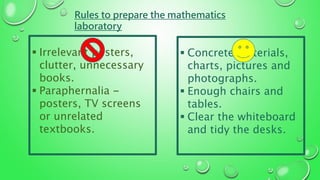
This document discusses mathematics laboratories, which provide a collection of games, puzzles, and teaching aids to help students explore, learn, discover, and develop mathematical concepts. Mathematics laboratories were introduced in 1994 for primary, secondary, and higher secondary levels. The document outlines rules for preparing the lab, such as including concrete materials and ensuring enough space, and lists common equipment for different grade levels, like geometry boxes, flash cards, and measuring tapes. It describes the functions of the lab as permitting abstract learning, discovering principles, arousing interest, and allowing students to learn by doing. The goal is to remove weaknesses, generate interest in math, and develop thinking and problem-solving skills through hands-on activities.