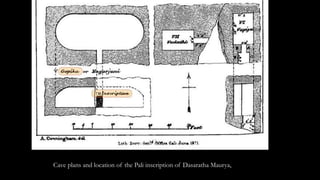
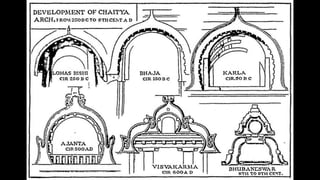
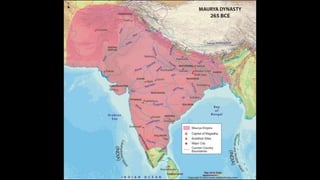
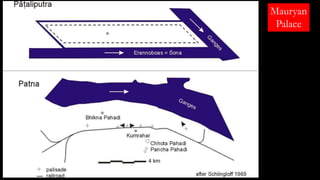
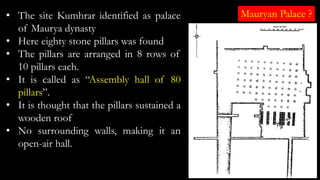
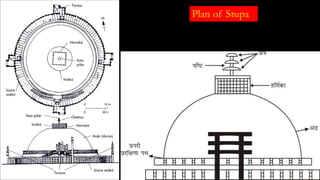
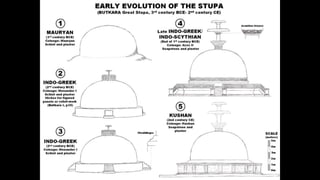
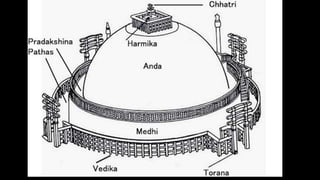
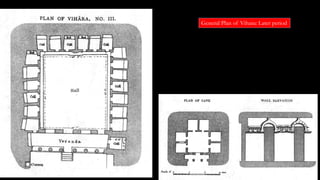
The document discusses Mauryan architecture, highlighting its significance in ancient India through the shift from wooden to stone and brick construction. It details key structures such as the palatial complex in Pataliputra, stupas related to Buddhism, and early rock-cut caves. The document emphasizes the architectural legacy of the Mauryan period, which laid foundational techniques and styles for future Indian art and architecture.



































![Lājinā Piyadasinā duvāḍasa-[vasābhisitenā] / [iyaṁ
Nigoha]-kubhā di[nā ājivikehi]
“King Priyadarsin, in the 12th year of his reign, this cave
of Banyans was offered to the Ajivikas”.
—Ashoka inscription of the cave of Sudama](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mauryanarchitecture-231214145256-01d6cc1f/85/Mauryan-Architecture-pptx-43-320.jpg)