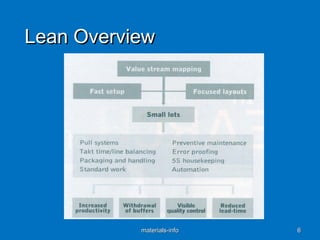
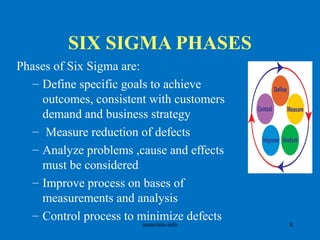
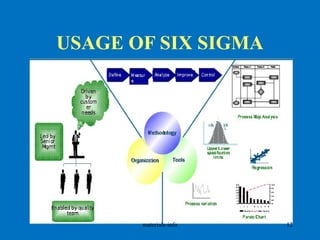
The document discusses various process improvement services offered by Materials Info, including lean manufacturing, six sigma, change management, quality systems, and process improvement. It provides examples of specific tools and methodologies used, such as 5S, value stream mapping, standard work, and kaizen. It also lists common pain points experienced by customers, such as high rejection rates, low yields, and high costs, and describes Materials Info's solutions to address these issues through methods like root cause analysis, process optimization, and early supplier involvement.