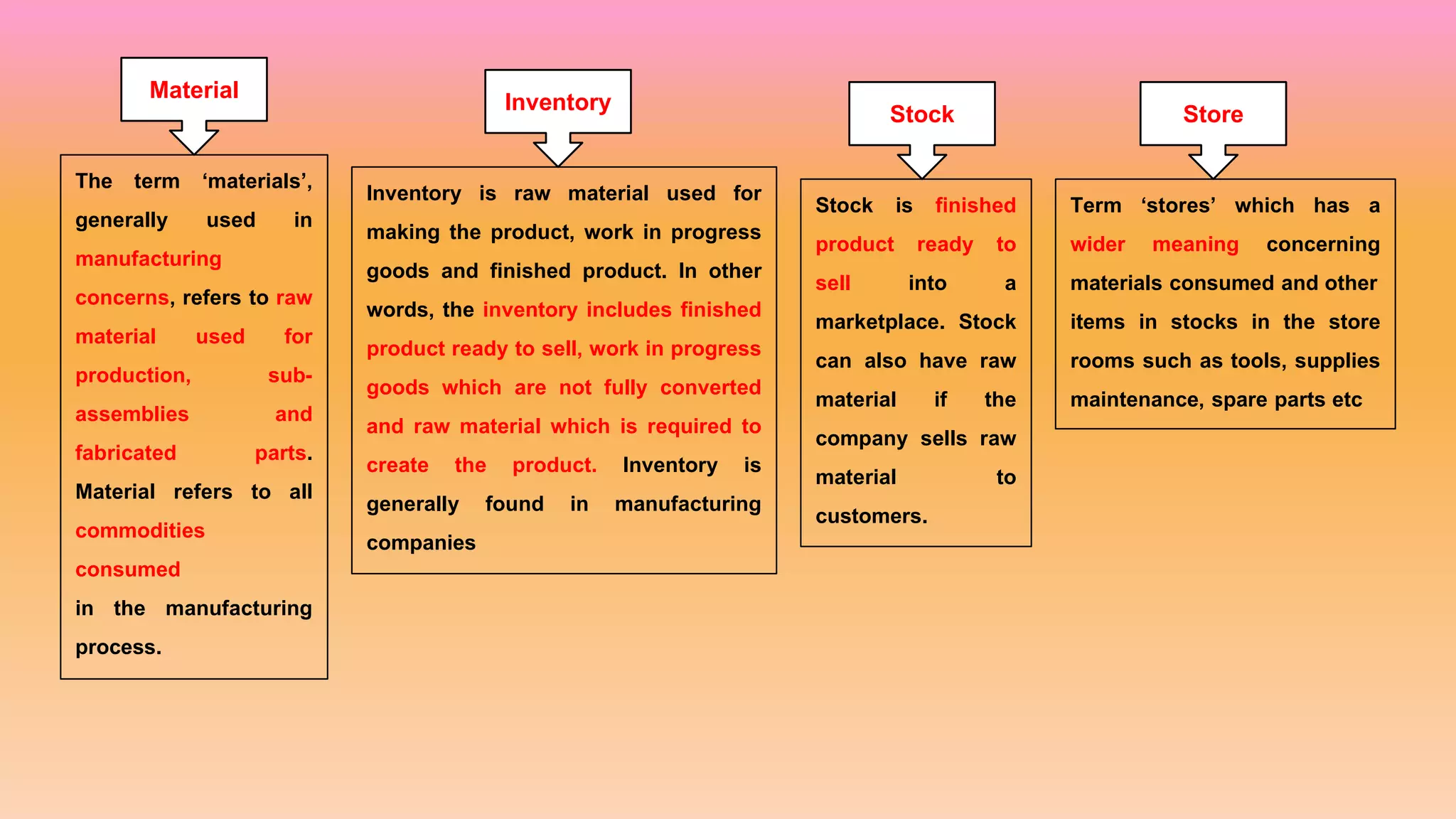
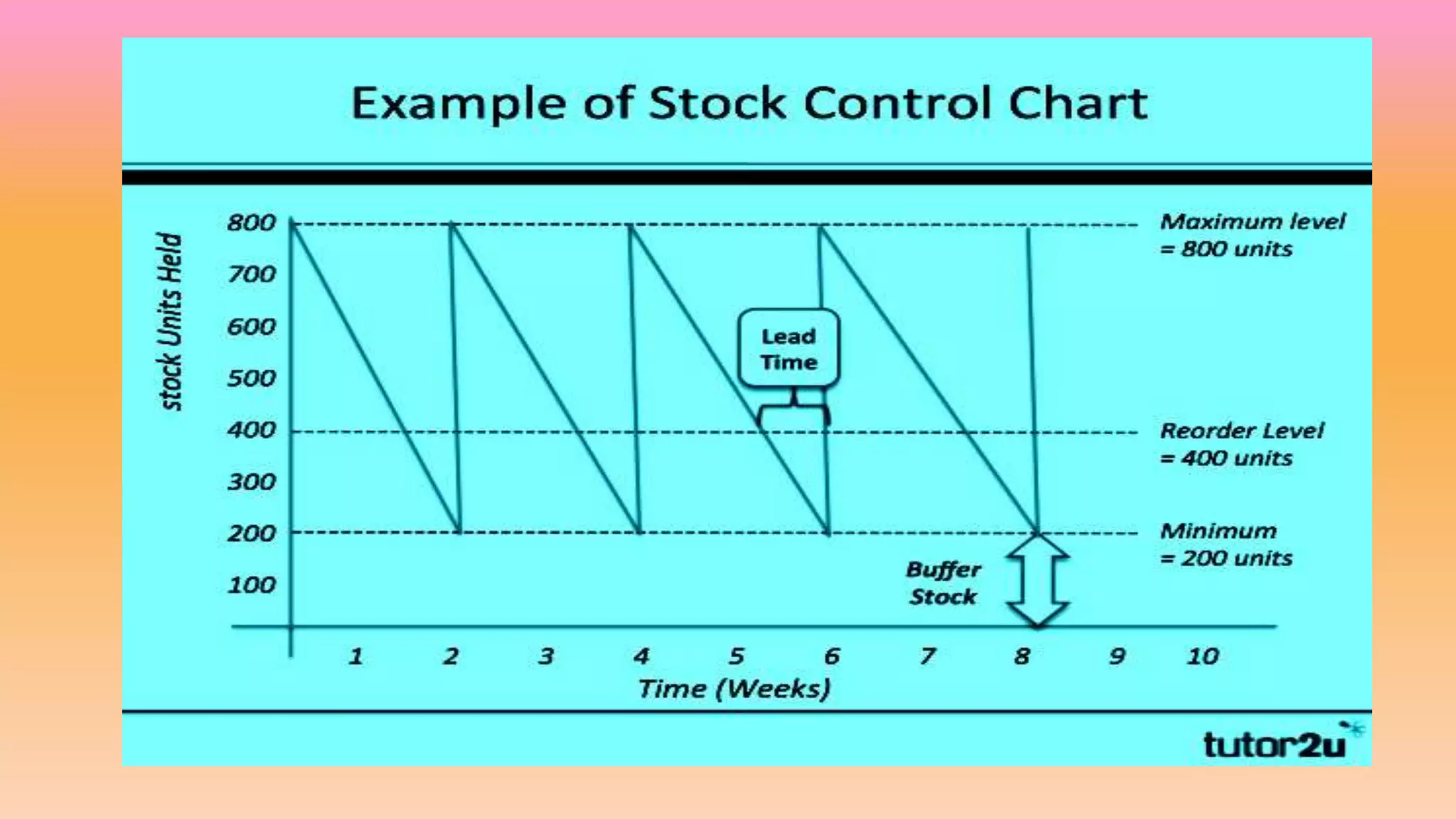
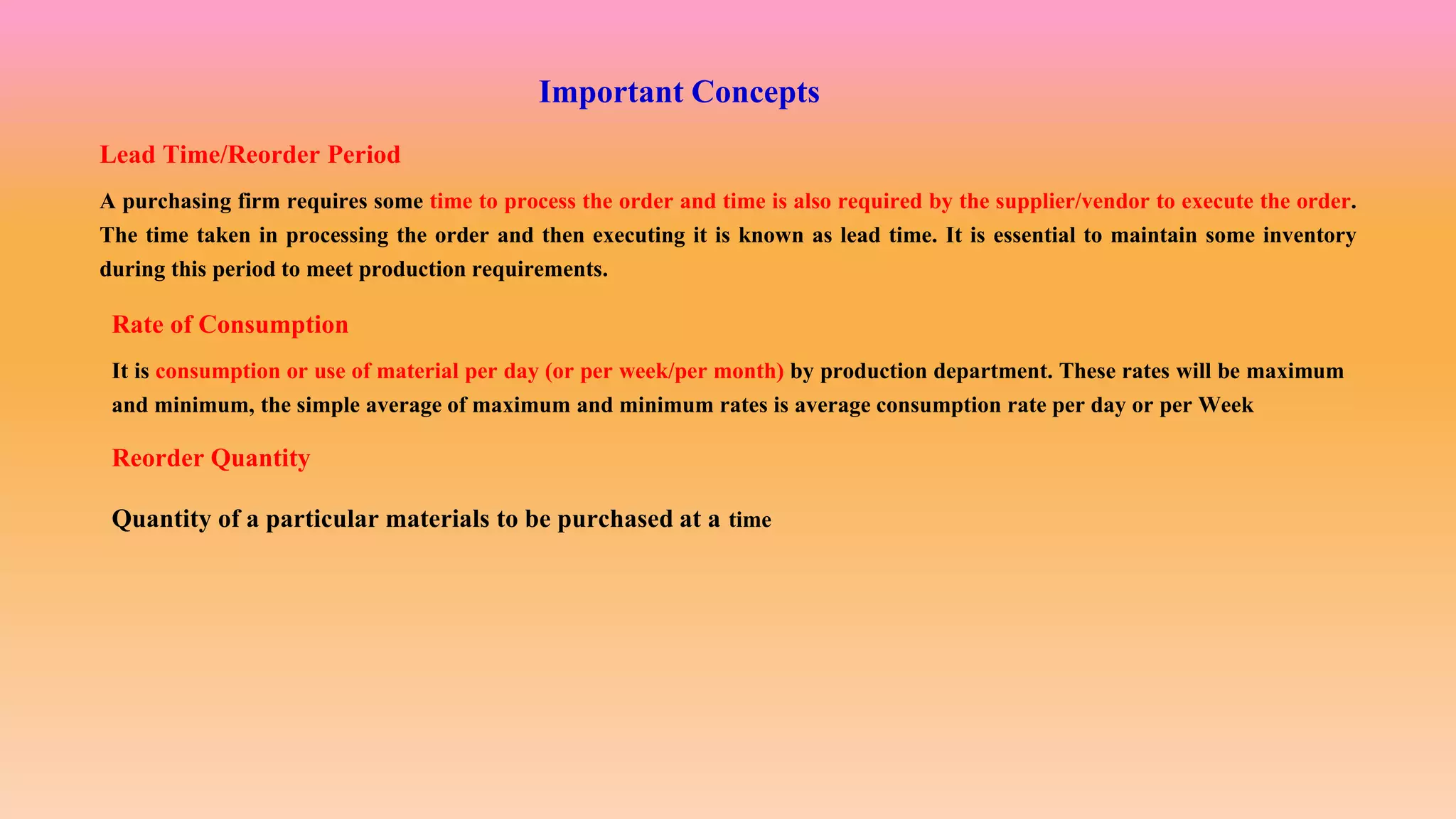
This document discusses inventory and stock control methods used in manufacturing. It defines key terms like inventory, stock, materials, and stores. Some common inventory control methods are described like setting stock levels, economic order quantity, just-in-time inventory, and ABC analysis. Stock levels discussed include reorder level, minimum level, maximum level, average level, and danger level. Formulas for calculating various stock levels are provided. Lead time, consumption rate, and reorder quantity are also important concepts covered.