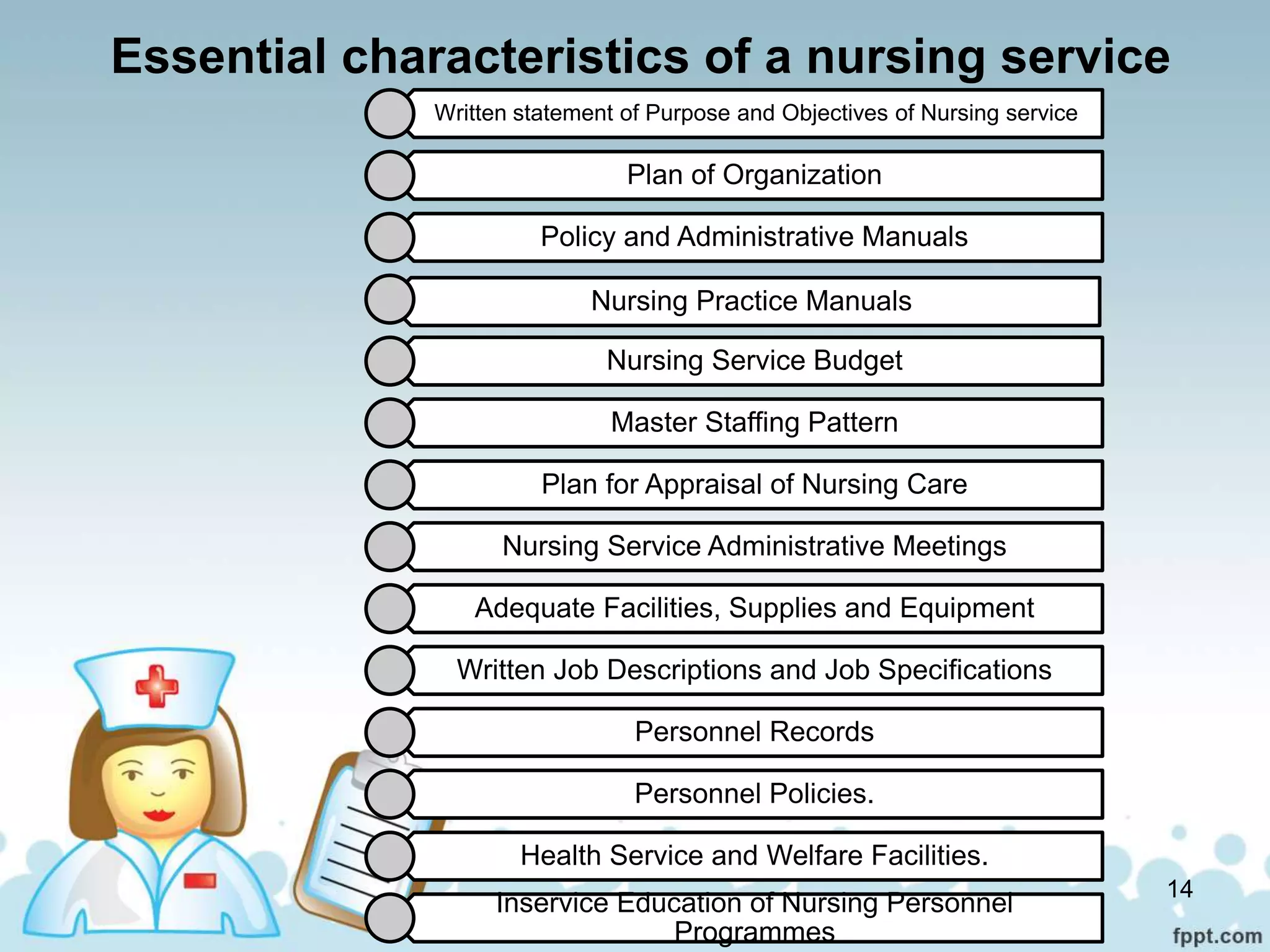
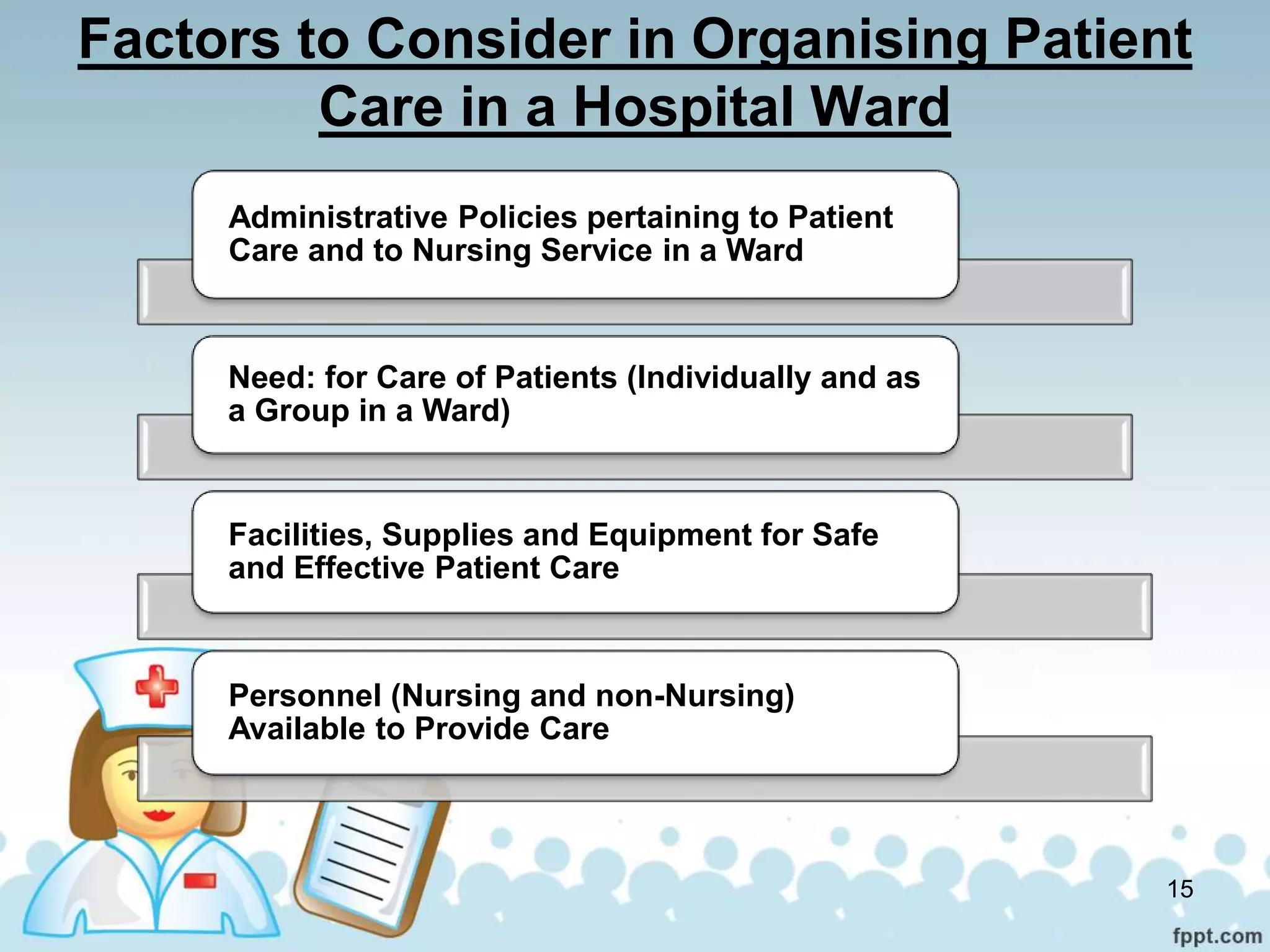
The document discusses the organization and functions of nursing services in hospitals and communities. It describes how hospital nursing services are organized with roles like the chief nursing officer, nursing superintendent, ward sister and staff nurses. It also outlines the functions of community health nursing which focuses on protecting and improving the health of entire geographical communities. Nursing services in both settings aim to provide preventive care, health education and rehabilitation in addition to curative services.